There are various communication technologies exist in today’s digital world. The development of powerful computing devices and need for connectivity or communication and transfer of information to long distance lead to advancement in networking technologies.
Let’s understand more about GSM technology in the below sections
About GSM: A Mobile Technology
GSM stands for ‘Global system for Mobile communication’ and it is developed by European Telecommunications Standard institute (ETSI). This standard defines the (2G) second generation protocols used in digital cellular networks. It replaced 1st generation (1G) cellular networks. Its idea originated from Cell based radio system at Bell Labs in early 1970s. GSM is operating in 200 countries covering Western Europe and America and Asia in digital cellular radio network. GSM uses Narrow band Time division multiplexing (TDMA) and Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) technology to separate users and for signal transmission.
It is used for voice, data, and text messages. GSM enabled phone can be used by user to connect his laptop to send and receive emails, fax, Internet browsing, security checks etc. GSM uses a SIM card to connect a mobile phone with its network.
GSM operates in three different frequencies – 900 MHZ used by original GSM System, 1800 MHZ used to support large number of subscribers, 1900 MHZ mainly used in USA.
GSM functionalities
- GSM provides most robust wireless data connectivity to access the Internet
- With GSM we can send and receive faxes wherever GSM is available
- GSM provides secured access in Corporate LAN. It encrypts air links and gives additional security for emails and faxes.
GSM technology is used in Mobile telephony, GSM-R, Telemetry system, Fleet management, Automatic meter reading, Toll collection, Remote control and fault reporting of DG sets, Value added services etc.
History of GSM
GSM was developed by Group Special Mobile (Which was found in 1982) it was an initiative of CEPT (Conference of European Post and Telecommunication) the aim was to replace the incompatible Analogue system.
GSM standardization is the responsibility of special mobile group under ETSI (European telecommunication Standards Institute).
More than 135 countries use GSM with more than 1300 million subscribers in India there are more than 45 million subscribers
How GSM Technology works?
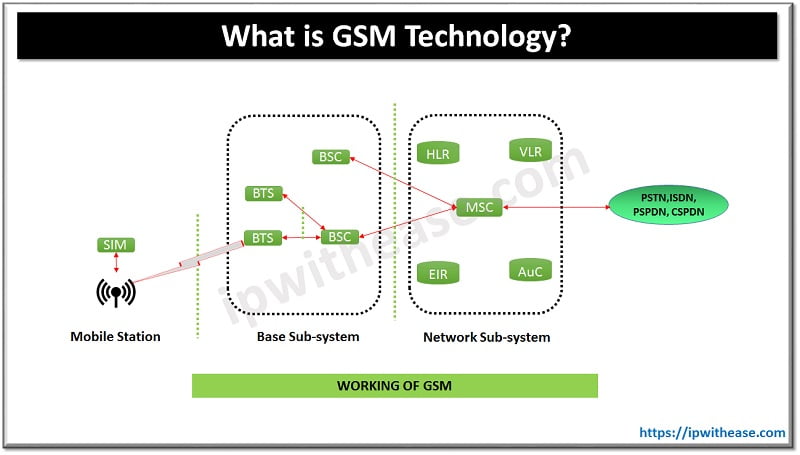
In GSM geographical areas are divided into hexagonal cells, power of transmitter and load on receiver decides the side. At the Cell center, the base station comprises of a transceiver and antenna. It is a combination of TDMA (Time division Multiplexing) and FDMA (Frequency division multiplexing) and frequency hopping. GSM used two bands initially 25 MHZ width: 890 to 915 MHZ frequency band for up-link and 935 to 960 MHz frequency for down-link. Later 2 more bands added 24 MHZ is divided into 124 channels having 200 KHz width and balance 200 KHz is unused as Guard band to evade interference.
Components of GSM
- Media station (MS) is a physical equipment like mobile phone, radio transreceiver and SIM card. It is meant to provide air interface to the user with GSM networks. It also provides various data services and acts as receptor for SMS services.
- Base transreceiver system (BTS) is radio component with Mobile station, it houses radio transceivers which define a cell and handle the radio link protocols.
- Base station controller (BSC) allocates timeslots between BTS and MSC and it handles radio channel setup, frequency hopping and handovers etc.
- Home location register (HLR) is database of subscriber having details like subscriber’s ID, location details, authentication key, activity status etc.
- Visitor location register (VLR) contains copy of HLR data stored temporarily until subscriber is active
- Equipment identity register (EIR) database maintains list of valid mobile equipment on the network its International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) identifies each MS useful in tracking stolen devices
- Authentication center (AuC) component to perform authentication of subscriber and it stores a secret key in subscriber SIM card which is used for authentication and Ciphering purpose of radio signal. It provides protection against frauds in cellular world to network operations.
Features of GSM
Some of the key features of GSM are:
- Supports International roaming
- It uses TDMA and FDMA technology for voice and data transmission
- Its transmission rate is slow compared to CDMA
- It uses EDGE data transfer technology
- It requires a SIM card for communication
- Less prone to radiation
- Less secure communication compared to CDMA
- Requires additional encryption as it has no in-built encryption
- Enables worldwide roaming
- It uses encryption to make phone calls more secure
- High quality speech /voice
- Management of SIM phonebook
- Compatible with Integrated services digital network (ISDN)
- Low cost mobile sets and base stations (BS)
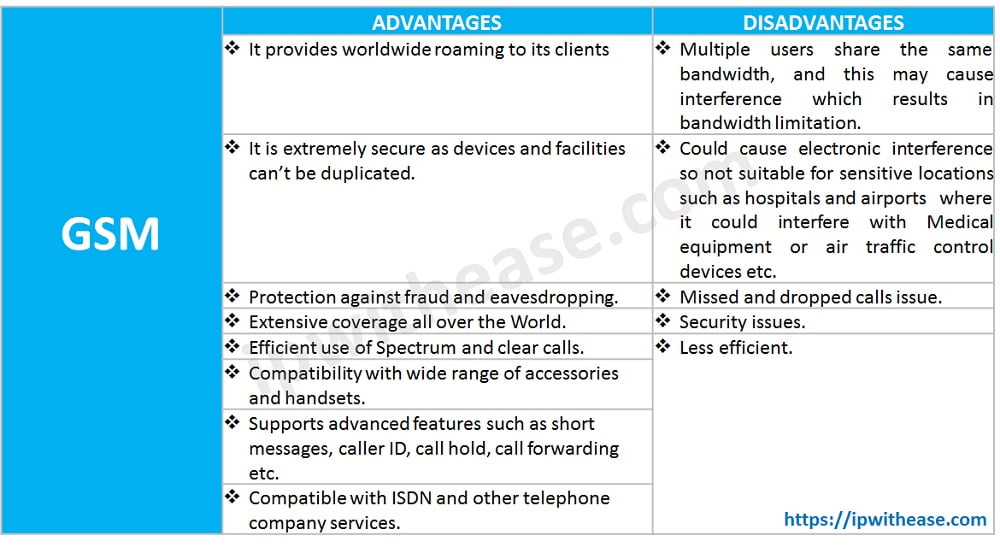
Advantages and disadvantages of GSM Technology
To summarize, the advantages and disadvantages of GSM Technology are:
Continue Reading:
How To Decide On The Best VoIP Phone Service?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj