What is Linux?
Nowadays, in the IT community we define Linux as a free distribution, open-source Unix-like operating system, with a kernel capable of running on many different types of computer hardware specifications; initially released in 1991 by Linus Torvald, a graduate technologist in Finland.
Due to the fact that it was written from scratch, Linux Operating System does not contain any code of behavior. It is assembled under the general model of free and open source software development and distribution policy. Linux became famous as a leading operating system for servers and other big systems such as mainframe computers and ultra-fastest computers.
Another revolutionary ability is that It also runs on coordinated systems which have built in Operating Systems from microcode, such as smart phones, tablets running android, Linux derivatives, network routers, televisions, video games and smart watches.
As a general rule, the source code may be used, modified and distributed with respect to GNU general public licenses. The most popular Linux distributions are DEBIAN, UBUNTU, LINUX MINT, FEDORA, ARCH LINUX, RED HAT and SUSE Linux organization server edition.
Top Linux Books for beginners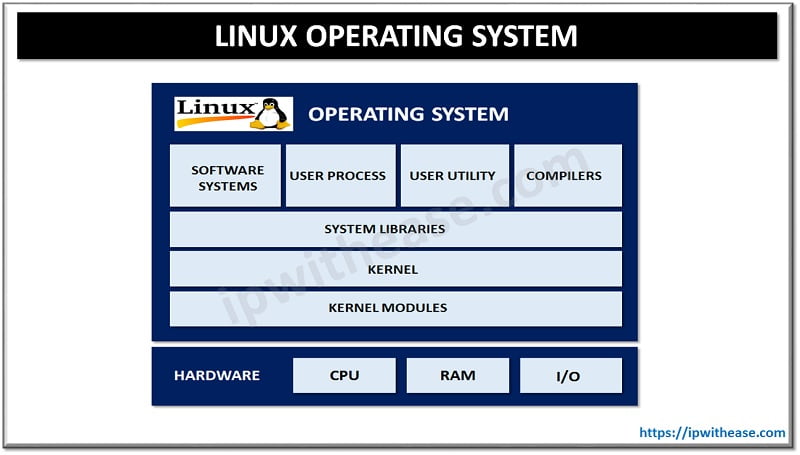
Kernel Architecture
As a general rule modules or sub-systems that provide the operating system functions define the core of an operating system and are commonly written in C programming language.
- File System: It is mainly used for storing data on disk and fetching updates of this information. Generally, the file system is accessed through system calls such as: open, read, and write. Examples of file systems are: FAT16, FAT32, NTFS ext2, ext3.
- Process Management: The Unix OS designed to be a time-sharing system. We observe that any process is regular to run for a specific period of time (known as: time slice). The Kernel creates, succeeds and deletes processes.
- Device Driver: As on many operating systems, the main functions of the driver: are setting up hardware or data manipulation. It also brings the connected devices inside and outside services. In addition, it receives data from hardware and passes it back to the kernel. Finally, it sends data from the kernel to the device, while detecting and manipulating device errors.
- Memory Management: As a rule of thumb, in Linux the physical memory is divided into portions of equal allocated sizes called Pages. The general types of memory management are:
- Physical memory.
- Virtual memory.
- Swap memory.
- Networking: According to history, the initial incorporated communication ability in UNIX was created for Berkeley UNIX 4.2 depending on sockets execution lists. Usually sockets provide a programming interface for networking architecture.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Linux
The most famous advantages of Linux operating system are the following:
- Cost of License: The most advanced benefit of installing Linux is the fact that it is free to download where Microsoft products are available for a powerful and sometimes periodical payment fee. As a general rule, Microsoft Windows licenses are typically allowed only to be used on a single computer, whereas Linux OS distributions can be installed on multiple computers without paying a single penny.
- Security: The security specifications of Linux OS are advanced compared to that of Microsoft Windows. The Linux operating system has been successfully maintained to stay secure in the realm of viruses, spyware and adware. The simplest advantages of Open License code to establish are increased network security, responsiveness and functionality.
- Reliability: The subject field of Linux is superior to Windows because critical operating system functions are enforced in such a way that batty programs can’t cause the computer to become unstable and crash.
- Capabilities: Linux usually comes with the Apache web server, an email server, router/firewall ability and SQL information. In addition to that Linux is POSIX non-resistant which means that most of the applications developed for Linux can be operated on other POSIX non-resistant UNIX procedures with a minimum of process utilization.
On the other hand, there are not many disadvantages for Linux OS, we have addressed only the following:
- Non-Compatible Software: Due to the official license terms, developers don’t invest time and money on creating everyday software that common people use, such as (Office, Adobe Photoshop, etc.).
- Unsupported Hardware: Another disadvantage of Linux, is the compatibility with Hardware. Many large device manufacturers don’t invest in drivers for Linux operating systems. As a result, many people cannot use Linux properly or with some functionality problems.
Conclusion of Linux Operating System
In this article, we have described the accommodative field surroundings for Linux operating systems as a solution for interdependence and advanced computer systems architecture. We addressed the advantages and disadvantages compared to other OS and hope in the future, the IT community will fund Linux Projects from the beginning and provide full user support.
Continue Reading:
Best Linux Operating Systems (OS)
Are you preparing for your next interview?
Please check our e-store for e-book on Linux Interview Q&A. All the e-books are in easy to understand PDF Format, explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj