Hi viewers, in this post we will be discuss a scenario where eBGP neighborship across 2 BGP enabled Routers dropped on enabling NAT Overload on same Router.
Example Scenario: BGP Neighborship Drops when NAT is Enabled
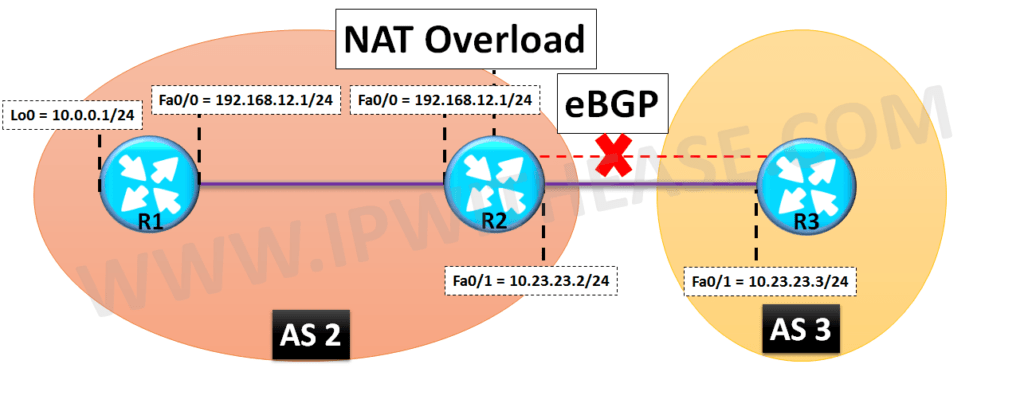
Diagrams below depicts the connectivity across Router R1, R2 and R3.
While R1 and R2 will have static Route for reachability, R2 and R3 will form eBGP neighborship between AS 2 and AS3 respectively. Also, network 10.0.0.0/8 (Behind R1 and shown as Loopback0 for test scenario) will be NATted with Inside Global IP of 200.200.200.1 on R2.
Base Configuration across R1, R2 and R3
The base configuration across R1, R2 and R3 is as shown below –
R1
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.12.2
!
End
R2
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip nat outside
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.23.23.3
ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1
!
ip nat pool NATPOOL 200.200.200.1 200.200.200.1 prefix-length 24
ip nat inside source list 1 pool NATPOOL overload
!
access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
!
End
R3
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
!
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.23.23.2
!
end
Configure BGP across R2 and R3
Now that we have NAT Overload in place (10.0.0.0/8 gets NATted to 200.200.200.1) ,next step is to configure BGP across R2 and R3 as below –
R2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.23.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 10.23.23.3 remote-as 3
no auto-summary
R3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.23.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 10.23.23.2 remote-as 2
no auto-summary
After configuring eBGP, still both Routers are showing neighborship as “Active” as below –
BGP table version is 2, main routing table version 2
1 network entries using 117 bytes of memory
1 path entries using 52 bytes of memory
2/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 248 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 417 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 3/2 prefixes, 4/3 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.23.23.2 4 2 290 295 0 0 0 00:02:25 Active
BGP table version is 2, main routing table version 2
1 network entries using 117 bytes of memory
1 path entries using 52 bytes of memory
2/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 248 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 417 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 2/1 prefixes, 3/2 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.23.23.3 4 3 290 291 0 0 0 00:03:11 Active
Let’s take help of debug command to troubleshoot why BGP neighborship is not forming.
To stop unwanted traffic from being captured in debug , we take help of access list as below –
*Mar 1 08:51:47.301: IP: s=200.200.200.1 (FastEthernet0/1), d=10.23.23.3, len 44, rcvd 0
*Mar 1 08:51:47.305: TCP src=21387, dst=179, seq=4006275843, ack=0, win=16384 SYN
R3#
As seen from output of debug command, the source forming neighborship with R3 IP 10.23.23.3 is 200.200.200.1 and not 20.23.23.2.
On further analysis , we get to know that Source IP (R2 Fa0/1) 10.23.23.2 is also being NATted to 200.200.200.1 which should not be the case.
To overcome this situation , we need to change the source list used for NAT (in this case access list 1) to exclude interface fa0/1 of R2 (10.23.23.2) as below –
R2(config-std-nacl)#do sh access-list
Standard IP access list 1
5 deny 10.23.23.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255 (4 matches)
10 permit 10.0.0.0, wildcard bits 0.255.255.255 (320 matches)
Once configured , lets verify the neighborship status as below –
BGP table version is 2, main routing table version 2
1 network entries using 117 bytes of memory
2 path entries using 104 bytes of memory
3/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 372 bytes of memory
1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 617 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 2/1 prefixes, 4/2 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.23.23.3 4 3 363 364 2 0 0 00:08:55 1
BGP table version is 2, main routing table version 2
1 network entries using 117 bytes of memory
2 path entries using 104 bytes of memory
3/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 372 bytes of memory
1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 617 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 3/2 prefixes, 5/3 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.23.23.2 4 2 363 368 2 0 0 00:08:39 1
The eBGP neighborship is now up and able to receive Routes from neighbors.
Hence, as verified from the troubleshooting exercise, Source Subnet to be NATTed may disrupt with the BGP neighborship if both are using overlapping IP address. To mitigate this condition, we need to deny eBGP subnet from Source list (Access list) for NAT overload.
Continue Reading:
Configure eBGP Neighborship in Junos
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

this blog is great thank you so much