Table of Contents
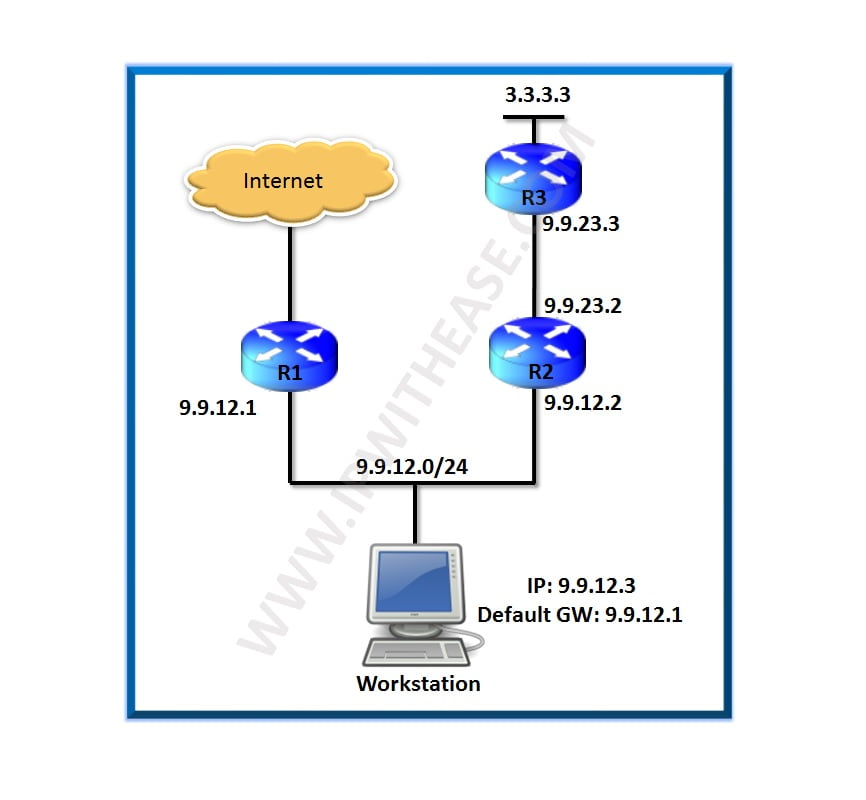
Juniper Virtual Router and VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) both provide routing table isolation, but they serve different purposes and are used in different networking contexts. Let’s understand more clearly the difference between Juniper Virtual Router (VR) and VRF.
Introduction
Juniper Virtual Router and VRF are two terms interchangeably used in JUNOS platforms where multi-tenancy and logical segregation of segments via layer 3 instances is required. While both VRF and VR are responsible for allowing multiple instances of the routing table to exist on the same Router, both have some observable differences.
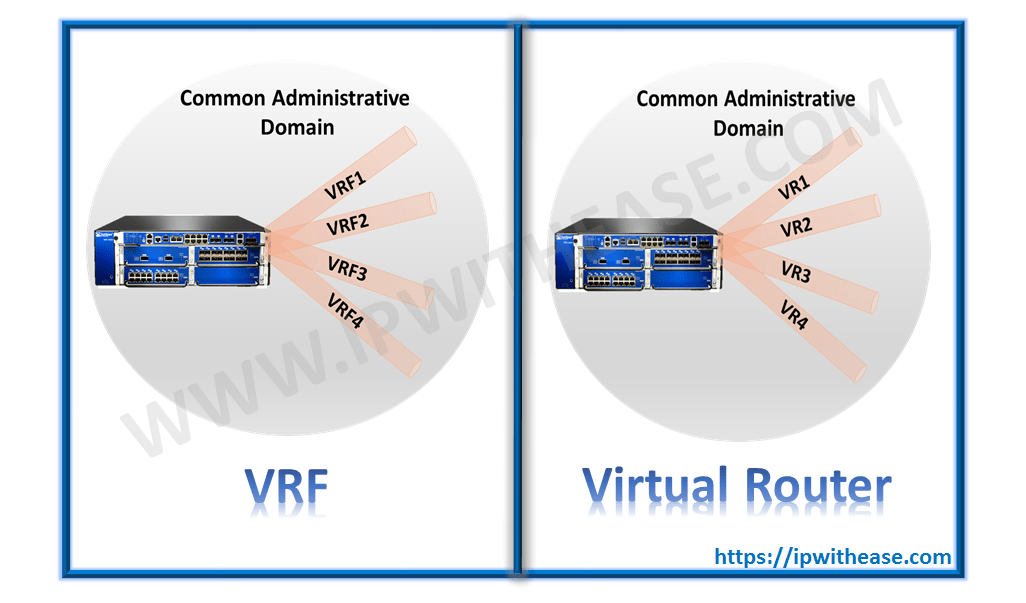
Difference between Juniper Virtual Router and VRF
Purpose
The purpose of VR is logical separation of routing tables. While, the purpose of VRF is VPN services and customer isolation in MPLS networks.
Usage
In terms of usage VR is used in non MPLS/VPN environments, whereas VRF is used in MPLS/VPN environment.
Route Distinguisher/Route Target
Route Distinguisher and Route Target are not required for Juniper VR configuration. But VRF requires RD and RT while configuring in MP-BGP environment.
Complexity
Virtual router or VR is simple. On the other hand, VRF is complex as it often includes RD, RT, etc.
Use Cases
VR is used in Labs, service separation, multi-tenant L3. And VRF is useful in Carrier networks, MPLS VPNs for customers.
Comparison Table: VR vs VRF
Below table summarizes the technical differential points of both along with a configurational example:
| PARAMETER | VRF | VIRTUAL ROUTER |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Preference to be used in MPLS/VPN environment | Preference to be used in non MPLS/VPN environment. |
| Route Distinguisher & Route Target in Configuration | RD and RT are required while configuring VRF in MP-BGP environment. | RD and RT are not required to be configured in VR instance |
| DN-BIT and Route TAG | OSPF inside VRF automatically sets DN-bit and route-tag | OSPF inside Virtual Router does not automatically sets DN-bit and route-tag |
| MP-BGP Route Import | VRF automatically imports MP-BGP routes with matching route-target | Does not automatically imports MP-BGP routes with matching route-target |
| Licensing | Supported in base license | Requires EFL (Enhanced Feature License) in EX Series platform |
| Configuration Example | [edit routing-instances] user@switch# set routing-instance-name instance-type vrf user@switch# set routing-instance-name interface device-name:type-fpc/pic/port.logical-unit-number user@switch# set routing-instance-name route-distinguisher RD-number set device-name:type-fpc/pic/port unit logical-unit-number family inet address ip-address | [edit routing-instances] user@switch# set routing-instance-name instance-type virtual-router user@switch# set routing-instance-name interface device-name:type-fpc/pic/port.logical-unit-number set device-name:type-fpc/pic/port unit logical-unit-number family inet address ip-address |
Download the comparison table: virtual router vs vrf
Continue Reading
Juniper Virtual Router vs Logical System
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj