Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how your computer knows where to send the websites you want to visit? Or how Netflix knows you’re trying to sneak into a different country’s catalog? Welcome to the world of IP addresses and proxies, where your online identity and location are determined and, sometimes, cleverly disguised.
What is an IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique string of numbers separated by periods (IPv4) or colons (IPv6). It acts like your home address but for your computer on the internet, guiding data to the correct destination. Imagine you’re sending a letter to a friend; without their address, the letter wouldn’t know where to go. Similarly, your IP address ensures that the digital information you request reaches you accurately.
IPv4 Addresses
IPv4 addresses are the most common type of IP address, written as four decimal numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.0.1). Each of these numbers can range from 0 to 255. This format is known as dot-decimal notation.
IPv6 Addresses
With the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, IPv6 was introduced, providing a much larger address space. IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0120:7344).
How Does an IP Address Work?
IP addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and are either static (permanent) or dynamic (temporary).
A dynamic IP address can change each time you connect to the internet, whereas a static IP address remains constant.
When you type a website URL into your browser, your device sends a request to a DNS (Domain Name System) server to find the corresponding IP address. Once located, your request is routed through various servers and networks until it reaches its destination. The process then reverses, sending the requested data back to your IP address.
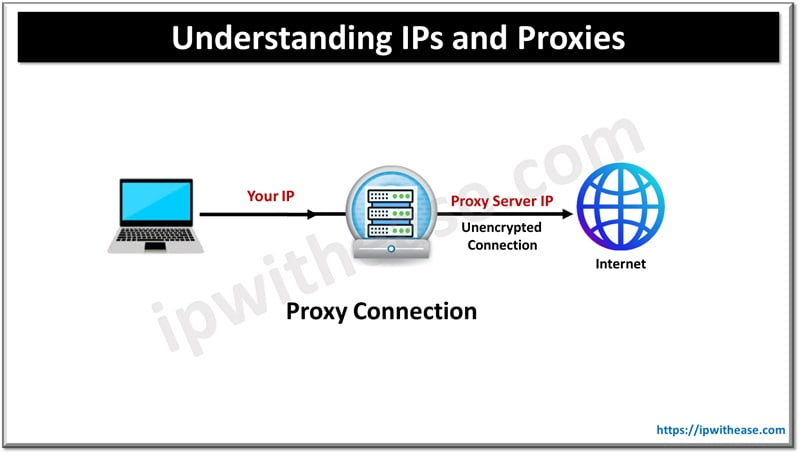
How Proxies Can Alter an IP Address
Now that you know how IPv4 and IPv6 addresses work, let’s go into how proxies can alter your IP address.
Proxies basically act as intermediaries between your device and the internet. When you connect to a website through a proxy server, the website sees the proxy’s IP address instead of yours. This can be useful for several reasons, from enhancing privacy to bypassing geographical restrictions.
Types of Proxies
- HTTP Proxies: These are specifically designed for web traffic. They can cache web pages and filter content, providing faster access to frequently visited sites and blocking unwanted content.
- SOCKS5 Proxies: More versatile than HTTP proxies, SOCKS5 proxies handle various types of traffic (e.g., email, file transfers) and offer better performance and security.
- Transparent Proxies: Often used by organizations to monitor and filter internet usage, transparent proxies do not hide the user’s IP address but still act as intermediaries.
- Mobile Proxies: These are specifically to be used on mobile devices (iphone, androids etc.). Mobile proxies are typically available as 5G/LTE and work to hide your mobile device’s IP.
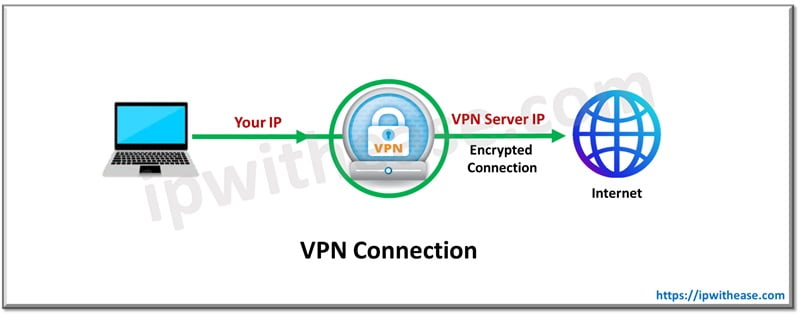
How a VPN Can Alter an IP Address
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) also masks your IP address but with some added benefits. When you connect to a VPN, it creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your whole devic (not just one app or the browser) and the VPN server.
In short it means: All your internet traffic is routed through this tunnel, making it appear as though it originates from the VPN server’s IP address.
Related: Types of Virtual Private Network (VPN) & its Protocol
How It Differs from a Proxy
While proxies only reroute traffic from specific applications, VPNs encrypt and reroute all traffic from your device. This includes background apps and services, offering a higher level of privacy and security. VPNs protect against eavesdropping and cyber threats, making them ideal for secure internet browsing.
Who Would Need a Proxy or VPN?
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN depends largely on your specific needs and usage scenarios. Here are some examples of who might benefit from using these tools.
- Privacy and Security: Individuals concerned about their online privacy or wanting to secure their data from hackers.
- Streaming and Gaming Fans: Users who want to access content or gaming servers that are geographically restricted.
- Bypassing Geo-blocks: People who need to access websites or services unavailable in their country.
- Social Media: For those who need to manage multiple social media accounts or scrape data without being detected, mobile proxies use IP addresses assigned by mobile carriers, making them harder to block.
Pros and Cons of Each
Both Proxies and VPNs have their strengths and weaknesses, depending on the specific use case. Let’s explore the pros and cons of each to help you make an informed choice.
| Feature | Proxy | VPN |
| Scope of Coverage | Single app or service | Entire device |
| Encryption | None (usually) | Yes |
| Speed | Generally very fast | Slightly slower due to encryption |
| Cost | Comparibly cheap | Usually requires a subscription that is more expensive |
| Anonymity | Moderate (depends on type) | High |
| Ease of Use | Easy setup | Requires installation and setup |
| Security | Basic (better with SOCKS5) | High (encryption protects data) |
Do You Need Both?
Using both a proxy and a VPN can provide the best of both worlds. A proxy can handle specific tasks like accessing geo-blocked content, while a VPN can secure all your online activities. However, for most users, a VPN alone offers sufficient privacy and security. For corporations that do a lot of web scraping, a proxy server from reputable providers like Litport may be a better choice.
Final Words
Understanding your online options ensures you stay safe, private, and unrestricted while surfing the web. Choose the tool that best fits your needs, and enjoy a secure online experience. Make sure to read out other articles on proxies, security and privacy.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.