Table of Contents
Underlay Network is the physical infrastructure (like routers, switches, and links) that provides the foundational connectivity. Overlay Network is a virtual network built on top of the underlay, enabling abstracted or logical communication paths (e.g., VPNs, SD-WAN). This blog discusses the differences between the 2 types network overlay technologies in detail.
Introduction to Underlay Network and Overlay Network
IT industry is making great strides towards efficiency and scalability to meet the virtualization demand. The key ask is for the demand of multitenancy and virtualization features like VM mobility as turnkey projects.
Related – HLD and LLD
Network Overlays
Network overlays is the latest solution to meet these demands, in fact, this technology can speed configuration of new or existing services. Overlays solve several problems in modern networking like:
- Scalability: Easily create and tear down networks without touching the hardware.
- Multi-tenancy: Isolate networks for different users or applications.
- Mobility: Move workloads without reconfiguring physical networks.
- Security: Control traffic flow with segmentation and encryption.
Underlay Network
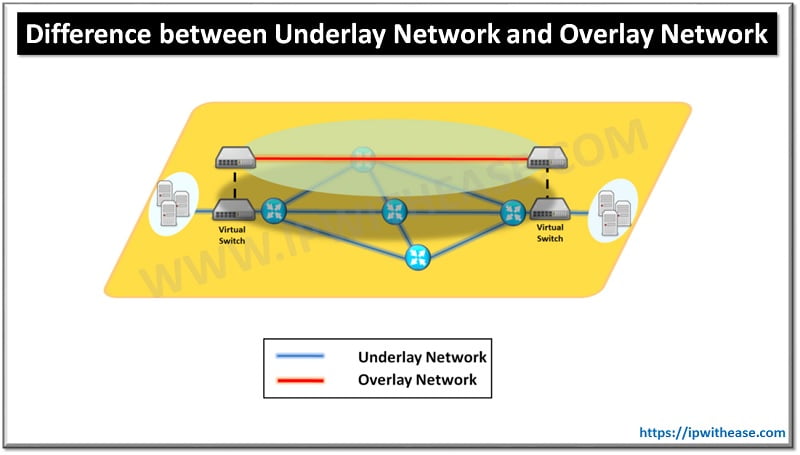
Underlay Network is different from Underlay Network which IT industry has known for years. Underlay Network is physical infrastructure above which overlay network is built. It is the underlying network responsible for delivery of packets across networks. Depicted in blue color in the diagram.
Components
- Physical routers and switches
- Cables and wireless links
- Routing protocols (e.g., OSPF, BGP)
- IP addresses and subnets
Overlay Network
An Overlay Network is a virtual network that is built on top of underlying network infrastructure (Underlay Network). Actually, “Underlay” provides a “service” to the overlay. Overlay networks are used to provide segmentation, isolation, or abstraction, in complex environments like data centers or multi-tenant clouds. Depicted in red color in the diagram.
Components
- Virtual routers and switches
- Tunneling protocols (e.g., VXLAN, GRE)
- Encapsulation mechanisms
- SDN controllers (for management)
Related- Networking Scenario Based Interview Questions
Comparison Table: Underlay Network vs Overlay Network
Below table enumerates the difference between Underlay Network and Overlay Network:
| PARAMETER | UNDERLAY NETWORK | OVERLAY NETWORK |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Underlay Network is physical infrastructure above which overlay network is built. | An Overlay network is a virtual network that is built on top of an underlying Network infrastructure/Network layer (the underlay). |
| Related protocols | Ethernet Switching, VLAN , Routing etc. | VXLAN , OTV , VPLS |
| Scalability | Less Scalable due to technology limitation | Designed to provide more scalability than underlay network. For e.g. – VXLAN (underlay Network) provides 4096 VLAN support while VXLAN (Overlay Network) provides upto 16 million identifiers. |
| Packet control | Hardware orchestrated | Software orchestrated |
| Packet delivery | Responsible for delivery of packets | Offloaded from delivery of packets |
| Packet encapsulation and overhead | Packet delivery and reliability occurs at layer 3 and Layer 4 | Needs to encapsulate packets across source and destination, hence incurs additional overhead. |
| Managing multitenancy | NAT or VRF based segregation required which may face challenge in big environments | Ability to manage overlapping IP addresses between multiple tenants. |
| Multipath forwarding | Less scalable options of multipath forwarding. Infact using multiple paths can have associated overhead and complexity. | Support for multi-path forwarding within virtual networks. |
| Deployment time | Less scalable and time consuming activity to setup new services and functions | Ability to rapidly and incrementally deploy new functions through edge-centric innovations |
| Traffic flow | Transmits packets which traverse over network devices like Switches and Routers. | Transmits packets only along the virtual links between the overlay nodes. |
Download the comparison table underlay vs overlay network
Final Words
The underlay network is the physical infrastructure or say backbone, and the overlay is the smart layer that helps us use that backbone more effectively. Both are essential, but they serve different roles. As networks continue to evolve, especially with cloud and SDN adoption, understanding this distinction becomes even more critical.
Continue Reading
Difference between VxLAN and OTV
Watch Related Video
Know more about Cloud Overlay network in this video: