For enthusiasts new to IP Networking terminology, VLAN and IP Subnet terms may look confusing. Many times in technical discussions things like Inter VLAN communication, interchangeably using terms like VLAN A / VLAN B or Subnet A/Subnet B are used. This further adds salt to the wound.
So, let’s have brief on terminologies of VLAN and IP Subnet and before discussing the difference (vlan vs subnet) from each other.
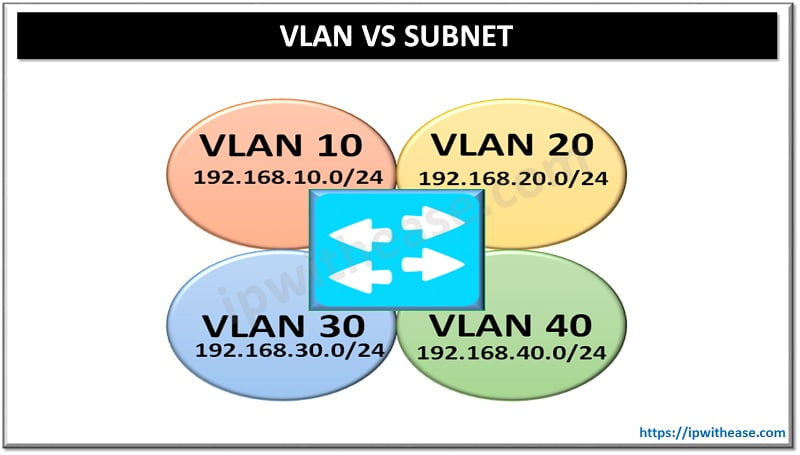
Introduction to VLAN & Subnet
A VLAN is a layer 2 term, usually referring to a broadcast domain. Layer 2 is where MAC addresses are used. A subnet is a layer 3 term.
Layer 3 is the IP layer where IP addresses as used. Although one can have more than one subnet or address range per VLAN, it is recommended that VLANs and Subnets are 1 to 1. In general, we will have a 1:1 mapping of subnets and VLANs i.e. One subnet per VLAN.
Comparison Table: VLAN vs SUBNET
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
| PARAMETER | VLAN | SUBNET |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | VLAN is a logical local area network that contains broadcasts within itself and only hosts that belong to that VLAN will see those broadcasts. | Subnet is an IP address range of IP addresses that help hosts communicate over layer 3. |
| Logical and Physical Networks | VLANs allow us to create different logical and physical networks | IP subnetting allows us to create logical networks through the same physical network. |
| Network Member control | In VLANs, the network to which a host belongs to is decided by the interface to which it is connected (layer 2) i.e. port of Switch to which host is connected. | In subnets, the network to which host belongs is decided by the ip address assigned to the host (layer 3). |
| OSI Layer | VLAN is a Layer 2 term where MAC addresses work | Subnet is a layer 3 term where IP Layer works |
| Hardware /Software based | More of Software based terminology | More of Hardware based terminology |
| Security & Control | VLANs provide more robust Control for the network | Subnetting has limited level of control in comparison to VLAN |
| Major benefit | The primary advantage of VLANs is that they break up the broadcast domain | The primary advantage of IP Subnetting is for communication across hosts in same IP subnet and same VLAN |
| Related terms | MAC Address, dot1q tag, Layer 2, Broadcast domain. | IPv4/Ipv6 address, Layer 3, InterVlan Routing |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
Continue Reading:
How to configure VLAN trunk between HP and CISCO switch?
To know more about VLAN Concepts –
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj