Introduction to Operating Systems
Mobile and computer operating systems are developed in different ways and for different purposes. Computer OS are older and have higher spread and penetration among larger groups of people. Microsoft Windows and Apple Mac OS have emerged as two major operating systems and there were some open-source operating systems also like Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD and GNU. Computer operating systems are not designed for usage on mobile use over wireless networks. The mobile operating system is a newer concept, in many ways the mobile OS has built on what computer OS has already accomplished.
Today we look at major differences between Mobile operating systems and Desktop operating systems, their features, advantages and disadvantages etc.
Mobile Operating System
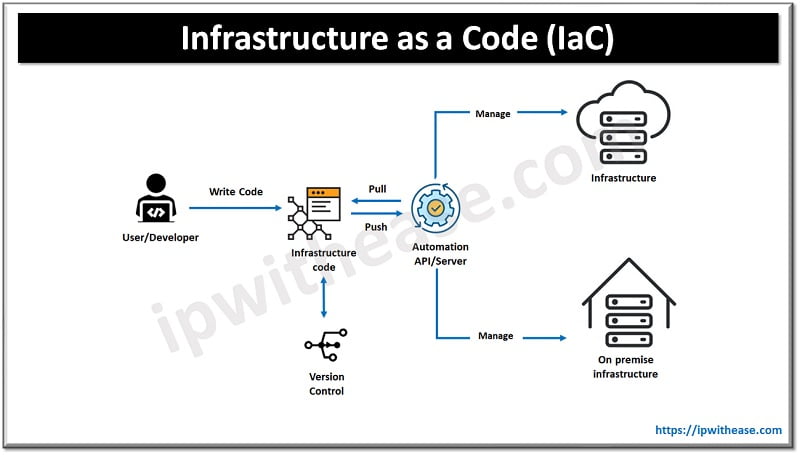
A mobile operating system is an operating system which helps to run application software on mobile devices. It is similar to desktop operating systems to some extent but simpler and lightweight compared to their counterpart. The operating systems found on smartphones include Symbian OS, iPhone OS, RIM’s Blackberry, Windows mobile, Palm webOS, Android, and Maemo. Android, WebOS, and Maemo are derived from Linux operating system. The iPhone OS is originated from BSD and NeXTSTEP both are related to UNIX.
Mobile operating systems combine features of computer and hand-held devices. They typically contain a cellular built-in modem and SIM tray for telephony and Internet services. If we buy a mobile device it comes preloaded with an OS specific to the device. Some popular mobile OS are Android OS, Bada (Samsung electronics), Blackberry OS, iPhone OS / iOS, Symbian OS, Windows Mobile OS, Harmony OS, Palm OS, WebOS (Palm/HP). Android OS is the most popular operating system as of today. It is a mobile based Linux kernel and open-source software. It was developed by Google and the first Android device was launched in 2008.
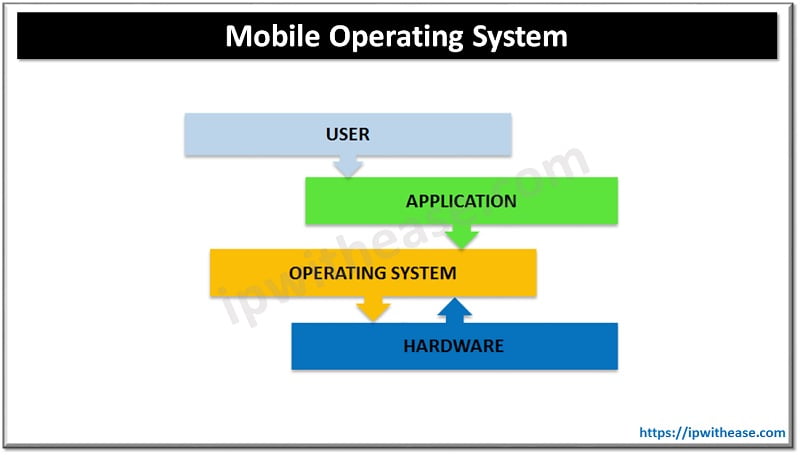
Functions of Mobile Operating system:
- Memory Management.
- Process Management/CPU Scheduling
- Device Management
- File Management
- Device Security
- Error detection
Desktop Operating System
An operating system is the software that allows a user to run crucial applications on his/her computing device. It helps to manage computer systems hardware and software resources. It supports basic functions such as scheduling tasks, controlling peripherals, printing, input / output and memory allocation. The operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware.
Some operating systems require installation or may be pre-installed with purchased computers. The most common operating systems for desktop systems are Microsoft Windows, MacOS, and Linux. Modern operating systems use Graphical User Interface (GUI). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons and menus and everything is displayed on screen using a combination of graphics and text.
Microsoft Windows operating was launched in the mid-1980s, there are different versions of Windows, and the most recent ones are Windows 10 (2015), Windows 8 (2012), Windows 7 (2009) and Windows Vista (2007). Windows comes pre-loaded on most new PCs which makes it the most popular operating system in the world. MacOS is another popular operating system created by Apple. It comes preloaded on all Macintosh computers. Some major versions include Mojave (2018), High Sierra (2017), and Sierra (2016).
MacOS market penetration is less than 10% of global operating systems much lower than the Microsoft Windows market share (More than 80%).
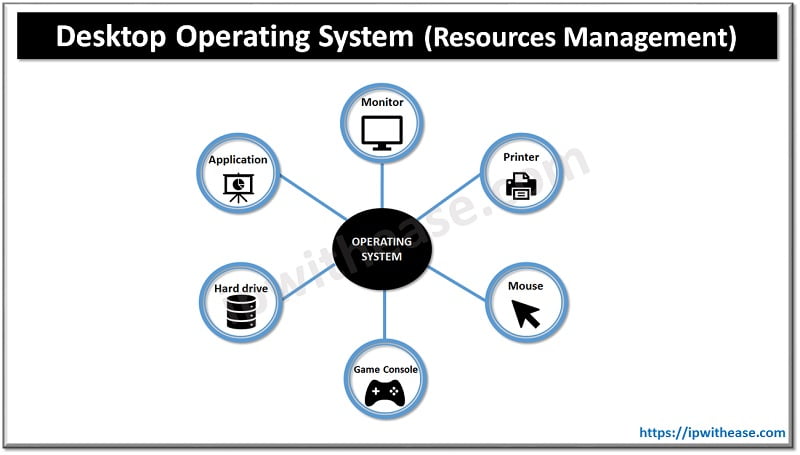
Functions of Desktop Operating System:
- Memory management
- Processor management
- Device/hardware management
- Run software applications
- Data management
- Evaluate system health
- Provides user interface
- Input/output management
- Time management
- Interrupt handling
Comparison: Mobile Operating System vs Desktop Operating System
FUNCTIONS | MOBILE OPERATING SYSTEM | DESKTOP OPERATING SYSTEM |
| Definition | It allows smartphones, tablet PCs, and other devices to run applications and programs | Main control program or environment through which user controls a personal computer and it manages all applications and programs in a computer |
| Purpose | Manages cellular and wireless connectivity, and phone access | Manages hardware and software resources of the system |
| Boot time | Boots faster than desktop OS | It boots much slower |
| Storage | Uses flash drive to store data/information | Uses hard drives / flash drives to store data/information |
| Power requirements | Optimized to work under minimal power requirements and have feature to prevent energy loss | Desktop OS is not readily optimized for energy loss |
| Interface | Mobile Os operates with touchscreen or touch pad | PC operates via many input devices such as mouse, keyboard etc. |
| Memory usage | Optimized to work on minimum RAM | Requires good amount of memory to operate |
| Features | -Specialized for specific set of devices -Don’t offer complete access to system hardware (such as administrator or root) -Limited or no interoperability (Mobile apps are strictly hardware specific) | -Full featured. Designed to take advantages of fast CPUs, large amount of disk space, and RAM -Based on X86 majorly it is more flexible in terms of interoperability
|
| OS flavours | Apple iOS, Google Android, Bada (Samsung electronics), Blackberry OS, iPhone OS / iOS, Symbian OS, Windows Mobile OS, Harmony OS, Palm OS, WebOS (Palm/HP) etc. | Windows 10, MacOS, Windows Vista etc. |
Download the comparison table: Mobile OS vs Desktop OS
Continue Reading:
Firmware vs Operating System: Sneak Preview
What is Distributed Operating System (DOS) ?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj