Table of Contents
In the case of black box testing, the tester does not have details about the internal working pattern of the software system. The testing emphasizes on the behaviour of the software and it can be applied onto every level of the software including unit, integration, the system as well as the acceptance. Meanwhile, white box testing denotes the form of testing where the tester is familiar with the working pattern of the system, it generally cover code statements, paths, branches and conditions. It is also termed as code base, transparent box, glass box and clear box testing.
Introduction
In any form of software driven configuration, system or process, the segment of ‘testing’ plays an indispensable role. It is on the grounds of software testing that we can reach onto the inference of the loopholes, the efficiency and the scope of the software.
The basic testing is categorized into:
- Black Box testing
- White Box testing
Though both the forms of testing are used over the internal structure design and implementation, there are distinctions between the two. The example of white box testing tools are SAST tools while the example of black box testing tools are DAST tools.
Related: What is White-Box Switching
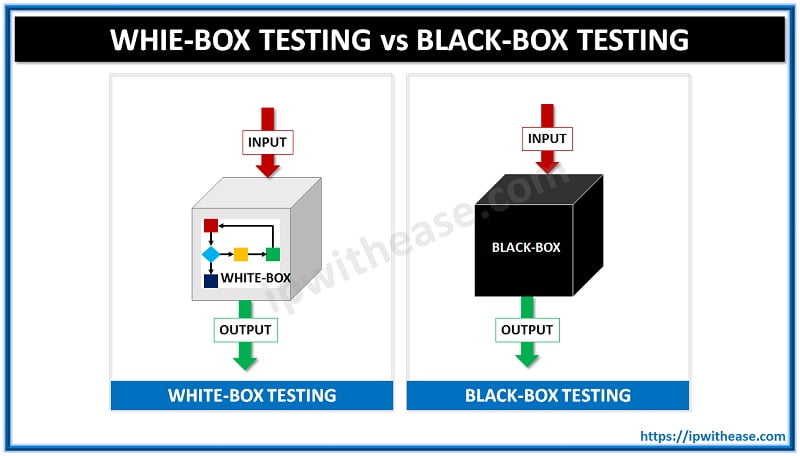
White Box Testing vs Black Box Testing: Distinctive Features
| Parameter | Black Box Testing | White Box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| The Definition | A testing approach used to test the software in absence of the knowledge about the internal application or program structure. | A testing approach with the knowledge of internal structure to the tester. |
| Also Known As | Also termed as data-driven, data-functional testing and box testing. | Also termed as structural testing, code-based testing, glass box testing or clear box testing. |
| Testing Base | It is done on the grounds of external expectations; and the internal behaviour pattern of the application should remain unknown. | Familiar with the internal working pattern, and the test is conducted by the tester in accordance with the pattern. |
| Utilization | Perfect for higher level tests such as System Testing, and Acceptance Testing. | Ideal for lower level tests such as Integration Testing and Unit Testing. |
| Programming Knowledge | Not required to execute Black Box testing. | Required to successfully execute White Box testing. |
| Implementation knowledge | Not necessary to conduct Black Box testing. | Absolute knowledge is indispensable to implement White Box testing. |
| Automation Process | Both programmer and test are dependent on each other, hence automation is a daunting task. | While comparing this parameter over white box testing vs black box testing, it is quite easy to automate with white box testing. |
| Motto | The chief motto is to assess the functionality of the system which is under test. | The chief motto is to evaluate the quality of the code. |
| Foundation for Test Cases | Testing should commence right after the preparation of requirement specification document. | Testing should commence right after the preparation of Detail design document. |
| Tester | The testing is performed by authorized tester, developer as well as the end user. | The testing authorization is generally confined to developers and testers. |
| Granularity | Contains low granularity. | Contains high granularity. |
| Testing method | Based on the technique of trial and error. Example: exploring something over the search engine Google with the help of keywords. | Tested over internal boundaries and data domain. Example: by putting input to check and then verify loops. |
| Time Period | It is less time-consuming | It is a more time-consuming and exhaustive approach. |
| Algorithmic Test | Not the best way to conduct algorithmic testing. | Ideal for algorithmic testing. |
| Code Access | Code access is not mandatory for Black Box Testing. | It is mandatory for white box testing. Hence, in case the testing is outsourced, the code could be stolen. |
| Advantage | Efficient and perfectly suited for large code segments. | It authorizes the elimination of extra lines of code, which can introduce concealed defects. |
| The Level of Skill | Testers with substandard skills with no knowledge of OS or programming language can execute it successfully. | Vast testing knowledge is mandatory and essential in order to successfully perform this test. |
| Implemented Techniques | 1) Equivalence partitioning is the Black Box testing technique implemented. 2) Equivalence partitioning segregate the input values into the valid and invalid partitions and subsequently choose corresponding values right from each partition of the tested data. 3) Boundary value analysis 4) Verify boundaries for the input values. | 1) Statement Coverage, Path coverage, and Branch coverage are certain White Box testing techniques. 2) Statement Coverage reinforces the fact whether each and every line of the code is correctly performed at- least once. 3) Branch coverage reinforces the fact whether each of the branch is executed at- least once 4) Path coverage method checks all paths navigated by the program. |
| Drawback | If you modify the application on a frequent basis, then an update to automation test script is necessary. | Automated test cases can turn out to be futile if the code base is changing at a rapid rate. |
| Testing Type Examples | Functional Testing Non-functional Testing Regression Testing | Path Testing Condition Testing Loop Testing |
Download the comparison table: White Box Testing vs Black Box Testing
Conclusion
From the table displayed above containing a wide range of parameters, it is easy to bifurcate the components that draws a clear picture of distinction between the two testing methods. While drawing the comparison between white box testing vs black box testing, it is pretty evident that the White box testing requires more advanced skills and techniques and renders in-depth analysis. There have been testing type examples provided in the table to help you classify the test more easily the next time you perform it. Both the forms of tests have their advantages but also carry fair share of disadvantages as well. Hence, it is advised to observe them and act accordingly.
Continue Reading:
DAST – Dynamic Application Security Testing
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) – Cyber Security
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj