Table of Contents
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are vital components of modern cybersecurity strategies. However, these systems are not without their challenges, particularly when it comes to the accuracy of threat detection. False positives and false negatives are two common issues that can reduce the effectiveness of IDS/IPS, leading to unnecessary alerts or missed attacks. This blog post will explore what false positives and false negatives in IDS/IPS are, why they happen, and most importantly, how to minimize them for a more efficient security infrastructure.
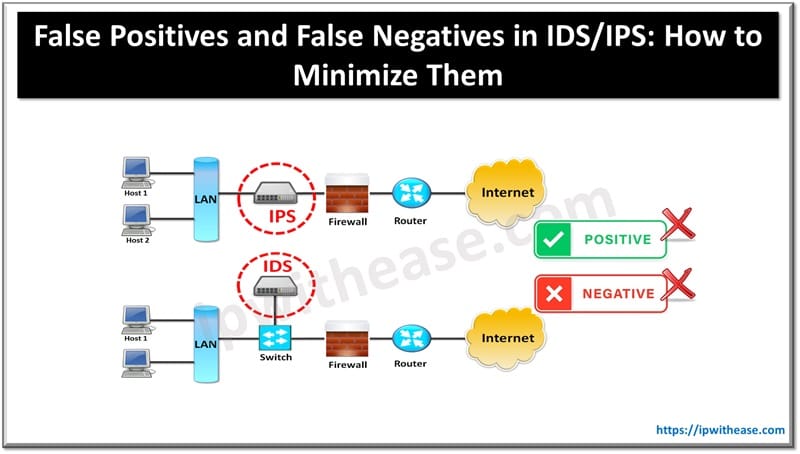
What Are False Positives and False Negatives in IDS/IPS?
- False Positive: When the IDS/IPS flags legitimate traffic as malicious. This results in unnecessary alerts, which can overwhelm security teams and lead to alert fatigue.
- False Negative: When malicious traffic goes undetected. This is the more dangerous of the two, as it leaves the system vulnerable to actual attacks.
Both scenarios can reduce the overall effectiveness of IDS/IPS, but they arise for different reasons. Understanding the causes is the first step to mitigating their impact.
Why False Positives and False Negatives Occur?
- Signature-Based Detection Limitations – IDS/IPS often rely on signature-based detection to identify known threats. This approach is effective against well-known attacks but may lead to false positives when legitimate traffic exhibits patterns that match those of malicious activities.
- Anomaly-Based Detection Complexity – Anomaly-based IDS/IPS monitor baseline network behavior and flag anything that deviates from the norm. This can cause false positives in dynamic environments where legitimate changes occur, such as during software updates or system reconfigurations.
- Insufficient Tuning – Default configurations of IDS/IPS are often not tailored to specific environments. Without proper tuning, these systems may produce a flood of false positives or fail to detect tailored, sophisticated attacks.
- Encrypted Traffic – Modern IDS/IPS struggle with analyzing encrypted traffic. Attackers can exploit this blind spot, leading to false negatives where the system is unable to inspect encrypted malicious payloads.
How to Minimize False Positives and False Negatives
- Regularly Update Signatures and Rules – Ensure that the IDS/IPS has up-to-date threat signatures and rulesets. Regular updates reduce the likelihood of false negatives by enabling the system to recognize the latest known threats.
- Properly Tune IDS/IPS Configurations – Tuning is crucial for reducing false positives. Customizing detection rules, thresholds, and filters based on the specific network environment and normal traffic patterns can significantly improve accuracy. For instance, adjust the sensitivity of detection algorithms for critical assets to avoid flagging normal business operations.
- Utilize Machine Learning and Behavioral Analysis – Modern IDS/IPS solutions employ machine learning algorithms to better distinguish between normal and abnormal traffic patterns. This adaptive approach can help minimize both false positives and negatives by learning over time what constitutes legitimate traffic.
- Implement Network Segmentation – Segmenting the network can help isolate suspicious traffic and minimize false positives by reducing noise. By focusing on critical areas, the IDS/IPS can better monitor for genuine threats without being overwhelmed by benign traffic.
- Deploy SSL/TLS Inspection – While encrypted traffic poses a challenge, implementing SSL/TLS decryption solutions can help IDS/IPS inspect encrypted data for malicious content, thereby reducing false negatives.
- Use Multiple Detection Methods – A combination of signature-based, anomaly-based, and behavior-based detection mechanisms can provide a more comprehensive approach to threat detection, reducing the likelihood of both false positives and negatives.
- Whitelist Trusted Traffic – By whitelisting known, trusted sources of traffic, you can significantly reduce the number of false positives. However, whitelisting should be done with caution, as it can lead to security blind spots if misconfigured.
- Monitor and Analyze Alerts – Implement a robust alert management process. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools can help by correlating alerts and identifying patterns, reducing the manual effort needed to distinguish false positives from real threats.
- Test and Validate Regularly – Regularly test and validate IDS/IPS performance with penetration testing and red team exercises. This helps ensure that the system is effectively identifying real threats and not overwhelmed by false alerts.
- Collaboration with Threat Intelligence Feeds – Leveraging threat intelligence feeds can help enhance IDS/IPS performance by providing real-time data on emerging threats. This helps reduce false negatives by ensuring that the system is aware of new attack techniques.
Conclusion
Minimizing false positives and false negatives in IDS/IPS is a continuous process that requires constant monitoring, tuning, and adaptation. By combining advanced technologies like machine learning, updating signatures, and properly configuring rules, organizations can significantly reduce the noise of false positives while ensuring that legitimate threats are not missed.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj