Introduction to CDMA & GSM
In mobile communication there are two most popular technologies – CDMA ‘Code Division Multiple Access’ and GSM ‘Global system for Mobile communication’. The advent of these two technologies have changed the way world communicates today.
Let’s explore more about both technologies, identify the difference between the two, their benefits and disadvantages or limitations and so on.
About GSM
GSM is an acronym for ‘Global system for Mobile communication’ and it is developed by European Telecommunications Standard institute (ETSI). This standard form the basis for 2G. GSM phones have two components – the handset and the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card. SIM contains all information related to user and SIM can be put in another mobile handset and activate it for same user.
GSM uses GPRS for data transfer which provides slow data transfer rate. The entire area is divided into cells and each cell has a network tower which provides services for all mobile sets operating within the range of these cells.
GSM is based on TDMA (Time division multiple access) in which channels are sliced into different time slices and in FDMA (Frequency division multiple access) multiple users can access is granted by separation of frequencies in a channel. GSM supports roaming worldwide.
There are three major services of GSM:
Tele services – Comprising mobile phones, emergency calling etc
Data services – Short message service (SMS), fax, voice mail, email etc
Supplementary services – Incoming and Outgoing calls, call forwarding, call waiting, conferencing etc
History of GSM
GSM was originated way back in 1975 by Henry Kieffer from the Swiss PTT who advised for to have a new spectrum for mobile at 900 MHz the GSM standard was built by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks for mobile communications. It was first deployed in Finland Dec’1991. GSM is become global standard and took over 90% of market share.
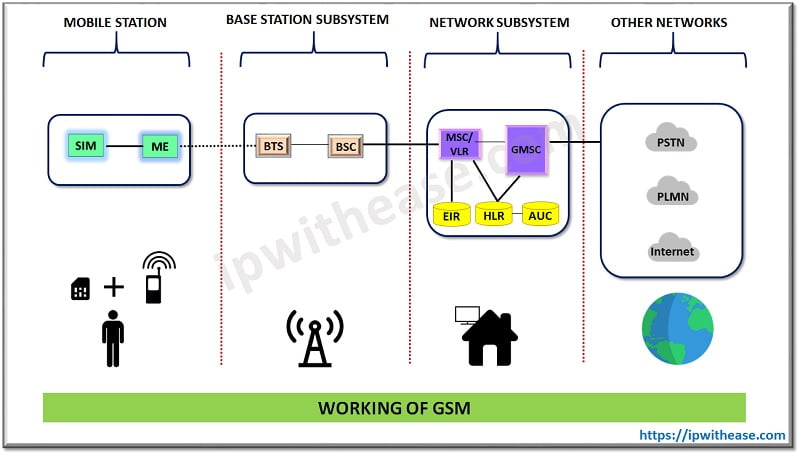
How GSM Technology works?
The main components of GSM system are – Network subsystem, Radio subsystem and Operation and maintenance subsystem.
Components of GSM :
- Network subsystem – perform call processing and subscriber related functions and it includes
- MSC – Mobile switching Centre controls radio subsystem and it comprises of BSC (base station controller) and it is responsible for signalling to / from BTS, frequency allocation & power control. BTS (base transceiver station) maintains air interface , paging information, radio level power control, speech processing and handles ciphering functionality.
- HLR – Home location register contains subscriber details such as Subscriber ID (IMSI and MSIDSN), current location, subscriber status, authentication key, mobile subscriber roaming number
- VLR – Visitor location register provides local database for subscriber and contains copy of information (related to subscriber) stored in HLR.
- AuC – Authentication center used for authentication of a mobile subscriber into the network
- EIR – Equipment identity register stores International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) numbers and it is specific to handset
- GMSC – gateway MSC is a used to route calls outside the mobile network
About CDMA
CDMA acronym stands for ‘Code Division Multiple Access’ and it forms the basis for 3G mobile phones. There is no removable SIM card in CDMA phones. The information about the user is stored within the handset only. Each device is allocated a specific access code. The transmission happens across entire frequencies by network stations. The handset is identified by code theory in the mobile network. The data transmission rates are faster in CDMA as it uses EVDO (Evolution-Data Optimized) which provides faster data rate by providing wireless transmission using radio signals. In CDM multiple users in a channel are isolated using a specific code which is used to send signal. It is not a worldwide accepted standard hence it has limited roaming capacity.
History of CDMA
CDMA technology was used during World War II by English soldiers to stop German solider attempts to jam transmissions. So instead of doing transmission of signals over one single frequency English soldiers decided to transmit signals over multiple frequencies to make it difficult for German solider to intercept the complete signal. In 1949, Claude Shannon and Robert Pierce developed the idea of CDMA, in July 1993 the TIA approved CDMA as technology standard. 22 countries now support CDMA, Verizon is the largest carrier and second largest carrier is AT&T using CDMA.
How CDMA Technology works?
CDMA is a spread spectrum technology which rather than using separate radio frequencies or channels unique digital codes are used to distinguish subscribers. The codes used by base station and mobile companies are called ‘pseudo-Random Code Sequences’. Users are separated by a unique code and not by time slot and frequency.
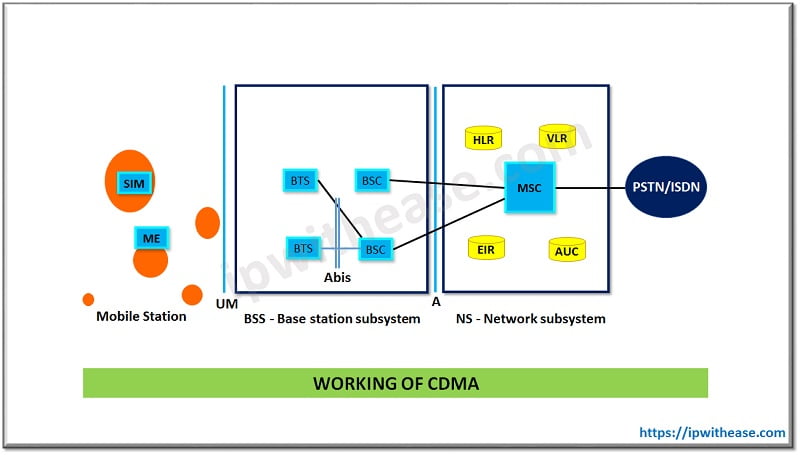
Components of CDMA:
- Mobile Station (MS) – provides personal mobility and have IMEI (International Mobile equipment Identity) and IMSI (International Mobile subscriber identity)
- BTS (Base transceiver station) – defines the cell and handles the radio link protocol with the mobile station
- BSC (Base station controller) – provides transmitter power and handoff control, allocates and de-allocates channels, manages radio resources for BTS
- MSC (Mobile Switching center) – does call setup/supervision and release, call routing, collection of billing information, management of mobility, paging and cancellation of echo, connectivity to other BSC and other local exchange networks, access to Home location and Visitor location register
- Home Location register (HLR) – per CDMA one HLR is maintained which contains the database of all subscribers in the network, mobile station routing number
- Visitor Location register (VLR) – is a temporary visitor database and per MSC there is one VLR maintained, it provides authentication , encryption and security and maintains the IMEI number (Unique to device)
Some of the limitations of CDMA are it is expensive to setup base station with complex communication equipment and costs the 1.5 times of GSM (TDMA), Near far problem, don’t offer international roaming.
Comparison Table: CDMA vs GSM
Below table describes the difference between the two technologies:
PARAMETER | CDMA | GSM |
| Definition | CDMA is ‘Code division multiple access’ | GSM is ‘Global system for Mobile Communication’ |
| Technology | CDMA technology callers in a channel are separated using a code (CDM) | Called identification happens using TDMA(Time division multiple access) and FDMA (Frequency division multiple access) technology |
| Availability | Not widely accepted standard hence has limited roaming capabilities | Used and accepted worldwide due to its roaming capability |
| Data Speed | 3..6 Mbps | 42 Mbps in HSPA (3G) |
| Features | CDMA is handset specific; CDMA don’t support data and voice transmission ,CDMA uses EVDO which provides higher data transmission rates , offers relatively higher security, automatic signal encryption supported , radiation emission is less in CDMA as it does not produce pulses, Lower power requirements | GSM is SIM specific; simultaneously Data and voice both are transmitted simultaneously, GSM uses GPRS hence provides low data transmission rates , offers less secure communication, no built-in encryption, radiation emission is more in in GSM as it continuously transmits wave pulses |
| Providers | Sprint, Verizon, and US Cellular, MTS India, Reliance, and TATA Indicom | AT&T ,T-Mobile, Airtel, Idea, Vodafone, Reliance, BSNL, Tata, Aircel |
Download the CDMA vs GSM Comparison Table.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj