Honeypot is a network attached system set up as a decoy to lure cyber attackers and detect, deflect and study hacking attempts to gain unauthorised access to Information System. In simple words you are using or making it very lucrative for the attacker to deflect their attention to their system which when they compromise doesn’t affect the actual network.
Sandbox is an environment isolated virtual machine in which potentially unsafe software code can execute without affecting Network resources or Local applications.
Let’s study them one by one to identify the differences.
What is a Honeypot?
Take an example of co-operate network where we get attack/malicious traffic from outside network
This network includes your users, Servers, routers, Internet Firewall, DMZ network, attackers and your Honeypot system. There is no such rule to put honey pot systems in the network i.e., you can put multiple Honeypot systems in the network as per the requirement OR as per the network topology.
Either you can put the Honeypot system in the inside Network or put it on the Gateway of the Network.
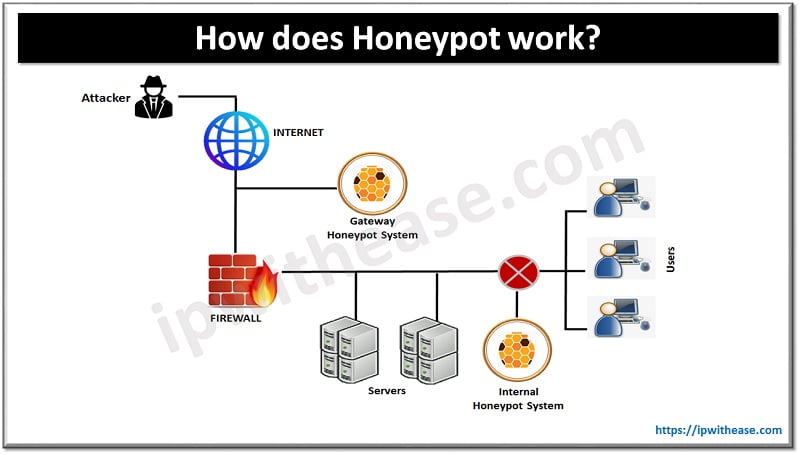
What’s the advantage that we get when we put the Honeypot system in the DMZ or outside network?
- Honeypot doesn’t increase the risk of an internal network which means an attacker is trapped inside the Honeypot, it wouldn’t crawl inside your internal network.
- External Honeypot reduces the alerts issued by firewall. Means lower number of alerts that are produced by external firewalls.
Related: Understanding Types and Benefits of Honeypot in Network Security
However there are disadvantages as well.
- External Honeypot cannot trap an internal attacker which means if the attacker is already inside your network Honeypot failed to identify it.
Honeypot placed inside the Network along with the servers
- It can also detect a misconfigured firewall which means if your firewall failed to stop the attacker and the attacker made it inside the network.
However there are some disadvantages as well.
- A compromised Honeypot if placed inside the network opens more doors for the attacker’s to attack internal systems which is a security risk.
- Moreover your firewall must adjust your filtering rule to allow traffic to Honeypot. You have put additional rules in the firewall to allow traffic towards the Honeypot server. Basically, it means you have to make the changes in your network configuration and network topology.
What is a Sandbox?
Most Sandboxing environments are applicable in the Software domain. Sandboxing offers a very safe and effective technique to validate your code, allowing you to analyse how the code works and how it provides security to your network and data from threats.
You might have heard about Virtual box or VMware box. So you can create virtual instances of your favourite operating system and apply software according to the environment. This is the partial example of the Sandbox. Whatever we perform here will be isolated from another VM machine/environment. We can test our code and rectify the loopholes from the running configuration. Furthermore you can test the Ransomware or Malware to check how it impacts the network.
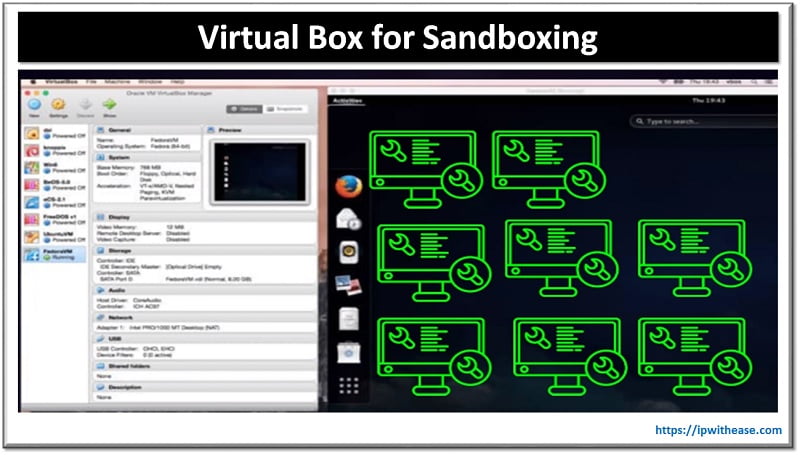
You can also learn a lot of things which you design for your environment and run it on the virtual machine. Similarly you can apply mitigation control in your Virtual machine and once you successfully implement the resolution then you can apply the same in a real environment.
Sandboxing can be provided by Vendors like McAfee, Sophos, and Kaspersky.
- If we have a sample of a malware file, we can directly upload it to an isolated environment where it will run as a piece of software or code in its own sandbox and provide you with the analysis.
- You can also set a piece of code or untested software to the 3rd party sandbox vendor and where it can be analysed and inputs will be shared with you.
Honeypot vs Sandbox: Comparison Table
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
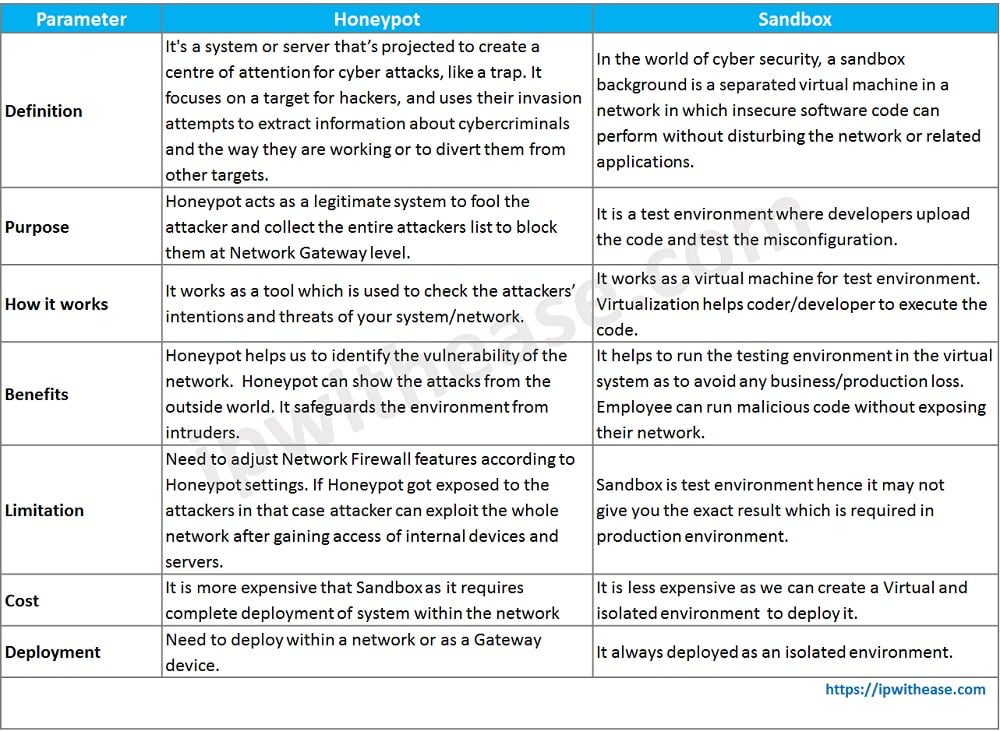
Download the comparison table: Honeypot vs Sandbox
Continue Reading:
Honeypot vs Honeynet: Complete Guide
What is the difference between Sandbox & Development Environment?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj