Table of Contents
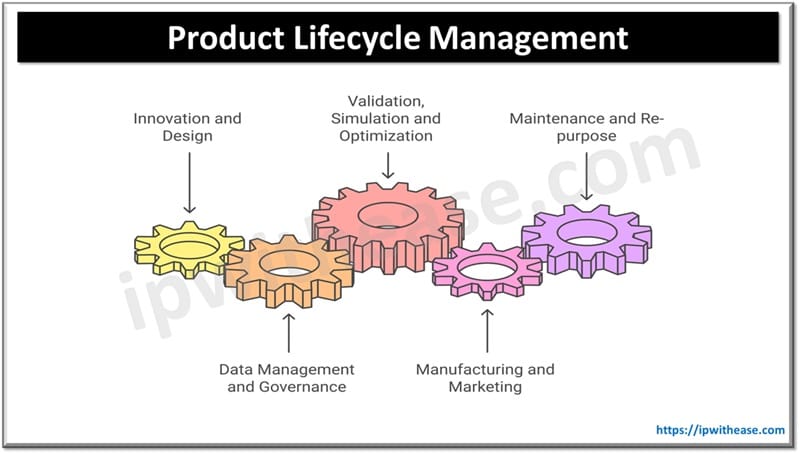
Product development is a discipline in itself. Every new product goes through a series of stages within its life cycle starting from its inception or idea to its creation, maintenance, development, testing and finally the retirement. Products are made and discarded as per the product life cycle management process. It is a holistic approach towards product development which incorporates every aspect of the PLM – innovation and design, data management and governance, simulation and optimization, manufacturing and marketing, maintenance and re-purpose and so on.
In today’s topic we will learn about product life cycle management process and discipline, its stages and key characteristics, and its importance in product development.
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
As per Gartner definition product life cycle development is a philosophy, a discipline, supported by software to manage products though various stages in its life cycle starting from its inception or conceptualization to retirement. As a discipline it has grown from mechanical design and engineering focus to being implemented across different industry verticals to address challenges in product development’. PLM platforms are a suite of products which bring people, processes ,data together and establish a conducive environment to make product development simpler and sustainable.
PLM platform is only a set of tools which support development teams and each individual within team need to be prepared to take an entirely new approach for product development.
Product life cycle has several stages. We will look at each stage in more detail in this section.
Stage I. Innovation and Design
The 1st stage in the product development life cycle is a basic concept or idea. New product ideas are evaluated and designers bring product to levels of maturity which is required for development of design. At the design stage of development of product multiple engineering disciples are applicable. During this stage product design is matured, virtual and actual prototypes are created for testing purposes until product meets the acceptable operating conditions. This phase is often repeated to ensure it meets the customer requirements as per the laid specifications.
Stage 2. Data Management and Governance
Data management ensures all design versions current and historic are accessible to organizations which are their Intellectual Property (IP) to keep it secure and accessible only to those who are authorized to use it.
Stage 3. Validation, Simulation and Optimization
Validation, simulation and optimization tools are used to perform a variety of tests on the product. Stress analysis to finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics are some tests used in product testing. Fully functional simulation model of the product is created which can react to real time data and provide invaluable insight into analysis of the product for the real world.
Stage 4. Manufacturing and Marketing
Once design is complete manufacturing starts. Tools such as product planning enable organizations to develop an agile product. Objective is to achieve fast time-to-market. Marketing strategy is devised to position products with a target audience. Several communication methods are used to bring products to market.
Stage 5. Maintenance and Re-purpose
Organizations collect feedback on their product performance in order to optimize and maintain it for revised versions of products released. Maintenance, repair and operational tools enable customer support. PLM tools are used to recycle, repurpose and reuse products to reduce waste and cut back on resource outlay for all future development of products.
On reaching the end of its life (EOL), some decisions needed to be taken regarding product retirement.
How PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) is Managed?
When it comes to management it is a much broader concept having multiple facets such as project management of product which involves product design , data and dealing milestones and project planning. It includes everything which revolves around the product.
Collaborations are another key aspect of product lifecycle management as it involves each component being able to work internally and externally in a structured manner.
Process management will cater to how product development will happen and information related to it such as documentation, change process and operating manuals.
Change management tracks the way changes pass through to get insight into tasks and responsibilities.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj