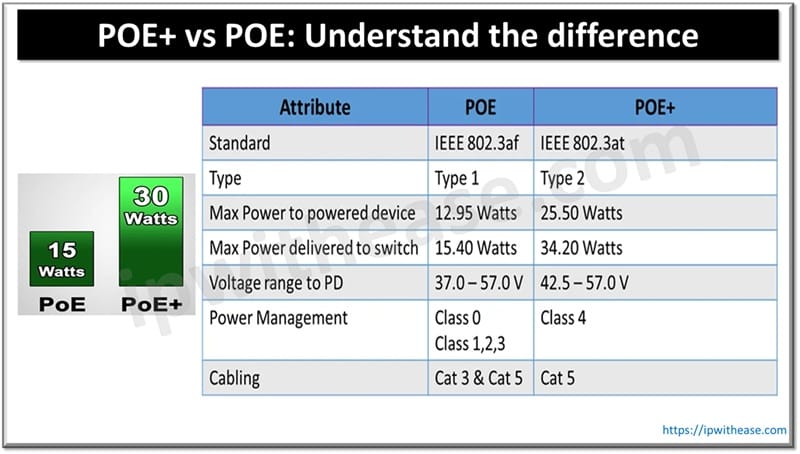
Table of Contents
Data centers are the backbone of cloud computing environments. The demand for huge capacities from enterprises is bound to increase as more and more organizations are moving their IT operations over the cloud. Increased regulations around the third-party hosting on service provider cloud ecosystems force them to take zoning approvals. As data centers consume a lot of energy and water they come up under the scrutiny of environmental groups also.
In today’s topic we will learn about zoning in data center, and its requirements.
What is Zoning in Data Center?
Zoning in a data center refers to the division of the facility into different areas or zones, each with specific purposes, security levels, cooling needs, power requirements, and other operational characteristics. This helps in organizing the data center for better management, security, and efficiency.
What is the need of Zoning in Data Center?
As dependence on technology and data is growing, data centers are being built in more diverse geographical locations around the globe to keep up with the growing need for information. Zoning is the law of the area dictating usage of property and its construction. Zoning laws govern regulations related to construction, location, modification and use of land and structures within the city. The design of any building project must respond to local planning and zoning as well as local, state, federal and international code requirements.
Keeping all rules in mind it is important to have design of data center architecture simple and scalable with redundancy in backbone interconnects. Designing of hierarchy to simplify data center management in the meantime allowing maximum level of direct interconnect to ensure high degree of performance.
Related: Data Center Tier Classification Explained
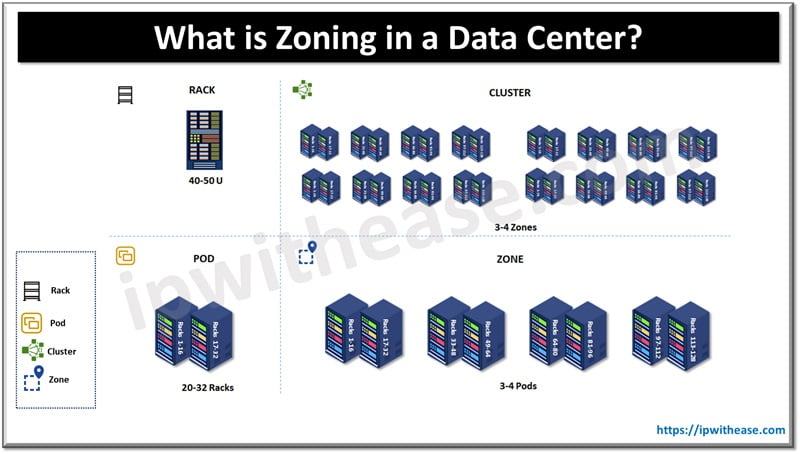
Zoning in Data Center: Architecture
A typical architecture with clusters can host 1,500 racks or more with a decent backbone any-to-any interconnect. Small data centers can have 2 level hierarchy with pods and zones or be it only pod level.
The data centers are ideally built in a central location within a building complex and approximately 4000 sq. feet area is required for a typical data center. The flooring should be capable of holding the data center equipment. The data center is logically segregated into zones based on the level of security.
Zone A: data center server room which has server racks, storage racks, and other networking equipment. The area required for zone A is about 1500 sq. ft.
Zone B: is for NOC room, reception, helpdesk, call center and testing/ monitoring room. Which is supposed to be approx. 1500 sq. ft.
Zone C: has power panels, BMS room, AHU, UPS, telecom etc. this area is about 1000 Sq. ft.
The racks are designed taking into consideration the amount of cooling requirements of equipment and servers. Separate air conditioning for zone A is required to maintain temperature requirements. Zone B and C could have a common air-conditioning system.
Importance of Zoning in Data Center
Zoning is important because it allows for:
- Enhanced security: By restricting access to certain zones, sensitive data and critical systems are protected.
- Improved cooling and power efficiency: Different zones can have tailored cooling and power configurations, reducing energy waste.
- Better management and maintenance: Zoning helps in managing different systems and infrastructure within the data center, making it easier to maintain and upgrade.
Related: Data Center vs Cloud: Understand the difference
Related FAQs
Q.1 How does zoning affect data center security?
Zoning enhances security by controlling access to different parts of the data center. Only authorized personnel can enter certain zones, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive equipment or data.
Q.2 Can zoning help in disaster recovery?
Yes, zoning can assist in disaster recovery by isolating critical systems and data. This separation helps in preventing the spread of damage and enables quicker recovery of essential services.
Q.3 How is zoning implemented in a data center?
Zoning is implemented through a combination of physical barriers (walls, cages), environmental controls (cooling, power), and security measures (access controls, surveillance). It also involves logical zoning through network segmentation and software-defined boundaries.
Q.4 What are the challenges of implementing zoning in a data center?
– Complexity in design and implementation
– Cost of setting up physical barriers and specialized systems
– Maintenance of different zones with varying requirements
– Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards
Q.5 Is zoning applicable to all types of data centers?
Zoning is a best practice for most data centers, regardless of size or type. However, the complexity and specifics of zoning will vary depending on the data center’s purpose, size, and the criticality of the systems it houses.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj