Table of Contents
Introduction to Cisco SD-WAN
SD-WAN (Software Defined WAN) is a term that nowadays every Network Engineer working on enterprise networks or on Service Provider domain must have heard.
There are various vendors in the market available today offering the SD-WAN solutions and supporting hardware products.
Few such companies are listed below:
- Nokia Nuage
- Riverbed Network
- Cisco Viptela
- Citrix NetScaler SDWAN
- Cisco Meraki SDWAN
- Juniper Contrail
Benefits of Cisco Viptela SD-WAN over the traditional network:
- Reduced Opex and reduced Capex.
- Increases application performance with the help of application-aware routing.
- Automated provisioning
- Better security
In this particular post, we will focus on the Cisco Viptela SD-WAN solution and list the various steps involved in the Fabric bring-up process.
Cisco SD-WAN Fabric
Viptela solution isn’t dependent on the transport medium and hence can work with MPLS, Internet, LTE or any other transport medium as long as all the devices are connected together.
Cisco’s Viptela solution involves 4 basic components that form the complete SD-WAN fabric and these are listed below:
1. vManage: It is the centralized network management system that offers the GUI for the provisioning of the SDWAN network. It isn’t physical hardware and runs as a VM on an ESXi or hypervisor on a server.
2. vSmart: It is the brain of the Viptela solution controlling the flow of data through the overlay network. vSmart controller works with vBond orchestrator to authenticate the vEdge routers as well as they join the network. isn’t physical hardware and runs as a VM on ESXi or hypervisor on a server.
3. vBond: It is the orchestrator in the Viptela solution which authenticates every device on the Viptela network. Initiates the bring-up process of every vEdge device, at the first step, it creates a secure tunnel with vEdge and informs vSmart and vManage about its parameters like for instance IP address.It has to be fully connected with every device. vBond needs to have the public IP address so it can be reached over the internet. It also runs as a VM on ESXi or hypervisor on a server.
4. vEdge: vEdge routers are placed at the customer sites or at the data centre sites at the edge of the network. They can either be hardware devices placed in the premises or software vEdges also called a vEdge cloud. vEdge router receive complete control and data policies from the vSmart, it is able to run routing protocol like OSPF, BGP to create connectivity on LAN side but also with MPLS provider if necessary.It establishes secure IPSec tunnels with others vEdges depending on selected topology.
Related – Overlay Management Protocol in Viptela
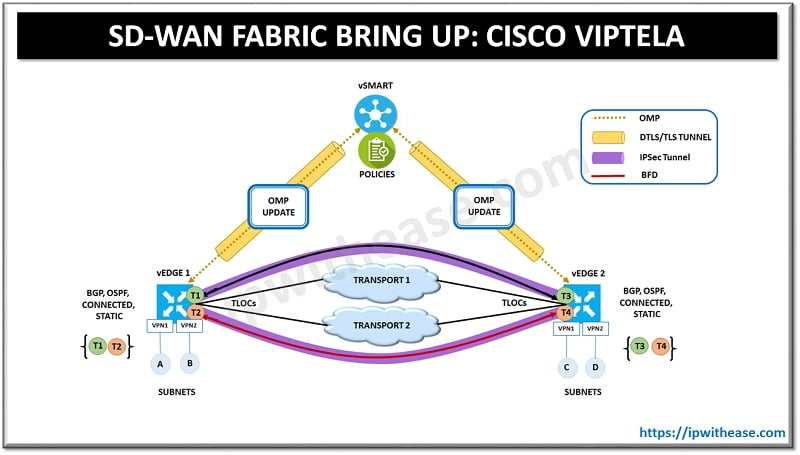
Cisco Viptela SD-WAN Fabric bring up Steps
- Spin up the vManage VM on a server in the data centre with its minimal configuration (System IP, vBond IP, Organization name etc).
- Spin up the vSmart VM on a server in the data centre with its minimal configuration (System IP, vBond IP, Organization name etc).
- Spin up the vBond VM on a server in data center with its minimal configuration (System IP, vBond local command, Organization name etc).
- Once all the devices are spun up they authenticate and validate each other with the help of the certificate exchange and form the permanent secure DTLS connection among themselves. (vBond to vSmart, vSmart to vMange, vBond to vManage).
- Once authenticated the vManage NMS sends the configuration to vSmart and vBond devices.
- Next, we spin up the vEdge routers in our network.
- vEdge router has the vBond IP address as the part of the initial base configuration and hence connect to the vBond and authenticate themselves with vBond over DTLS connection.
- Once authenticated the vBond shares the IP address & a serial number of the vSmarts to vEdge and also the IP address of vManage.
- vEdge then authenticates itself with the vManage and receives it full configuration from the vManage over a permanent DTLS connection formed between them.
- vEdge also authenticates with the vSmart controllers in the network over a secure DTLS connection.
- Once authentication is successful a permanent DTLS connection is formed between them and OMP peering is established between both the devices.
- Over this OMP peering session vEdge router relays the control plane information to the vSmart so that vSmart can learn the network topology.
- Control plane information includes the LAN side prefixes learnt on the vEdge via static or dynamic routing. These are advertised to the vSmart and also the TLOC (transport location) are advertised which is the address of the interface that connects to the WAN transport network.
- vSmart controllers install the OMP updates in routing database and advertise these to other vEdge routers in the overlay network.
Related – OMP Path Selection Checklist in Viptela
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj