IP address is the designated address used for communication between computers. Whether we need to access a web page or download a file, we rely on the IP address to deliver the desired content. IP address serves as the location identifier for the specific file or webpage. There are two types of IP addresses:
- IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
- IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
What is IPv4?
Address Length: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and has approximately 4.3 billion unique IP addresses.
Address Notation: IPv4 addresses are written in a decimal format, such as 192.168.1.1.
NAT: NAT is often used to allow multiple devices in a private network to share a single public IPv4 address, enabling them to access the internet.
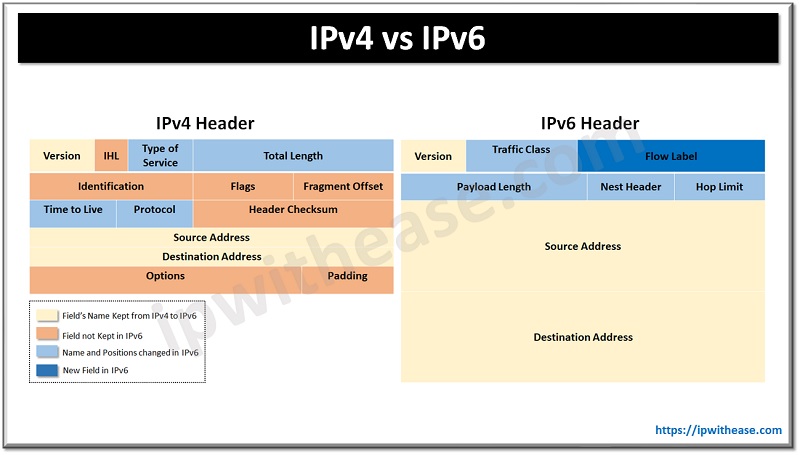
Header Complexity: IPv4 headers can be relatively complex, and there is less support for packet prioritization and quality of service.
Security: Security features in IPv4, such as IPsec, are optional and are often implemented through additional protocols.
What is IPv6?
Address Length: IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, providing an almost limitless number of unique IP addresses, which is crucial for the continued growth of the internet.
Address Notation: IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal format with colons, such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
Address Allocation: IPv6 uses a hierarchical addressing structure, which simplifies routing and makes IP address management more efficient.
No NAT: IPv6 was designed with the intention of eliminating the need for NAT. Each device can have its unique global IPv6 address, simplifying end-to-end connectivity.
Header Simplification: IPv6 headers are simpler, with many optional features and fields from IPv4 being made mandatory or eliminated. Quality of service and packet prioritization are better supported.
Built-in Security: IPv6 includes IPsec as a mandatory part of the protocol, enhancing security and encryption features.
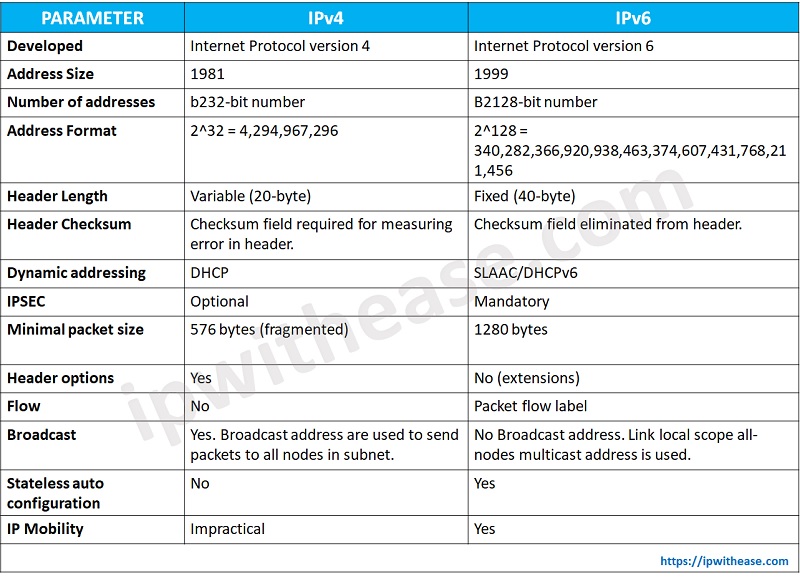
Comparison Table: IPv4 vs IPv6
Below table will help understand difference between IPv4 and IPv6 protocols:
PARAMETER | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Developed | Internet Protocol version 4 | Internet protocol version6 |
| Address Size | 1981 | 1999 |
| Number of Addresses | b232-bit number | b2128-bit number |
| Address format | 2^32 = 4,294,967,296 | 2^128 = 340,282,366,920,938,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 |
| Header length | Variable (20-byte) | Fixed (40-byte) |
| Header Checksum | Checksum field required for measuring error in header | Checksum field eliminated from header |
| Dynamic addressing | DHCP | SLAAC/DHCPv6 |
| IPSEC | Optional | Mandatory |
| Minimal packet size | 576 byte (fragmented) | 1280 bytes |
| Header options | Yes | No (extensions) |
| Flow | No | Packet flow label |
| Broadcast | Yes. Broadcast address are used to send packets to all nodes in subnet | No Broadcast address. Link local scope all-nodes multicast address is used. |
| Stateless auto configuration | No | Yes |
| IP mobility | impractical | Yes |
Download the comparison table: IPv4 vs IPv6
Benefits of IPv6 over IPv4
- Address Exhaustion: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, which limits the number of unique IP addresses to approximately 4.3 billion. With the exponential growth in the number of internet-connected devices, IPv4 addresses were quickly running out. IPv6, with its 128-bit address space, provides an almost unlimited number of unique IP addresses, ensuring that the internet can continue to expand and accommodate the growing number of devices.
- End-to-End Connectivity: IPv6 provides end-to-end connectivity, which means that every device can have its unique global IP address. This simplifies communication by eliminating the need for NAT. NAT can complicate network configurations and hinder certain applications like peer-to-peer connections.
- Improved Security: IPv6 includes IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) as a mandatory part of the protocol. IPsec provides encryption and authentication for network communication, enhancing the security of data in transit.
- Better Support for Mobile and IoT Devices: The proliferation of mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) has increased the demand for IP addresses. IPv6 can more effectively accommodate these devices due to its vast address space and improved support for mobile and wireless communication.
- Future-Proofing: IPv6 is designed to be a long-term solution that can accommodate the internet’s growth for many years to come.
- Global Standard: IPv6 has become a global standard, supported by all modern operating systems and network equipment. Its adoption is essential to maintain interoperability and ensure that the internet functions smoothly on a global scale.
Final Words
IPv6 addresses the critical issues of IPv4 address exhaustion, enhances security, simplifies network architecture, and supports the growing number of internet-connected devices. It is a foundational technology for the continued expansion and evolution of the internet.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj