There are various communication technologies exist in today’s digital world. The development of powerful computing devices and need for connectivity or communication and transfer of information to long distance lead to advancement in networking technologies.
This article will discuss about CDMA technology, which is a popular choice used in mobile communications.
About CDMA: A Mobile Technology
CDMA stands for ‘Code Division Multiple Access’ and is a spread spectrum multiple access technique. Spread spectrum technique spreads bandwidth of data in a uniform manner for the same transmitted power. It is a channel access method used primarily by mobile communication technologies. It allows multiple access which means several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communication channel. Different CDMA codes are assigned to different users and for the entire duration user can access complete bandwidth. There is no limit on user frequency range and user uses available bandwidth completely. There is no undue interference and users can share a band of frequencies. CDMA technology is used in military, commercial applications, mobile communications, Radar, and navigation systems.
History of CDMA
The CDMA technology was originated during World War II. It was developed by English allies for protection of their wireless transmissions from jamming from enemies. This technology was patented by Qualcomm post war and was made commercially available for use. The first CDMA system was launched in 1995 in Hongkong by Hutchison Telephone Company.
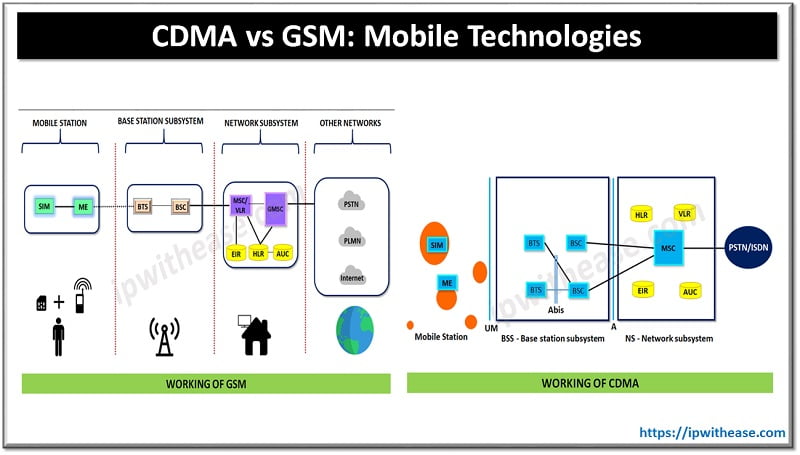
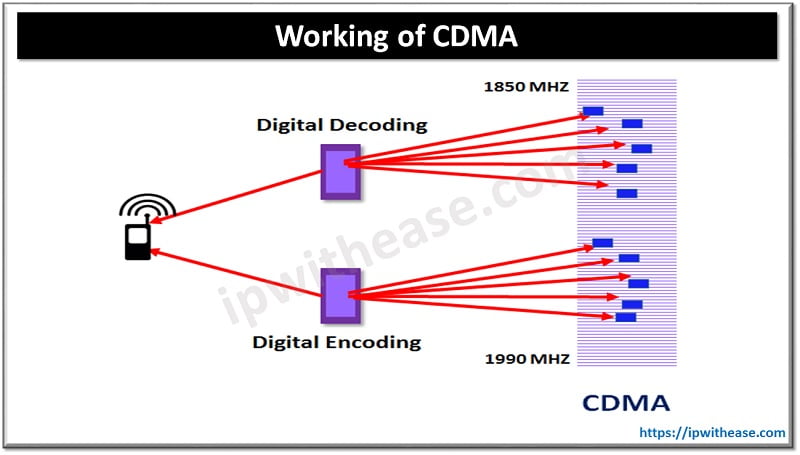
How CDMA Technology works?
Post digitization of data it is evenly spread over entire available bandwidth. Several calls are overlapped in a channel assigned a unique sequencing code ; it is a form of Spread Spectrum technique as mentioned earlier in which data is sent in small chunks over a number of frequencies available for use at any point of time within a specified range.
All user’s data will be transmitted in same way across wide band of spectrum. A unique spreading code is used to spread user signals over entire spectrum. At the receiving end , same code is used for signal recovery. It requires accurate time stamp on every chunk of signal . Multiple calls are carried out on same channel space as single analogue call.
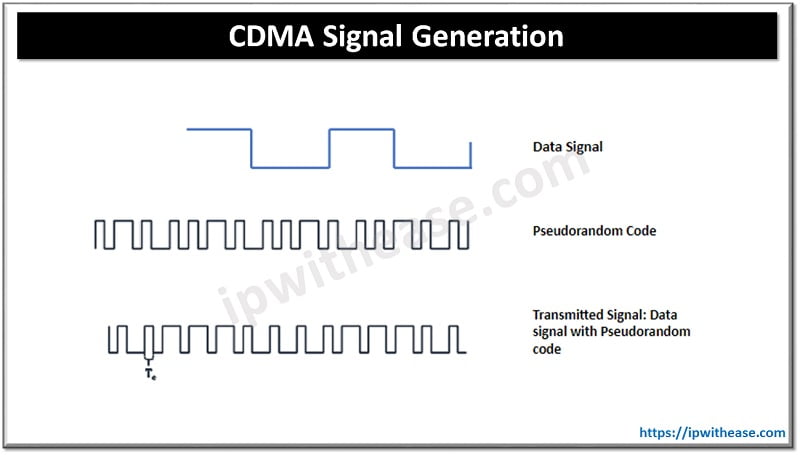
There are two types of Spread Spectrum communications – Frequency hopping and Direct sequence.
Frequency hopping – In this method the frequency is rapidly switched from one to another and receiver and transmitter are in synch always with an accurate clocking system.
Direct sequence – Data signal is multiplied by Pseudo-random noise code. The digital data coding happens at high range frequency and code generation happens pseudo randomly. The receiver is aware of the generation of same code and does correlation of received signal with the code used to extract the data.
Features of CDMA
Some of the key features of CDMA are:
- Used in Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Every channel uses full available spectrum
- Better capacity for voice and data communications
- CDMA does not require synchronization
- Allocation of code word to each user helps to reduce interference
- Used by several mobile companies (Qualcomm standard IS-2000 known as CDMA2000)
- Emits less radiation
- Faster data transfers
- CDMA supports high speed push to talk and push to email services
- UTMS 3G mobile phone standard uses W-CDMA
- OmniTRACS satellite system uses CDMA for transportation
Limitations of CDMA
Some of the Limitations of CDMA are:
- A large code length could induce delay or interference
- Time synchronization is required
- Reduction in capacity due to gradual transfers
- Constant tight power control is required resulting in multiple handovers (Causing dropped calls)
Types of CDMA Technologies
There are two types of CDMA technologies:
- Synchronous CDMA (orthogonal codes)
- Asynchronous CDMA (pseudorandom codes)
Difference between Synchronous CDMA (orthogonal codes) & Asynchronous CDMA (pseudorandom codes)
CDMA Technology | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best suited for |
| Synchronous CDMA | It exploits the mathematical properties orthogonally between vectors representing the data strings. |
|
| Mainly used by mobile telephone operators. |
| Asynchronous CDMA | Makes use of code space . Pseudo-random or pseudo-noise sequences are used. |
|
| Ideally suited for mobile networks having large number of transmitters are producing small amount of traffic at irregular intervals. |
Continue Reading:
Positioning and Navigation Help Industries Grow
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj