Table of Contents
There are many routing protocols available in the OSI 7-layer model. The most popular routing protocols use a mathematical algorithm to calculate the most efficient and shortest routing path to direct IP traffic on networks. OSPF is one such protocol which is designed by IEEE and a link state routing protocol which distributes routing information in a single autonomous system (AS).
In today’s topic we will learn about configuring the OSPF not-so-stubby area (NSSA).
What is OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA)
The OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) is mentioned in RFC 1587 and was first introduced in Cisco Software 11.2 release. It is a non-proprietary extension for current stub area feature which allows the injection of external routes into stub area in limited manner. NSSA area redistribution creates a special type of Link-State Advertisement (LSA) which is known as type 7 and can only exist in the NSSA area. An NSSA autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) generates the LSA and NSSA area border router (ABR) translates this LSA into type 5 which gets propagated into the OSPF domain.
NSSA is used to allow OSPF stub areas to carry external routes (routers learned using other protocols such as RIP, EIGRP, BGP and so on) stub areas are defined as areas which are not capable of importing routes which are not internal to OSPF.
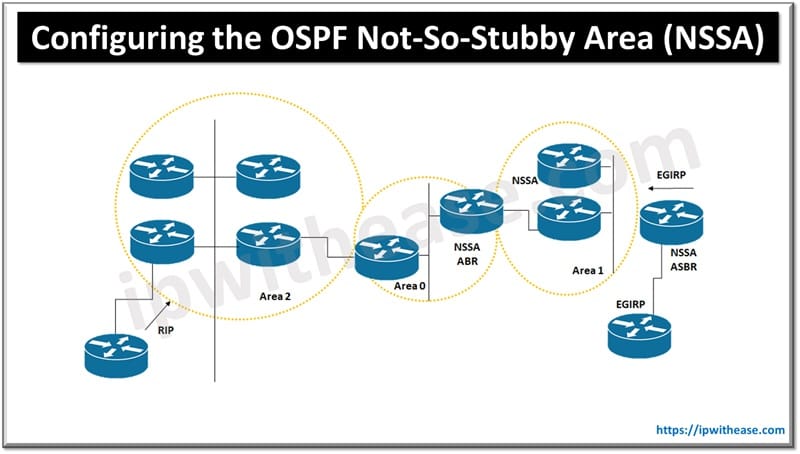
In the above diagram an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) stub network is configured to include OSPF.
Area 0 and area 1 using five devices. Device 3 is configured as NSSA Autonomous System Border
Router (ASBR). Device 2 is configured as an NSSA Area border router (ABR). OSPF area 1 is defined as Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA)
Configure OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA)
Enable privilege access mode
Device1>enable Enter global configuration mode
Device1#configure terminal Enable OSPF routing and enter router configuration mode
Device1(config)#router ospf 1Redistribute route from one routing domain to another domain
Device1(config-router) #redistribute rip subnetsDefine interface on which OSPF will run and area ID for those interfaces
Device1(config-router) #network 192.168.120.10 0.0.0.255 area 1Configure not-so-stubby area (NSSA)
Device1(config-router) #area 1 nssaLimit summary of NSSA during route summarization and filtering during translation
Device1(config-router) #summary-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 not-advertiseExit router configuration mode and return to privilege EXEC mode
Device1(config-router) #end Related FAQs
What is an NSSA in OSPF?
NSSA stands for Not-So-Stubby Area, a type of OSPF area that combines features of stub and non-stub areas. It allows external routes to enter the area but limits their propagation to reduce routing information overhead.
Why would you use an NSSA in OSPF?
NSSAs are used in networks that need to connect to external (non-OSPF) networks while minimizing the amount of routing information shared throughout the OSPF domain.
How does an NSSA differ from a Stub Area?
Unlike stub areas, which block external routes (Type 5 LSAs), NSSAs allow external routes to enter the area by translating them into Type 7 LSAs, which are later converted to Type 5 LSAs by the Area Border Router (ABR).
What are Type 7 LSAs in NSSA?
Type 7 LSAs are used in NSSAs to carry external routing information within the area. These LSAs are translated into Type 5 LSAs at the ABR before being distributed to the rest of the OSPF domain.
Can NSSA areas use a default route?
Yes, NSSA areas can use a default route, either automatically injected by an ABR or manually configured, to simplify routing toward external networks.
What is the role of an ABR in an NSSA?
In an NSSA, the ABR translates Type 7 LSAs into Type 5 LSAs and propagates them into other OSPF areas, allowing external routes to be accessible throughout the OSPF domain.
What is the significance of the “no-summary” keyword in NSSA?
The “no-summary” keyword is used on the ABR to suppress inter-area routes within the NSSA, making it an NSSA totally stubby area (NSSA-TSA). This further reduces the routing table size within the NSSA.
Can NSSA areas be a part of a backbone area (Area 0)?
No, NSSA areas cannot be designated as the OSPF backbone (Area 0). They must be configured as non-backbone areas and connected to the backbone through an ABR.
How are default routes configured in NSSAs?
Default routes in NSSAs can be automatically advertised by the ABR or manually configured by setting the ABR as an NSSA default information originator.
What is an example use case for NSSA?
NSSAs are useful in networks where an OSPF area connects to an external network, like the internet, but where you want to avoid flooding external route information into the entire OSPF domain, keeping routing tables smaller and more manageable.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj