Table of Contents:
VMware Distributed Switch:
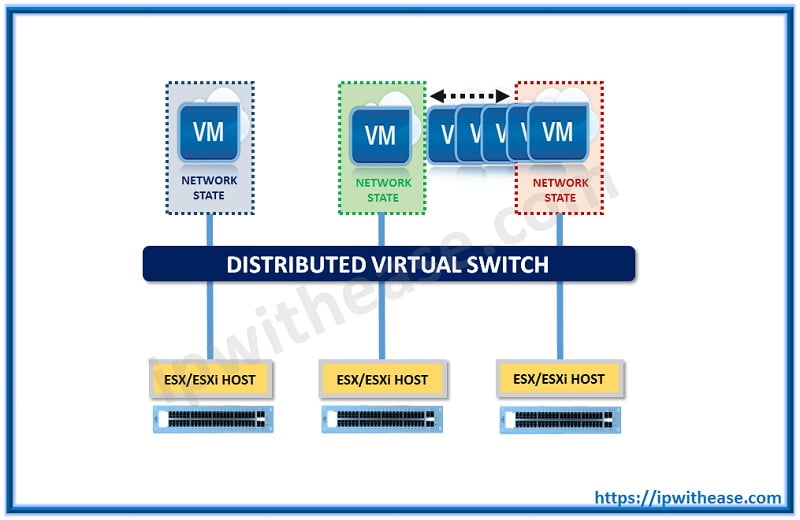
The functioning of the distributed switch is like a single switch athwart all the connected host of ESXi. Since their migration takes place across multiple hosts, they also allow maintaining the constant configuration of the network.
In VMware Distributed Switch vs Standard Switch, frames are forwarded by Distributed Switches at layer 2 similar to the standard switches and they too support NIC teaming, VLANs and shaping of outbound traffic etc.
Related – VMware Interview Questions in 2020
These two forms of virtual switches have the biggest difference in their configuration. A central unified interface of management is used for configuring the distributed switches via vCenter server.
The configuration of the virtual machine network is greatly simplified by this since complexity is reduced in clustered environments of ESXi.
Some advanced features of networking are also supported by distributed switches including port mirroring, I/O network control, checking network health and support for the protocols like Private VLAN, NetFlow, link layer discovery protocol, link aggregation control protocol etc.
VMware Standard Switch:
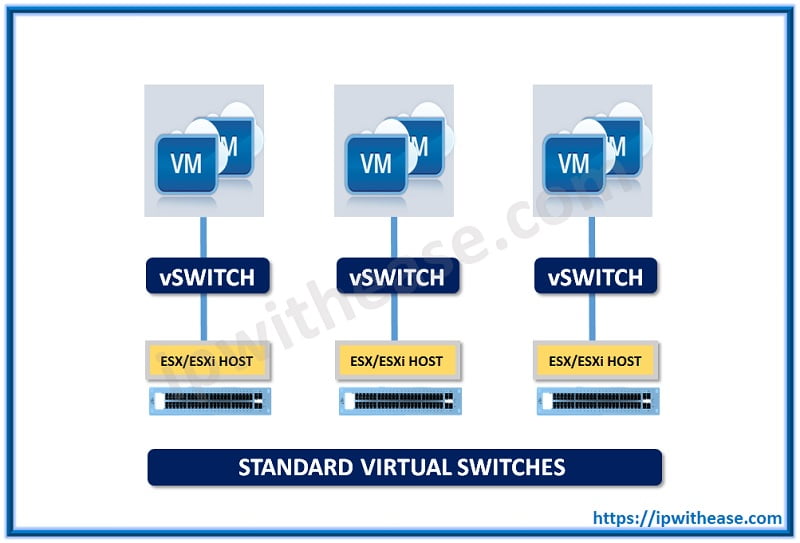
vSwitch is the other term by which the standard switches are sometimes referred. In VMware Distributed Switch vs Standard Switch when the installation of ESXi takes place, the Standard Switch is made by default.
It forward frames to other ports of the switch while working at layer 2 on the basis of MAC address. The features that it supports include port channels and VLANs.
Connection of standard switches has to be done with the physical NICs ESXi host as uplinks so that communication could be established with the remaining network.
At the host level, their configuration takes place that reflects that standard switches should be managed and created on every ESXi host independently.
Network connectivity is offered by standard switches between:
- Different ESXi hosts’ virtual machines
- Virtual machines present in same ESXi host
- Physical and virtual machines on the network
- Access for VMkernel to networks for iSCSI, vMotion, fault tolerance logging or NFS
Ability is there in the standard switch to move traffic of layer 2 internally among the virtual machines. This means that direct communication is possible between two virtual machines that are on the same ESXi host and the same subnet.
There is no need for the traffic to leave ESXi host. Some of the latest features of networking are also supported by standard switches.
These include NIC teaming, shaping of outbound traffic, CDP support, different policies of security etc.
Following are the configurable items featured in both the forms of switches:
- Port groups: virtual ports groups having a similar configuration
- Uplinks: connections to the outside world from the virtual switch
Along with this, the following are supported by both types of switches:
- The shaping of outbound traffic
- Handling of layer 2 traffic
- NIC teaming
- 1 Q tagging
- VLAN segmentation
Important Factors of Standard Virtual Switch:
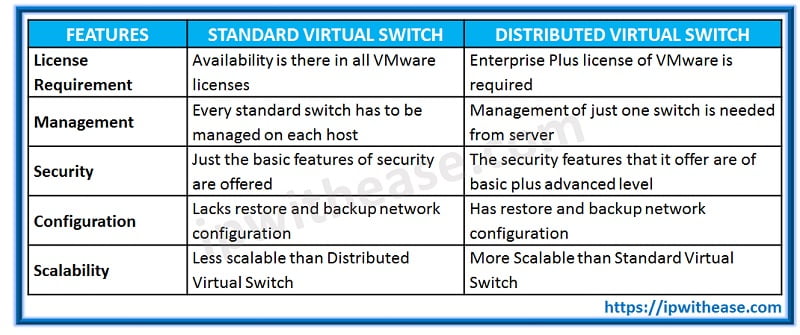
- There is one actual advantage of standard switch that there is no need pf licensing of enterprise plus for using it.
- Configuration sync is not there and therefore all groups of the port have to be created on every host exactly the same.
- When 10 virtual machines are required to be hosted on the same subnet and working of standard switches will be fine.
- For deploying the switches, scripts should be used and they should also be kept in sync so that the manual errors could be avoided.
- vMotions should always be attempted among all hosts prior to any change to ensure the fact that nothing is broken.
- The networking design should not be made complex.
Important Factors of Distributed Virtual Switch:
The distributed virtual switch is deployed to every ESXi host and configured by vCenter. Some other features include:
- Private VLANs: switches are required in this feature supporting PVLAN so that VLANs could be created among vLANs
- Teaming that is load based: the highest level of load balancing
- Port block of VM network
- Network vMotion: Because traffic stats of vCenter owns the dVS and information can travel among hosts with the movement of the virtual machine. This is not the case with standard switch since with vMotion, the information present on it is lost.
- LLDP: it enables port discovery from virtual to physical
- Netflow: netflow traffic could be outputted by dVS
- Port mirroring: configuration of ports could be done to mirror for purposes of security and diagnostic
Vmware Distributed Switch vs Standard Switch:
The following table explains the standard switch vs distributed switch difference & comparison –
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj