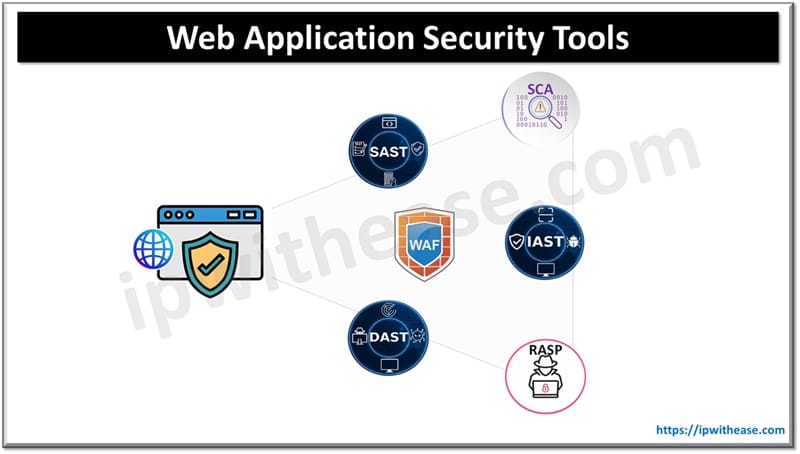
Table of Contents
Introduction to Cisco SD-WAN Security
Cisco SD-WAN security features are centrally configured via vManage in the security section through simple guided workflows. The guided workflow can assist the network administrator in building security policy based on well-known use cases such as Compliance, Guest Access, Direct Cloud Access, and Direct Internet Access or based on a custom use case.
SD-WAN offers complete transport flexibility and efficient access to cloud applications in Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) multi cloud environments. It creates a better user application experience and reduces the cost for organizations, the solution must also address increasingly sophisticated security threats and offer protection against network vulnerabilities.
Security benefits of Cisco SD-WAN
- Protection against all types of internal and external threats from branches.
- Improved user experience via secure direct internet access and cloud access.
- Increased overall network efficiency and reliability, network security with micro-segmentation and identity-based policy management.
- Centralized visibility and control for inbound and outbound traffic flow.
- It reduced cost and complexity using a single product for networking, security, and cloud.
- Simple and Automated Security Solution to deploy and ease of configuration and deployment of the SD-WAN security solution.
- Comprehensive SD-WAN Security capabilities such as Application-Aware Enterprise Firewall and IPS enabled on your WAN Edge device.
- Easy Deploy, troubleshoot, and monitor the SD-WAN overlay solution with security capabilities across the WAN Edge devices centrally via the Cisco vManage GUI.
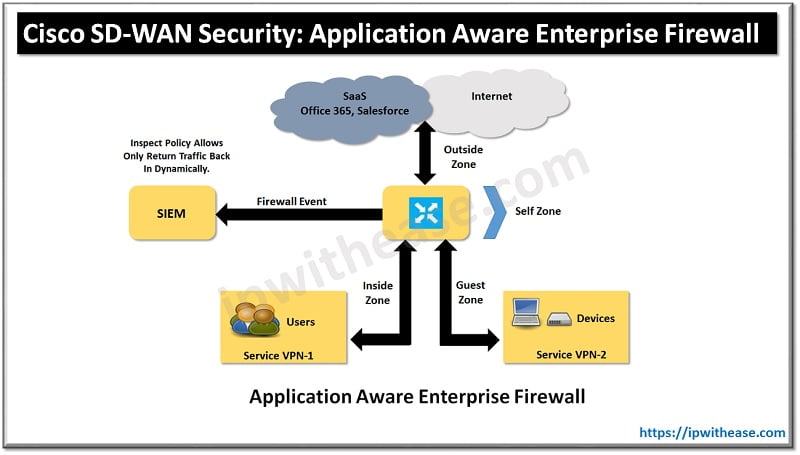
SD-WAN Security with Application-Aware Enterprise Firewall
One of the most basic yet crucial forms of security at the branch is firewalling. A firewall provides protection of stateful TCP sessions, enables logging, and ensures that a zero-trust domain is implemented between segments in the network. Cisco SD-WAN takes an integrated approach and has implemented a robust Application-Aware Enterprise Firewall directly into the SD-WAN. The Cisco SD-WAN firewall provides stateful inspection, zone-based policies, and segment awareness. Also, through network-based application recognition. These applications can be secured based on category or on an individual basis, depending on how the feature is leveraged in the security policy.
Because these policies are VPN aware, they can be applied within a zone, between zones on the same WAN Edge router, or between zones across the Cisco SD-WAN fabric. A zone is a group of one or more VPNs. Grouping VPNs into zones allows you to establish security boundaries in your overlay network so that you can control the flow of all data traffic that passes between these zones. Zone configuration consists of the following components:
- Source zone is a grouping of VPNs where the data traffic flows originate from first hop.
- Destination zone is a grouping of VPNs where the data traffic flows terminate at last hop.
- Firewall policy is a localized security policy that defines the conditions that the originating data traffic flow must match to allow the flow to continue to the destination zone.
- Zone pair is a container that attached with a source zone with a destination zone and that applies a firewall policy to the traffic that flows between the two zones.
Three categories of action subjected to firewall policy with matching flows:
- Inspect: When the action is set to Inspect, the Enterprise Application-Aware Firewall tracks the state of the flows and creates sessions. Since it maintains the state of the flows, the return traffic is allowed and there is no need to configure a separate policy to allow the response traffic.
- Pass: When the action is set to pass it allows the router to forward the traffic from one zone to another zone. It does not track the state of the flows. In other words, the firewall does not create sessions when the action is set to pass. The Pass action allows the traffic to flow in only one direction. You must have a corresponding policy to allow the response traffic.
- Drop: When the action is set to drop and packets match against the set match parameters in policy, that packet will be dropped.
Steps to configure a firewall policy in Cisco SD-WAN
The following is a summary of steps required to configure a firewall policy in Cisco SD-WAN:
Step 1. Create a new firewall policy. Name and describe the policy.
Step 2. Configure zones. Create your source and destination zones. Today, zones are equivalent to SD-WAN VPNs.
Step 3. Apply zone pairs. Group the source and destination zones into a zone pair to define traffic direction. The policy sequences will be applied to this zone pair.
Step 4. Configure a default action. This is the action that will take place if a sequence match is not found. Drop, Inspect, and Pass are valid options.
Step 5. Configure sequence rules. Match traffic using Layer 3–4 information (such as source data prefix lists, source ports, destination data prefix lists, and so on) or by matching on application category or name.
Continue Reading:
Cisco SD WAN Application Aware Routing
SD-WAN Fabric Bring Up in Cisco Viptela
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj