Table of Contents
VXLAN and GRE both the protocols are used to encapsulate network traffic but they differ in their usage. VXLAN encapsulates Layer 2 Ethernet frames within Layer 3 UDP packets, allowing Layer 2 networks to be extended over Layer 3 infrastructure. It enables scalable and isolated virtual networks. GRE encapsulates a wide variety of Layer 3 network protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over an IP network. It allows the creation of secure and direct connections between different network nodes.
Today we look more in detail about two most popular VLAN or virtual LAN tunnelling technologies namely VXLAN (Virtual extensive LAN) and GRE (Generic routing encapsulation), their differences (VXLAN vs GRE), features and use cases.
As enterprises are moving to cloud computing infrastructures, there is a drastic change in the way network technologies have been emerged to keep up the pace with demands of high scalable and performance-oriented infrastructure, secure and redundant infrastructure the concept of virtualization is also seeped in networks which is the backbone for any computing environment be it on premises or cloud hosted.
Gone are the days of heavy network equipment and it is replaced with software defined networking processes to combine hardware and software into a single virtual network. As technologies evolving so is the tunnelling protocols.
What is VXLAN?
VXLAN is network virtual technology for LAN expansions. It is meant to resolve issues of insufficient virtual networking in large scale cloud deployments and used to leverage VLANs to separate cloud applications and tenants in cloud environments.
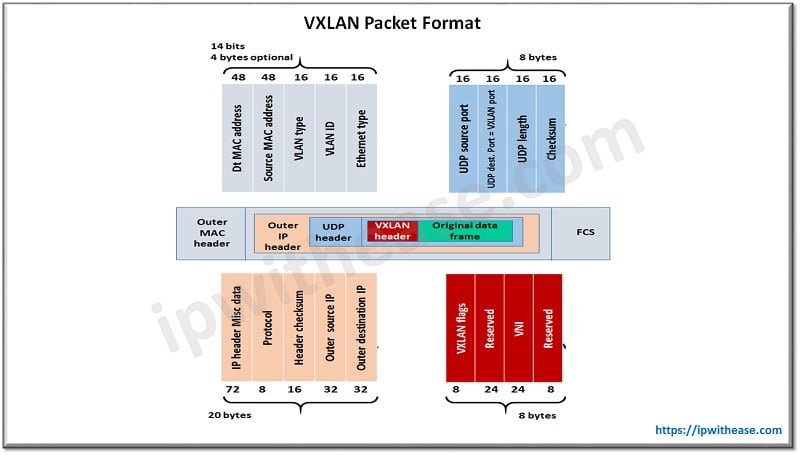
VLAN only allows up to 4096 network IDs to be assigned at a specific time which is deficient w.r.t to large cloud computing environments. So VXLAN was designed to extend the VLAN address space by addition of 24-bit segment ID to increase the number of available IDs to 16 million with logical secluding of tenants and cloud applications.
Millions of layer 2 VXLAN networks can coexist on layer 3 infrastructure. In dynamic VM migration MAC and IP addresses need to remain unchanged before and after migration and where VXLAN plays a critical role.
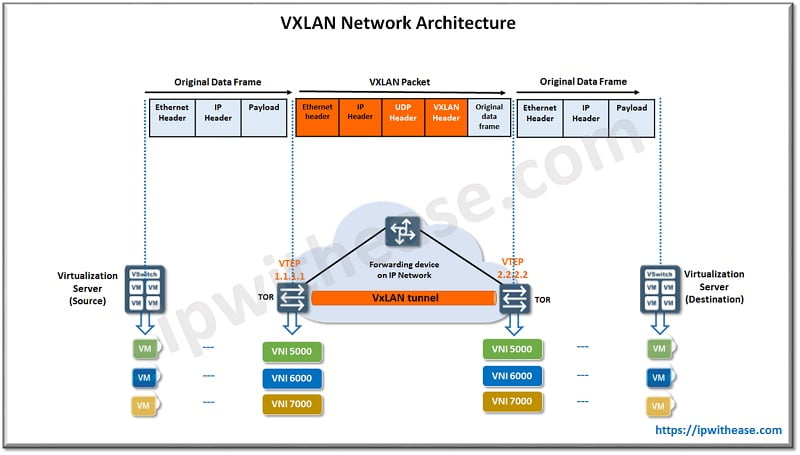
In above diagram a VXLAN tunnel is established between two rack switches to encapsulate original data frame sent from source into VXLAN packet and enabling original data frames to transmit onto IP network, TOR switch decapsulates the packets into original data frame before forwarding them to destination server.
Packet structure of VXLAN
What is GRE?
Generic routing encapsulation or GRE is an IP encapsulation protocol meant for transporting IP packets over a network. It was developed by Cisco but later became an industry standard (RFC 1701, RFC 2784, and RFC 2890).
It can tunnel any layer 3 protocol including IP. GRE allows routing of IP packets between private IPv4 networks which are segregated over public IPv4 Internet. It also supports encapsulating IPv4 broadcast and multicast traffic.
Uses of GRE
- GRE can be used to transport video, website traffic.
- It allows unsupported protocols to be transported across a network to its destination like IPv6 communication over IPv4 network.
- It offers DDoS protection.
- It creates a virtual link between two networks for routing and enables BGP communication among multiple networks without requiring a physical connectivity to each other as in case of conventional internet exchanges.
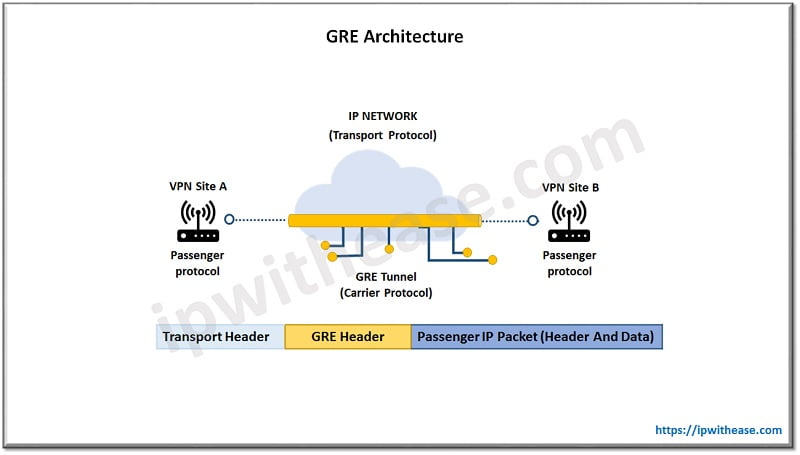
In the above diagram GRE is used to encapsulate traffic between two sites. Traffic will traverse across open Internet as tunnels do not encrypt traffic on its own, you can use encrypted tunnelling using VPN software also GRE tunnels are stateless hence destination is never made aware of this until the incoming data arrives at given destination.
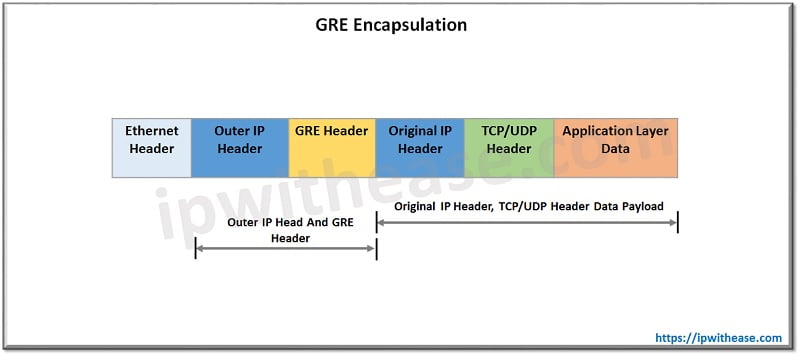
All GRE packets include both source and destination address to send data back and forth.
GRE IP Datagram
Difference: VXLAN vs GRE
The key points of differences between the two are:
- VxLAN is used to create the overlay networks while GRE is used for tunnelling framework over IP network.
- VxLAN is point to multi-point tunnel while GRE is point to point tunnel.
- VxLAN is used for network virtualization while GRE is used with VPN apps to provide a secure connection.
- VxLAN works at layer 2 of OSI model while GRE works at layer 3 of OSI model.
- Both support different internet standards in terms of RFC.
Comparison Table
Below table summarizes the points of comparison between the two i.e. VxLAN vs GRE
| Function | VXLAN | GRE |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Used to create Overlay networks which sit on top of physical network enabling use of virtual network of switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers and so on | Used for tunnelling of frames over IP network |
| Tunnelling | VXLAN is point to multi-point tunnel and it is an extension of layer 2 VLAN | GRE is point to point tunnel |
| Usage | VXLANs are used to virtualize network infrastructure and scale along with growing number of virtual machines | GRE is often used with VPN applications in which VPN provides a secure connection layer while GRE tunnel encapsulates traffic to where it must go |
| OSI layer | Layer 2 protocol | Layer 3 protocol |
| RFC supported | VXLAN is a formal internet standard, specified in RFC 7348 | GRE is formal internet standard specified in RFC 1701, RFC 2784, and RFC 2890 |
| Features | Uses 24-bit segment ID and enables up to 16 million VXLAN segments | GRE supports 1360 bytes segment size |
Download the comparison table: VXLAN vs GRE
Continue Reading:
What is the difference between VxLAN and OTV?
GRE vs IPSec: Detailed Comparison
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj