Table of Contents
A VLAN segments a network into isolated broadcast domains at Layer 2. SVI or Switched Virtual Interface, on the other hand, is a Layer 3 interface that provides IP routing capabilities for a VLAN. This document discusses the the two technologies in details, outlining their benefits and differences.
What is VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
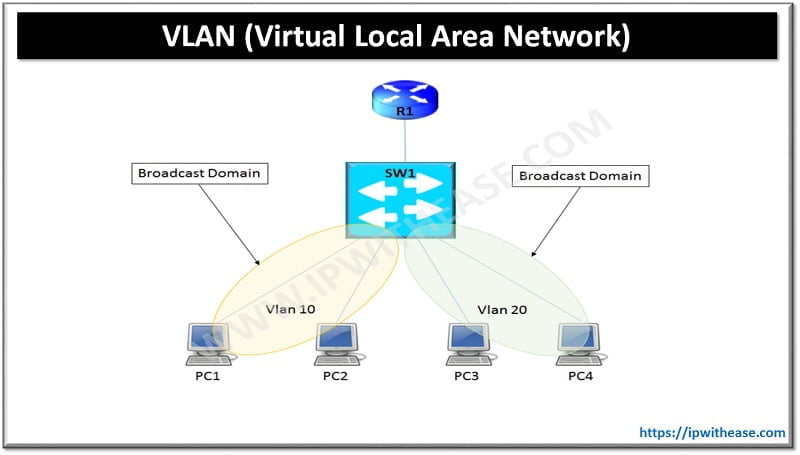
A virtual LAN or VLAN is any broadcast domain that is segregated and isolated at the data link layer OSI layer 2. VLANs reduce the load on a network by keeping local traffic within a VLAN. However, because each type VLAN its own domain, a mechanism is needed for VLANS to pass data to other VLANS without passing the data through a router.
The solution is SVI networking i.e. switched virtual interface.
Related – VLAN vs Subnet
Benefits of Using VLAN
- Improved Security – Isolates sensitive data by separating traffic between groups.
- Better Performance – Reduces broadcast traffic by segmenting networks.
- Simplified Management – Easier to manage and configure groups of devices.
- Flexibility – Devices can be grouped logically, not physically.
- Efficient Use of Resources – Minimizes unnecessary traffic and optimizes bandwidth.
What is SVI (Switched Virtual Interface)
An SVI interface is usually found on Layer 3 switches. With SVIs the switch recognizes the packet destinations that are local to the sending VLAN and then routes packets destined for different VLANs.
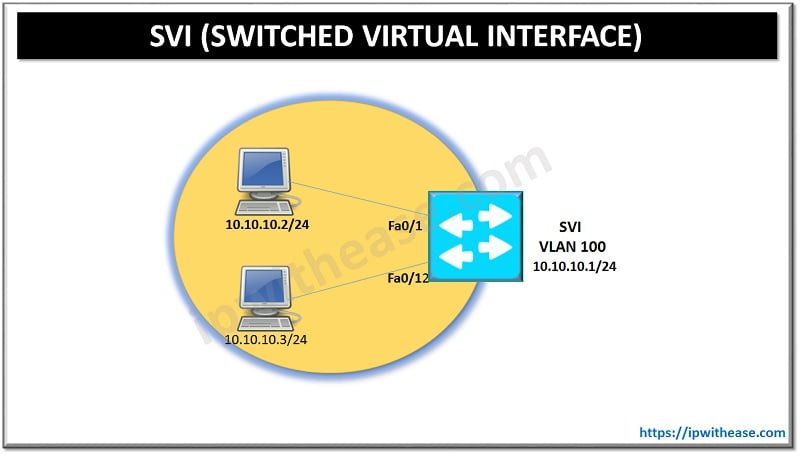
An SVI interface can be created for each VLAN that exists but only one SVI can be mapped to each VLAN. An SVI is virtual and has no physical port defined and performs the same functions for the VLAN as a router interface. SVI is also called Interface VLAN.
Benefits of Using SVI
- Enables Inter-VLAN Routing – Allows communication between VLANs at Layer 3.
- Simplifies Configuration – Easier to manage compared to physical interfaces for each VLAN.
- Supports Layer 3 Features – Enables IP addressing, routing, ACLs, and QoS on VLANs.
- Improved Network Performance – Reduces the need for external routers in switched networks.
Comparison Table: VLAN vs SVI
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
| PARAMETER | SVI | VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation for | Switched Virtual Interface | Virtual Local Area Network |
| Platform support | Only configurable on Layer 3 devices. | Can be configured on Layer 3 and Layer 2 devices |
| Routing across IP subnets | SVI can perform routing across IP subnets | Cannot perform Routing between VLANs |
| Configuration | Interface VLAN (VLAN ID) | Can be enabled via following command: VLAN (VLAN ID) |
| OSI Layer | Works on Layer 3 of OSI Model | Works on Layer 2 of OSI Model |
Download the difference table: VLAN vs SVI
Continue Reading
VLAN vs Subnet: Understand the difference
Are you preparing for your next interview?
If you want to learn more about VLAN, then check our e-book on VLAN System Interview Questions and Answers in easy to understand PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
Watch Related Video
(For Better Understanding)
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj