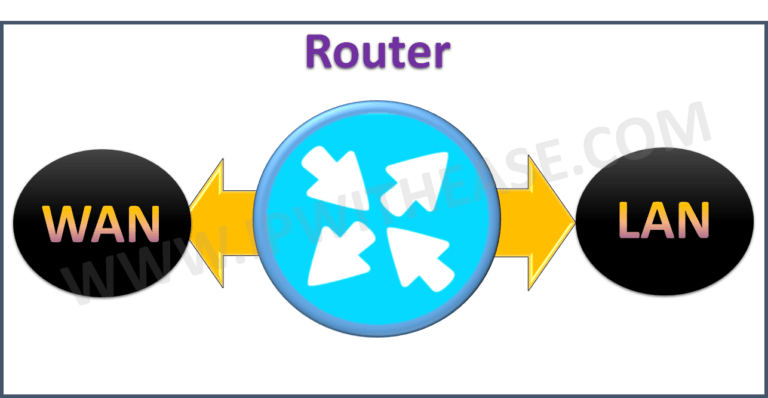
Network Router is a layer 3 and 4 networking device of OSI model which routes packets across different networks. Router supports reachability between source and destination in LAN and WAN environment. We need a device that knows the address of each segment and can also determine the best path for sending data traffic to the segment. This functionality is performed by a Router.
Unlike Hub and Layer 2 switch, All ports (integrated ports generally) on a Router are in the different broadcast domains and routers don’t forward broadcasts from one broadcast domain to another.
Routers utilize following mechanisms for reachability to remote networks –
- Static Routing
- Dynamic Routing protocols –
- IGP (Interior routing protocols) like RIP, EIGRP, OSPF
- BGP for reachability to remote networks in other domains
When using dynamic Routing protocols, Router will let other network devices know about topology of the network and network changes.
Routers work in network edge where LAN and WAN Network need to communicate. Whether it’s a remote branch office , head Office or even a Data Center , Router is the de Facto Device to be use for WAN link termination and communication to other sites. Routers may also be used between LANs for communication across various network segments.
Routers task is to build the map of the network in the form of the routing table.Routers understand the networks and not host addresses numbers. Routers will communicate with other Routers or Layer 3 devices over WAN until destination network is reached.
Some of well-known Router models in Cisco include cisco 3900, 2900 and 1900 Series Routers. Some new entrants in market are ISR G3 Series Routers of 4000 Series (4221, 4321, 4331, 4351, 4431and 4451 models)
KEY FEATURES/PARAMETERS ASSOCIATED WITH ROUTERS ARE AS BELOW –
- Static and/or Dynamic Routing
- Path determination and Path cost
- Optimal Path selection
- Packet transmission towards intended destination
- WAN and LAN connectivity
- Remote management
- WAN Throughput/capacity
- Support for multiple Routing and Routed protocols
- QOS
- Broadcast and Collision control/segmentation
- Array of WAN port types (Like Fiber, Copper, and ADSL etc.)
–
SOME ADDITIONAL FEATURES THE ROUTERS MAY SUPPORT INCLUDE –
- Network Address Translation
- Policy Based Routing
- Zone Based firewall or equivalent
- Switching/services Modules
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj