Table of Contents
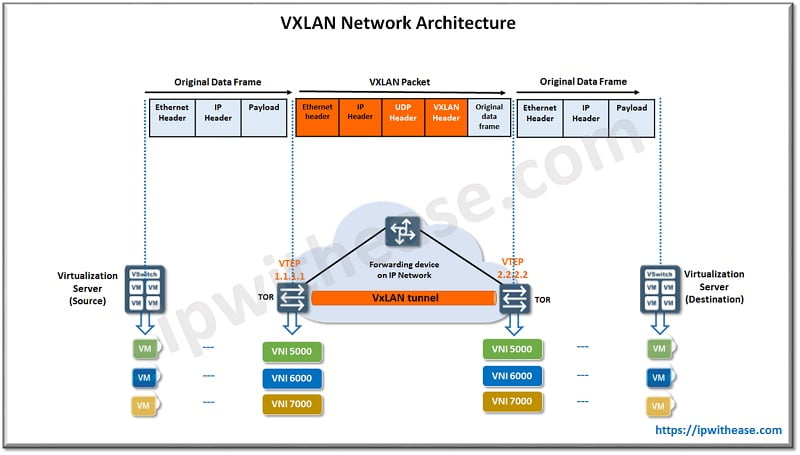
VxLAN is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates Layer 2 frames over Layer 3 networks. On the other hand, EVPN is a BGP-based control plane that manages MAC/IP address distribution for VxLAN overlays.
Enterprise networks are backbones to provide connectivity to critical applications and services. Many of the networks deployed a variety of overlay technologies to achieve business and technical requirements. As traditional overlay networks lacked manageability and scalability resulting in complexity of networks. The overlay protocols such as VxLAN to expand layer 2 network address space (4000 to 16 million). Ether VPN (EVPN) is used as an overlay in the control plane to provide virtual connectivity between layer 2 and layer 3 domain over an IP / MPLS network.
In today’s article we understand and compare VxLAN and EVPN, the purpose they are used for, their architecture and key differences.
What is VxLAN
VxLAN is a Virtual extensible LAN which provides layer 2 connectivity between networks (MAC-in-UDP) across an IP network. VxLAN are used to extend layer 2 segments across remote data centers and also provide multi-tenancy services ideally used in cloud ecosystems. VxLAN address runs over existing network infrastructure and provides functionality to extend layer 2 network. It is a layer 2 overlay scheme on a layer 3 network.
Each overlay is a VxLAN segment in which all virtual machines located within the same VxLAN segment can communicate with each other. VxLAN are identified by a unique 24-bit segment ID which is a VxLAN identifier and allows up to 16 million VxLAN segments within the same administrative domain. The VxLAN identifier (VNI) identifies the inner scope of the MAC frame and permits overlapped MAC addresses across segments with traffic isolation using VNI. The VNI is an outer header to encapsulate the inner MAC frame originated by the virtual host.
Use cases for VxLAN
- In cloud environments having large customer base or tenants which require customer network isolation
- Isolation of IoT traffic from production network applications traffic
What is EVPN
Ethernet VPN (EVPN) is used as an overlay control plane and facilitates Ethernet multipoint services over MPLS. EVPN supports multi-tenancy architecture and is highly extensible, using resources from diverse data centers to deliver to a service. It provides layer 2 connectivity over physical infrastructure to enable layer 2 routing for devices in virtual networks. It serves as a MAC address learning control plane in overlay networks hence it can support different encapsulation technologies in data planes such as MPLS and VxLAN.
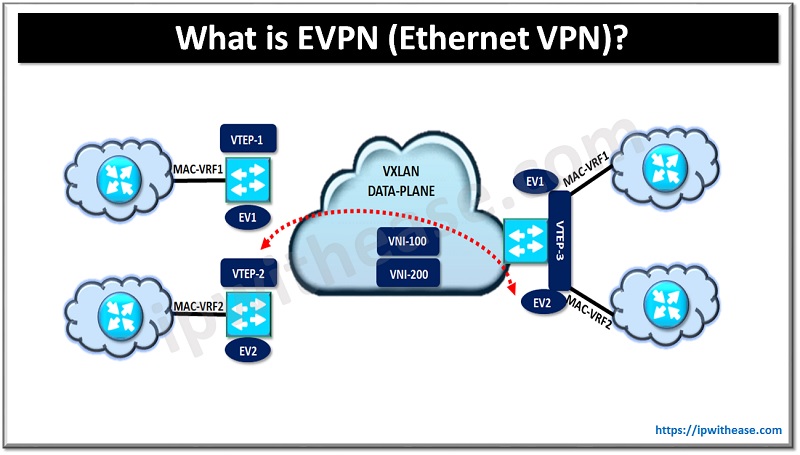
Use cases for EVPN
- Used in data centre connectivity requirements
- E-LAN and E-WAN connectivity
Comparison: VxLAN vs EVPN
| Parameter | VxLAN | EVPN |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | VxLAN is extension of legacy VLAN. This was designed to overcome the limitation of 12-bit segment supported in traditional VLAN. | This is a next generation VPN. Which extends LAN to WAN. Used commonly to interconnect layer 2 networks within and between large data centers. |
| Type | Overlay encapsulation protocol | Control plane for VxLAN (based on BGP) |
| Primary Function | Encapsulates Layer 2 Ethernet frames in UDP packets | Distributes MAC/IP reachability info via BGP |
| Overlay Technology | Yes | Yes (used with VxLAN for overlay) |
| Control Plane | None (original VxLAN used flood-and-learn) | BGP-based control plane |
| Configuration | Requires manual configuration to start sending and receiving virtual network traffic to/from a remote VTEP as member of virtual network | Manual configuration not required here. VTEP is automatically learned as member of virtual network from EVPN routes |
| Communication | Remote hosts are learned by data packets after decapsulation of VxLAN header in data plane | Remote hosts are learnt in control plane using EVPN type 2 routes and IP / MAC advertisements. |
| Encapsulation | VxLAN supports encapsulation of layer 2 ethernet frames into layer 3 UDP packet. | Supports multiple encapsulation technologies such as MPLS, VxLAN. |
| Purpose | VxLAN operates at control plane and handles data traffic | EVPN manages the guest list and directions. It can handle multi-sites and provides connectivity across locations |
| MAC Learning | Data plane learning | Control plane learning via BGP |
| Scalability | Limited (due to flooding and learning) | Highly scalable (due to BGP distribution) |
| Multitenancy Support | Yes (via VxLAN Network Identifier – VNI) | Yes (better isolation and scalability) |
| Loop Prevention | Limited (requires additional mechanisms) | Built-in loop prevention using BGP |
| Deployment | Simple for small-scale overlays | Preferred for enterprise/DC-scale overlays |
| Integration with L3 | Requires additional mechanisms | Native L2/L3 service support |
| Operational Complexity | Lower initially, grows with scale | Higher setup complexity but better for large environments |
| Vendor Support | Widely | Growing support; standard for VxLAN control plane |
Download the comparison table: vxlan vs evpn
Final Words
To conclude, VxLAN is a data plane encapsulation method. Whereas, EVPN is a control plane mechanism that enhances VxLAN’s functionality for scalability and efficiency.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj