Large enterprises have multiple site offices spanning geographical locations and are connected via MPLS service providers. As a standard practice, all the location office connect via BGP using the same AS Number assigned to a customer (Site-A and Site-B).
As a standard behaviour of BGP remote site (using same AS Number) prefix received by another site of the same customer will drop the route since it sees its own AS Number in the received packet.
Related – BGP AS Override Explanation
Below is a sample scenario to illustrate BGP default behaviour on receiving route having its own AS number in its AS Path.
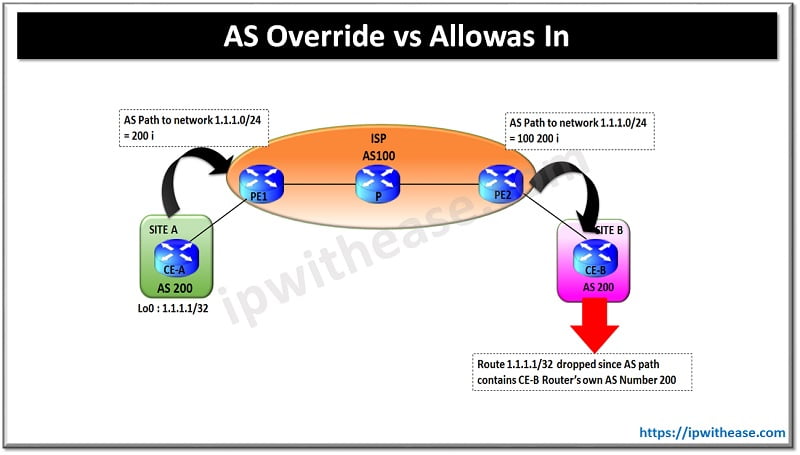
As shown above, Router “CE-A” at site A advertises network 1.1.1.1/32. The service provider receives the route having AS path as “200 I”. Now “PE2” Router advertised the same route towards Site-B Router “CE-B”.
However, on receiving the BGP route, it verifies the AS path attribute and finds its own AS Number of “200”. As a standard behaviour of BGP, Router CE-B drops the route.
The methodology to circumvent or mitigate default behaviour of BGP is to use the BGP features of “AS-Override” or else “Allowas-in”.
While former is used by PE to modify the AS Number in AS Path so that prefix is not dropped, the latter is implemented in CE device to introduce an exception in BGP AS path loop prevention mechanism.
Let’s further discuss on how “AS-Override” and “Allowas-in” differ from each other.
One significant difference is that “As Override” needs to be provisioned at the Service provider end while “Allowas-in” will be configured at the CE device at the customer site.
If the customer requires to keep minimal configuration at CE side and let the provider perform the BGP routing control, the best approach will be to use “As-Override“.
Related- BGP Allowas in
Allowas-in vs AS-Override
Below table enumerates the comparison between “As-Override” and “Allowas-in” –
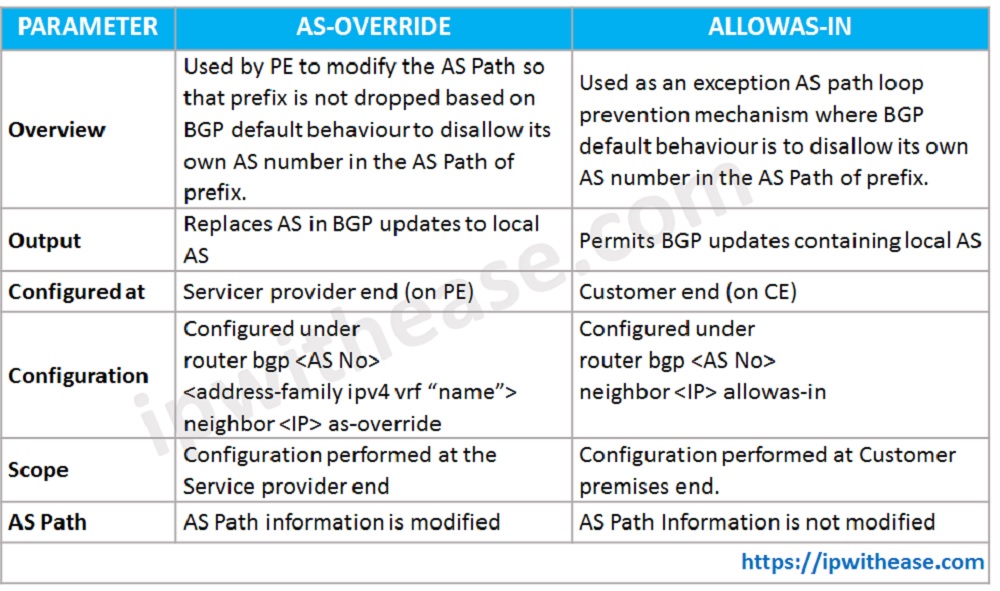
| PARAMETER | AS OVERRIDE | ALLOWAS-IN |
|---|---|---|
| Overview | Used by PE to modify the AS Path so that prefix is not dropped based on BGP default behaviour to disallow its own AS number in the AS Path of prefix. | Used as an exception AS path loop prevention mechanism where BGP default behaviour is to disallow its own AS number in the AS Path of prefix. |
| Output | Replaces AS in BGP updates to local AS | Permits BGP updates containing local AS |
| Configured at | Servicer provider end (on PE) | Customer end (on CE) |
| Configuration | Configured under router bgp neighbor | Configured under router bgp neighbor |
| Scope | Configuration performed at the Service provider end | Configuration performed at Customer premises end. |
| AS Path | AS Path information is modified | AS Path Information is not modified |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
Related – BGP Confederation
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj