While configuring switching environments, network engineers and Cisco Switching students tend to get tangled with the significance of Default VLAN and Native VLAN while using Dot1Q encapsulation over trunk links. Such challenges are bound to be faced and its equally essential that clarification between both VLAN types is clearly understood.
Though widely used terms, still both Default VLAN and Native VLAN are terms which tend to create doubt.
Related – What is VLAN?
A quick run-through Default VLAN and Native VLAN –
Both terms are related to 802.1q. The 802.1q standard defines a method of tagging traffic between switches to distinguish which traffic belongs to which VLANs.
What is Default VLAN?
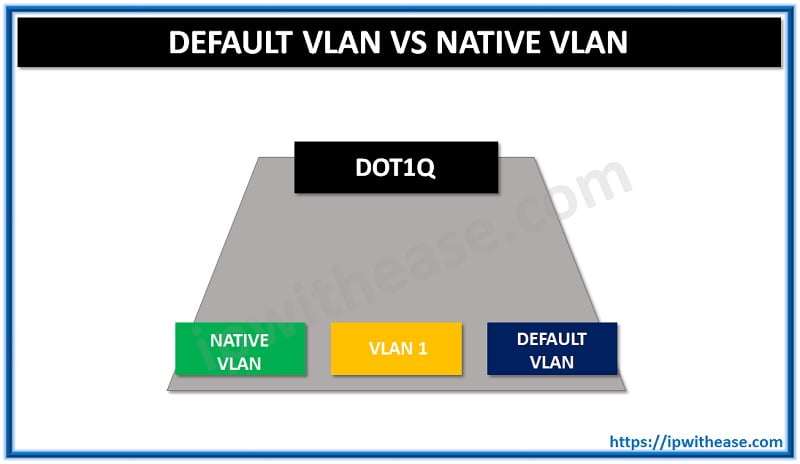
Default VLAN is VLAN 1 which cannot be shut down in any case and also it carries controlling traffic. In the case of Cisco (and most vendors), the Default Native VLAN is VLAN 1.Infact in a new switch.
DEFAULT VLAN = NATIVE VLAN = VLAN 1
What is Native VLAN?
Native VLAN concept exists in case of encapsulation type 802.1Q (802.1Q supports untagged traffic while ISL does not support untagged traffic). We configure trunk port with a Native VLAN, and whatever traffic arrives on that port without an existing VLAN tag, gets associated with your Native VLAN.
There are some more contrasting facts between Default and Native VLAN like Control traffic for CDP, PAGP, and VTP is sent over Default VLAN, whereas DTP Traffic is sent over Native VLAN. Lastly, the Default VLAN can only be one per switch, and divergent to it, the number of Native VLANs can be higher than one since it is equivalent to the number of Dot1q trunks on Switch.
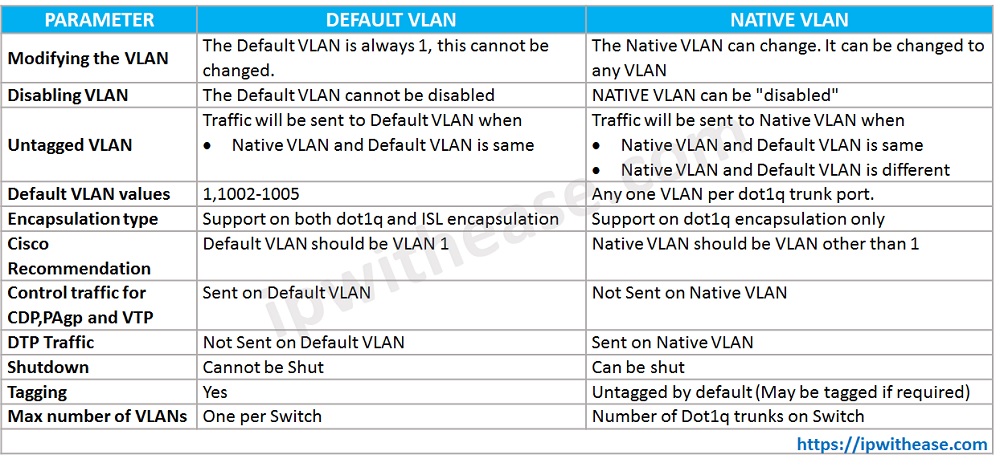
Native VLAN vs Default VLAN Comparison Table-
| PARAMETER | DEFAULT VLAN | NATIVE VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Modifying the VLAN | The Default VLAN is always 1, this cannot be changed. | The Native VLAN can change. It can be changed to any VLAN |
| Disabling VLAN | The Default VLAN cannot be disabled | NATIVE VLAN can be "disabled" |
| Untagged VLAN | Traffic will be sent to Default VLAN when: Native VLAN and Default VLAN is same | Traffic will be sent to Native VLAN when: Native VLAN and Default VLAN is same Native VLAN and Default VLAN is different |
| Default VLAN values | 1,1002-1005 | Any one VLAN per dot1q trunk port. |
| Encapsulation type | Support on both dot1q and ISL encapsulation | Support on dot1q encapsulation only |
| Cisco Recommendation | Default VLAN should be VLAN 1 | Native VLAN should be VLAN other than 1 |
| Control traffic for CDP,PAgp and VTP | Sent on Default VLAN | Not Sent on Native VLAN |
| DTP Traffic | Not Sent on Default VLAN | Sent on Native VLAN |
| Shutdown | Cannot be Shut | Can be Shut |
| Tagging | Yes | Untagged by default (May be tagged if required) |
| Max number of VLANs | One per Switch | Number of Dot1q trunks on Switch |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
I hope you would have got a good understanding of the comparison of Default VLAN and Native VLAN. For other information read our other related content.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj