Table of Contents
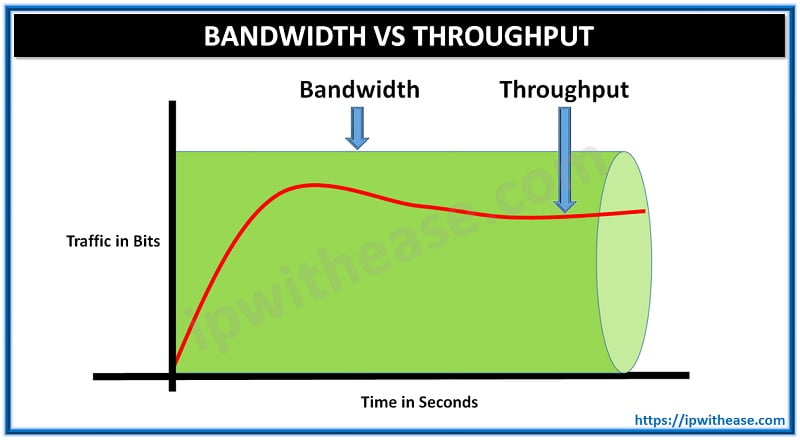
Bandwidth is the maximum data transfer capacity of a network, typically measured in Mbps or Gbps. While, throughput is the actual rate at which data is successfully transmitted over the network. In this blog, we discuss the difference between the two in detail.
What is Network Bandwidth?
Bandwidth actually gives the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted through a link or channel. Bandwidth does not consider latency and protocols type while considering the traffic traversing the link.
What is Network Throughput?
Throughput is defined as rate of successful information delivery over a communication link. That is the actual amount of data that gets transmitted back and forth from computer, through the Internet to the web server in a single unit of time. Several factors like delay, physical media and hardware capabilities can effect this reduction in the bandwidth. Protocols type and latency of link play a pivotal role in deciding throughput which is unlike in case of bandwidth.
Comparison: Bandwidth vs Throughput
AT first glance throughput vs bandwidth may appear to be same, like both having same measurement unit of bps, however both the terms are quite dissimilar with differences in table below:
| BANDWIDTH | THROUGHPUT |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can travel through a link or network. | Throughput is the actual amount of data that can be transferred through a network. |
| Bandwidth is always measured as physical layer property. | Throughput can be measured at any layer in OSI model. |
| A data rate measured in bits per second. | Average rate of successful message delivery over a communication channel. These data may be delivered over a physical or logical link, or pass through a certain network node |
| Bandwidth does not depend on latency on link | Throughput depends on latency on the link. |
| Theoretical performance | Real World performance |
Download the comparison table: bandwidth vs throughput
Scenario Example
A simple example of cars traversing a bridge would explain the difference in a better way.
- 1 car is taken equivalent to 1 bit of traffic
- 3 cars (3 bits) can simultaneously cross the bridge in half a second. This makes total of 6 cars (2 * 3 cars) that can cross the bridge in 1 second. Theoretically calculating, bandwidth of the bridge will be 6 bits per second (6 cars per second)
However the real conditions may differ. There are pits and speed breakers on the bridge which may incur delay and allow only 3 cars to take 1 second to cross the bridge .Now, considering the real conditions and delay caused by the road the throughput of traffic will be 3 bits per second (3 cars per second)
Summary
Bandwidth of traffic transmitted over the bridge = 6 bps
Throughput of traffic transmitted over the bridge = 3 bps
Both the terms may be defined as below –
Bandwidth == Maximum of the transmission media (Theoretically).
Throughput == Time taken to transmit given size of data (Real World)
Related FAQs
1. What is the difference between bandwidth, throughput, and latency?
Bandwidth is the maximum data capacity of a network connection, typically measured in bits per second (bps).
Throughput is the actual amount of data transferred over the connection in a given time period, which can be less than bandwidth due to network constraints.
Latency is the time delay for data to travel from the source to the destination, typically measured in milliseconds (ms). Lower latency is essential for real-time applications, like video calls or online gaming.
2. How does latency impact network performance?
High latency can cause delays in data transfer, making applications feel sluggish, especially for interactive services. It affects response times and user experience, even if bandwidth is sufficient. Reducing latency is essential for applications requiring real-time communication, like VoIP and video conferencing.
3. Can high bandwidth compensate for high latency?
No, high bandwidth cannot entirely offset high latency. While bandwidth increases the volume of data transferred, it does not reduce the time it takes for each packet to reach its destination. Thus, applications that need instant responses, like remote control systems or real-time gaming, can still suffer from high latency despite high bandwidth.
4. What factors can affect network throughput?
Several factors can influence throughput, including network congestion, hardware limitations, signal quality (especially on wireless networks), and protocol overhead. For example, a network may have high bandwidth, but if it’s congested, the throughput will be limited due to data collisions and retransmissions.
5. How can I optimize my network for low latency and high throughput?
To improve network performance, consider the following:
1. Upgrade hardware like routers and switches to handle higher speeds.
2. Reduce congestion by managing network traffic, implementing Quality of Service (QoS), and limiting unnecessary data-intensive applications.
3. Use wired connections over wireless where possible, as wired connections tend to have lower latency.
4. Optimize routing paths to shorten the distance data needs to travel across the network.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj