Table of Contents
MPLS can quickly transfer data from one node to another using short path labels instead of larger network addresses. This makes traffic flow faster and more efficient. In this post, we will explain what MPLS is, the types of network architectures it allows organizations to create, and real-world applications that use it. This will show why this older networking solution is still important in today’s modern networks.
Understanding MPLS Architecture
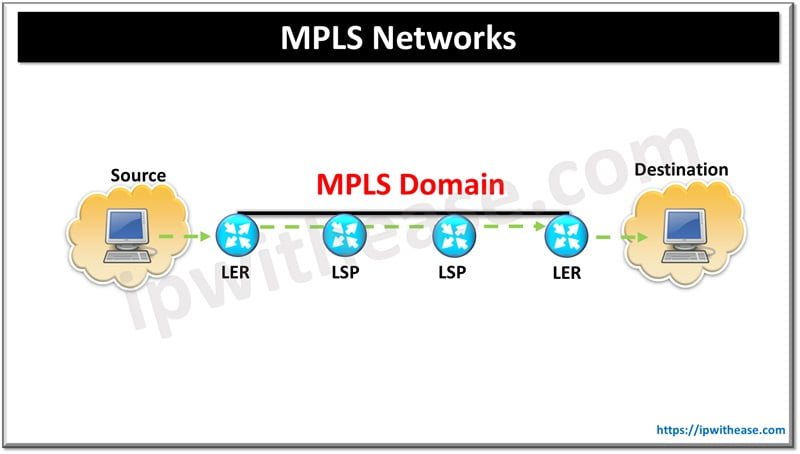
The method behind how MPLS operates involves tagging data packets with a label that designates the pathway for each packet to take. Labels are used so that the decision to forward a packet is made by looking at these, rather than having some complex organization of routing tables. The process involves:
- Label Edge Routers (LERs) – These are the points where an MPLS network begins or ends, they may know about their topological neighbors but do not participate in routing with them. An MPLS label is pushed by the LER when a packet enters this network.
- Label Switch Routers (LSRs) – LSRs are the cloud or core components that forward packets using labels to make it more fast and efficient compared with traditional IP routing.
- Label Distribution Protocol (LDP): LDP is to build label-switched paths (LSPs) across the network. It makes sure labels are being distributed and kept up to date on the network devices.
Related: Difference between MPLS & VPLS
Components of MPLS Networks
- Forwarding Equivalence Class (FEC): A set of packets that are forwarded over the same path and by performing similar operations on them.
- Label Stack: A list of labels that can be pushed onto a packet. The stack will help you to reach various layers of network paths and hierarchies.
- Control Plane and Data Planes, the control plane is responsible for creating routing information on a network; whereas in data planes packets with specific labels are forwarded.
Benefits of MPLS Networks
Enhanced Performance
A technology like MPLS through traffic engineering with QoS allows for the prioritization of traffic in the MPLS cloud. Critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth to prevent delays that could affect other users of the connection. This is particularly advantageous for those working at high speeds, such as with fibre internet. It not only improves connection speeds but also transmits data faster and reduces latency.
Improved Security
Although MPLS is not a security protocol, it does allow packets of different network layers to segregate traffic flows through label-switched paths that can traverse several nodes inside an autonomous system. This can protect data from unauthorized access and ensure compliance with various regulations.
Cost Efficiency
It can also save money due to the re-usage of network resources and avoid expenses for new costly hardware upgrades as MPLS is known by optimizing resource allocation. Prioritizing traffic, in turn, allows the redeployment of bandwidth for better cost efficiency.
Related: MPLS Cheatsheet
Use Cases of MPLS Networks
Enterprise Connectivity
MPLS VPN is extensively used in enterprise environments where the number of branch offices and data centers required to establish a network is large. It is also suitable for businesses that need their data exchange and collaboration to be continuous because it can efficiently manage traffic and provide consistent performance.
Service Provider Networks
MPLS is frequently signed by telecommunications companies to control their large-scale networks. This enables service providers to deliver premium services, such as VPNs and dedicated internet access (DIA), to their customers while ensuring high performance and resiliency.
Data Center Interconnects
Data centers are connected via MPLS, with options for redundant links ensuring application performance redundancy. This makes it suitable for data center environments, where a huge number of high-speed parallel writes take place.
Cloud Integration
As more businesses migrate to cloud-based services, MPLS serves as a reliable and efficient conduit bridging on-premises networks with those in the cloud. It offers the required bandwidth and reduces latency connections needed for good cloud computing.
Disaster Recovery
In the case of a disaster recovery situation, MPLS is essential as it allows fast and redundant data replication between primary and secondary sites. It manages traffic well and ensures backups behave in as predictable a fashion as possible.
Summary
While other solutions are taking market share from MPLS in some areas, it is still a critical part of the WAN toolkit and will be for the foreseeable future due to its ongoing network performance enhancements, efficient traffic control capability, and wide applicability. With its architecture, it helps in achieving data forwarding successfully along with advanced QoS features, which unquestionably attract enterprise and service provider users as well. While MPLS presents several challenges and is likely to be replaced by more modern alternatives in the coming years, it still has an important place as one of several foundational technologies that should be fully understood by networking practitioners.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.