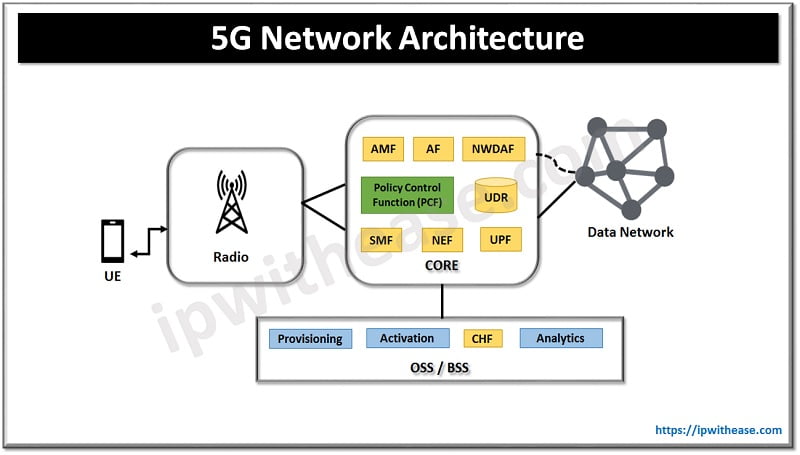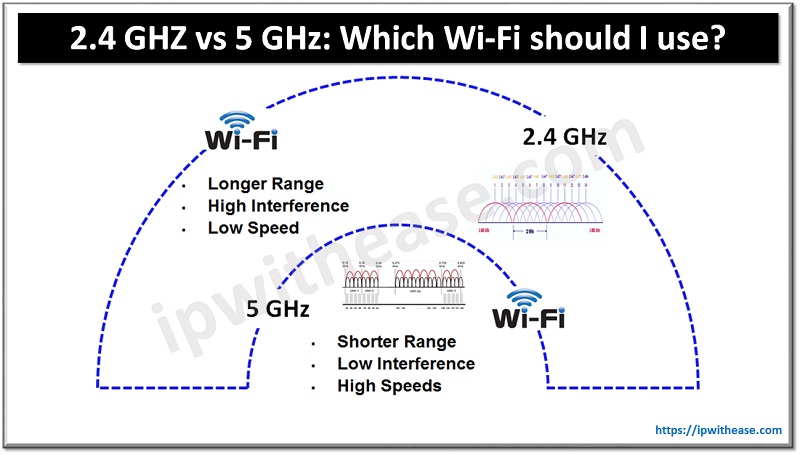
2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz
WiFi is a very popular system of networking that makes it possible for users to access it from any place. It works well with the majority of operating systems, game consoles, printers and other devices. It is a great alternate to wired technology, as it uses radio frequencies to transmit and receive data quickly.
The Wi-Fi router located in your home/workplace employs radio frequencies to disperse the Internet to various appliances. Typically, the two most common radio frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, are employed while constructing a WLAN system. Unfortunately, the majority of people are unaware of which radiofrequency to pick for their network needs.
This post is providing a thorough overview of the comparison between two radio frequencies, 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz, aiding in the selection of the most suitable one for setting up a Wi-Fi network.
What is 2.4GHz Wireless?
The most prevalent radio frequency employed by the majority of electrical devices is 2.4 GHz. The 2.4GHz spectrum is able to cover a much longer range but has a narrower bandwidth than 5GHz. Consequently, the data rate is much slower than 5GHz, leading to a lower file transfer speed and poorer video streaming quality.
One of its main benefits, however, is its ability to transmit signals over a long distance. This is because lower frequency signals can more easily pass through materials commonly found in buildings, thus allowing them to travel farther than higher frequency signals.
As per the WLAN norms and protocols, the frequency range of 2.4 GHz is split into 13 channels that overlap. Every channel occupies a unique bandwidth (20 MHz for 802.11g or 802.11n channel, and 22 MHz for 802.11b channel) and has its own center frequency.
Out of the 13 channels, there are 3 distinct channels which do not interfere with each other because they have non-overlapping frequencies. In the picture below, channels 1, 6, and 11 are the independent channels.
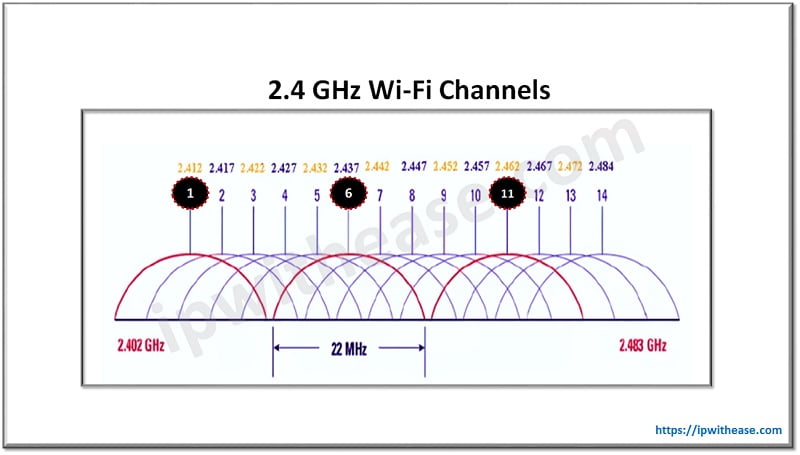
What is 5GHz Wireless?
Due to the fact that solid materials like walls and structures impede the transmission of high-frequency signals, the range of 5GHz is limited. Nonetheless, a high frequency of waves enables a faster rate of data transmissions.
Thus, the main benefit of 5 GHz Wi-Fi is its ability to transfer data at a more rapid speed. Subsequently, the speed of downloading and uploading documents is greater. It also assists high bandwidth applications, such as streaming videos, to work properly. To sum up, 5GHz can provide a much quicker data connection than 2.4GHz due to its wider bandwidth.
According to WLAN rules and regulations, the 5 GHz band is split into 24 individual channels, all with a bandwidth of 20 MHz. This provides enough channels for WLAN, and more independent channels make channel linking more advantageous. Channel linking is to attach two channels to create one channel to obtain greater bandwidths. For example, two 20 MHz separate channels can be bound to make a 40 MHz throughput, which is analogous to merging two roads into one to enhance roadway capacity.
As shown in the figure below, a black semicircle denotes an individual channel, and a red semicircle signifies a connected channel as suggested by the standards and protocols.
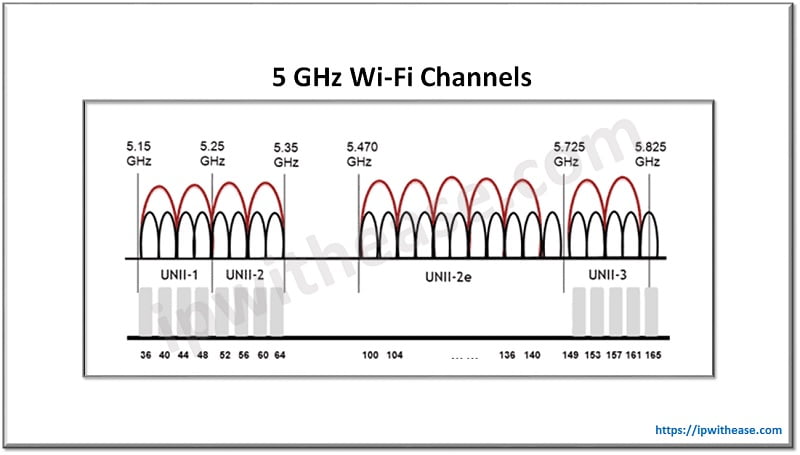
Differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi
We will provide you with a few details that will help you distinguish between the two radio frequencies.
Speed
The maximum transmission speed of 2.4 GHz wi-fi is low i.e. 600 Mbps whereas the maximum transmission speed of 5 GHz wi-fi is 1300 Mbps.
Operating Frequency
2.4GHz has an operating frequency of 802.11b/g/n while 5GHz has an operating frequency of 802.11a/n/ac.
Data transmission
The data transmission rate of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is not as fast as that of 5 GHz Wi-Fi. 5GHz has a higher transfer speed.
Operating Range & Coverage
2.4 GHz has a longer coverage range as compared to 5 GHz Wi-Fi. As stated above, the lower frequency signals can more easily pass through materials commonly found in buildings, thus allowing them to travel farther than higher frequency signals.
Compatibility & Interference
Given the fact that 2.4 GHz has a wide scope and can handle multiple gadgets at the same time, it is highly vulnerable to disruption caused by other networks. This problem is intensified by other electronic devices such as microwaves, which employ the same radio frequencies.
The 5 GHz frequency band has low levels of interference, allowing you to enjoy maximum speeds without any hiccups. However, its range is limited, so all your electronic devices must be confined to a smaller area.
Wall Penetration
In contrast to the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, the wall penetration capability of 5 GHz Wi-Fi is less powerful due to the electromagnetic wave’s physical characteristics. This is because a longer wavelength has weaker blocking power and can more easily pass through objects. Since 5 GHz signals are higher in frequency and have a shorter wavelength, they are more likely to be hindered when passing through obstacles and have a weaker wall penetration capacity.
Congestion
When multiple gadgets are trying to link to the same network, it can lead to overcrowding, resulting in slower performance. As 2.4 GHz frequencies can accommodate a great number of devices, they are more likely to suffer from congestion, resulting in less than optimal Internet speeds. As 5 GHz networks possess smaller wavelengths and can cater to a restricted number of gadgets, they are not as likely to become congested.
User Experience
The user experience is high with 5GHz wi-fi as compared to 2.4 GHz because of high data transmission speed.
Overlapping Channels
With 2.4 GHz, there is a potential for interference due to overlapping. The 5 GHz band, however, has 24 distinct channels that do not overlap, eliminating the issue.
Cost of Installation & Maintenance
When making the decision between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band for your WLAN network, the cost of installation should be taken into consideration. As the 5 GHz band is a more recent technology, it is pricier to install than the regular 2.4 GHz band. Therefore, if funds are available and you require a high-speed connection, then the 5 GHz band may be the better choice.
Comparison Table: 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz
Below table summarizes the differences between the two types of wireless:
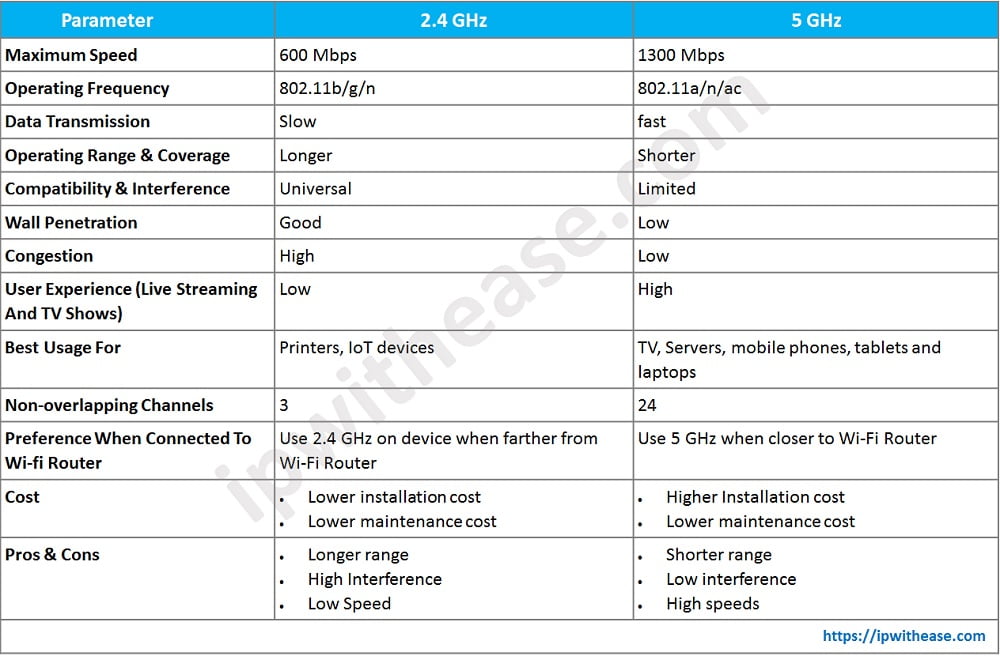
Download the comparison table: 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz
Which frequency is the most suitable for you?
2.4 GHz Most Suitable for a distant device
If you own a device that you use and move around a lot such as a smartphone and your home is quite large, the 2.4 GHz frequency is the most suitable. It has a further range and can penetrate walls or other objects more easily than the 5 GHz band. This makes it ideal for devices that travel from room to room or are a bit further away from the router. Nevertheless, newer routers that use 5 GHz 802.11ac WiFi could allow for the same range coverage on 2.4 GHz in certain circumstances.
5 GHz Most Suitable for a closer device
If the majority of your devices are in close proximity to your router, then 5 GHz is the optimal frequency for higher speeds. Additionally, if you are engaging in data-intensive activities such as gaming or video calls, it is best to use this frequency and move as close as you can to the router. If it is possible, it is even better to connect to the modem with an Ethernet cable, as this will provide a more reliable and faster connection than wireless. Finally, if you are in a densely populated area with many nearby units, 5 GHz will help you to avoid wireless network saturation.
Final Words
We have discussed in detail 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz. Two Wi-Fi frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, have their own individual benefits. When it comes to their needs, individuals can choose the frequency they prefer. If they prioritize speed, they can opt for a 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection. On the other hand, if they prioritize a large wireless range, they can select a 2.4 GHz WI-Fi.
Continue Reading:
What is Wi-Fi Offload? An Overview!
Future of Wireless Communication Technology
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj