Table of Contents:
As the digital era accelerates, the infrastructure underpinning the internet faces unprecedented demands. The surge in online activities, driven by video streaming, cloud computing, and an ever-growing number of internet users, necessitates a more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective approach to internet traffic exchange. Remote Peering emerges as a pivotal solution, promising to redefine how data is exchanged across the globe, especially for businesses.
Understanding Peering
Peering is the process through which internet networks exchange traffic directly, enhancing internet speed and reliability for end-users. Traditionally, this exchange required physical presence at Internet Exchange Points (IXPs), limiting accessibility and increasing costs for smaller networks or those located far from peering points.
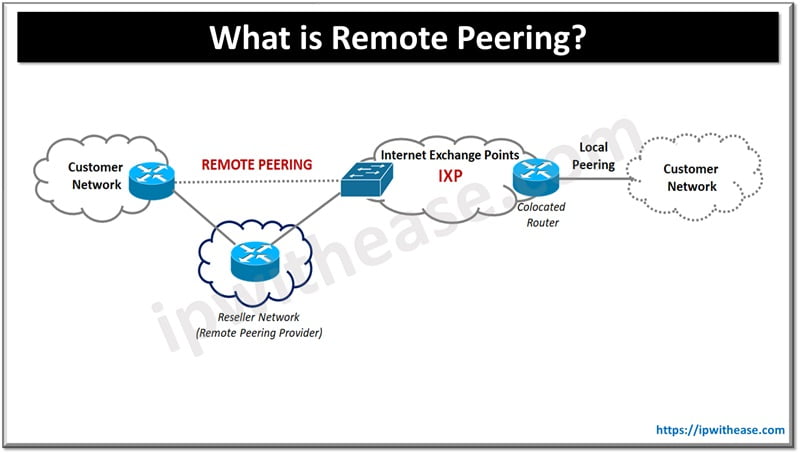
The Evolution Towards Remote Peering
Remote Peering represents a significant evolution, enabling networks to connect to IXPs without the need for physical presence. This approach has democratized access to peering, allowing a broader range of networks to participate in direct traffic exchange, thereby enhancing the global internet architecture’s efficiency and resilience.
Strategic Benefits of Remote Peering
In the evolving landscape of internet connectivity, Remote Peering presents a transformative approach to managing internet traffic exchange. As businesses and content providers strive to meet the burgeoning demand for seamless, high-speed internet access, the strategic advantages of Remote Peering become increasingly evident. This section delves into the key benefits that Remote Peering offers, each contributing to a more connected, efficient, and cost-effective global network.
Global Connectivity and Network Efficiency
Remote Peering breaks down geographical barriers, enabling networks to establish a presence at IXPs worldwide without the need for physical infrastructure. This global reach is vital for businesses aiming to provide consistent, high-quality digital experiences across various markets. By leveraging Remote Peering, networks can efficiently route traffic across continents, minimizing latency and enhancing user satisfaction.
Moreover, Remote Peering contributes to the overall efficiency of the internet’s architecture. By facilitating direct connections between networks at strategic points around the world, it reduces the reliance on transit networks, which can often lead to congested routes and higher latency. This efficiency not only improves the quality of service for end-users but also supports the scalability of the internet infrastructure to accommodate future growth.
Cost Reduction and Simplified Operations
The cost benefits of Remote Peering are significant. By eliminating the need for physical presence at IXPs, networks can save on the expenses associated with establishing and maintaining hardware, leasing space, and employing staff in multiple locations. Remote Peering provides a more economical alternative, offering the same level of connectivity and exchange capabilities without the hefty investment traditionally required.
In addition to cost savings, Remote Peering simplifies operational complexities. Managing peering arrangements and navigating the technical and regulatory challenges of international connectivity can be daunting. Remote Peering streamlines these processes, allowing networks to manage their peering relationships through a single service provider. This simplification reduces administrative burdens and enables networks to focus on their core business objectives, enhancing their competitive edge in the digital marketplace.
Enhanced Internet Performance
Remote Peering directly impacts internet performance by improving the speed and reliability of data exchange. By facilitating closer proximity to peering partners and content sources, it ensures that data travels along the shortest possible routes, reducing latency and packet loss. This improvement in performance is crucial for bandwidth-intensive applications such as streaming services, online gaming, and cloud-based solutions, where even minor delays can significantly affect user experience.
Furthermore, Remote Peering enhances the resilience of the internet by diversifying the paths through which data can travel. In the event of network outages or congestion, the ability to reroute traffic through alternative IXPs ensures continuity of service. This redundancy and flexibility are key attributes of a robust digital infrastructure, safeguarding against disruptions and ensuring the uninterrupted flow of information across the global internet.
The Role of Remote Peering in the Future of Internet Traffic Exchange
As internet usage continues to grow, the demand for efficient, scalable, and cost-effective traffic exchange solutions becomes increasingly critical. Remote Peering stands at the forefront of this demand, offering a forward-looking solution that supports the expanding needs of the global internet ecosystem.
Supporting the Growth of Digital Services
The future of digital services, from cloud computing to video streaming and beyond, relies on the seamless exchange of data across the internet. Remote Peering enhances the underlying infrastructure, ensuring that these services can grow and evolve without being hindered by traditional network limitations.
Facilitating Global Internet Expansion
Remote Peering plays a crucial role in facilitating the expansion of the internet into new regions and markets. By lowering the barriers to entry for peering, it enables networks in emerging markets to connect with global IXPs, fostering a more inclusive and accessible internet.
Conclusion
The future of internet traffic exchange is being shaped by the adoption of Remote Peering. With its ability to provide global connectivity, reduce costs, and enhance internet performance, Remote Peering is not just a technological advancement; it’s a strategic necessity for the continued growth and democratization of the internet. As we look towards a future marked by increasing digital demands, Remote Peering offers a promising path forward, ensuring that the infrastructure of the internet remains robust, efficient, and capable of supporting the next generation of digital innovation.
Continue Reading:
How to Improve Streaming Bandwidth
VPN vs VPS: What the Difference & Which One Is Better for Streaming
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.