Table of Contents
In the ever changing landscape of networking, virtual LANs become a defacto standard for secure communication. In cloud computing since everything is virtual including network and interfaces the MACVLAN drivers are used for connecting virtual machine interfaces and network types. It forms a basis on which communication between containers and outside world is established.
In today’s article we understand about MCVLAN and VLAN and understand how they work in virtualized environments.
What is MACVLAN
MACVLAN helps to configure sub interfaces of a parent physical Either network interfaces or upper devices as they called with a unique MAC address and its own IP address. Virtual machines, containers and applications can be grouped together to a sub interface to establish connectivity directly to a physical network using MAC and IP address.
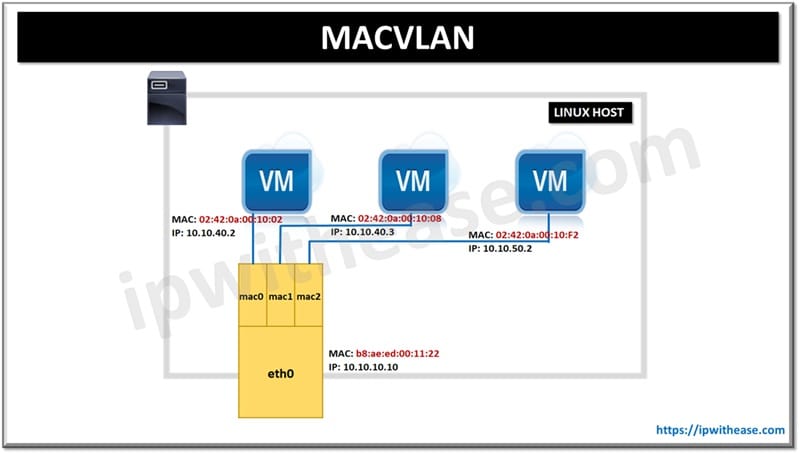
It is an ideal solution to connect native virtual machines and containers to physical networks. Containers communicate directly using routable IP addresses directly with any network resources which exist outside a Swarm cluster eliminating the need to use NAT or port mapping. This type of implementation is useful in network visibility and troubleshooting general issues and helps in reduction of network latency. MACLANs can be configured in different ways to achieve different functionalities.
Related: MACVLAN vs IPVLAN
Use cases for MACVLANs
- Required for network appliances or virtual network devices required to interact with external network
- Creation of containers which act as virtual routers
- Provide dedicated MAC address and IP address to containers on same subnet as host or on separate subnet
- Creation of individual network for tenants in multi-tenant environments
- Testing and development in container environments
- Media streaming, broadcasting and multicast communications can use MACVLANs for direct and efficient communication with hardware devices and services
What is VLAN
VLAN is networking technology to logically divide a single physical network into multiple virtual networks. Network administrators can create isolated broadcast domains on network switch. Using VLANs we can group devices together based on factors such as function, departments, security requirements irrespective of the physical boundary. VLANs are used to improve network performance, management flexibility and security. Logical separation of devices into different VLANs network traffic can be controlled to reduce unnecessary broadcast traffic and optimize flow of data.
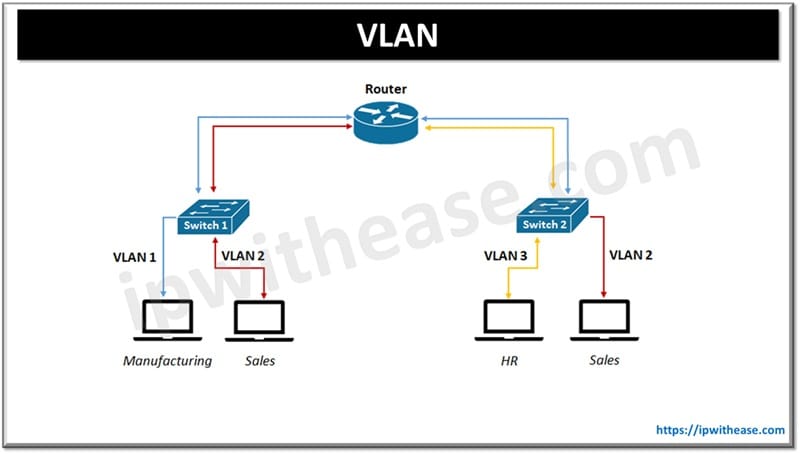
Segmentation using VLAN also enhances security as devices in VLAN are not allowed to communicate directly with devices in other VLANs unless explicitly allowed using access control lists (ACLs). VLANs are implemented on managed network switches with 802.1Q standard of IEEE or VLAN trunking protocol (VTP). VLAN is assigned a unique number known as VLAN tag which is inserted into the Ethernet frame to identify VLAN belongs to which frame.
Use cases for VLANs
- Network segmentation to establish more manageable sub networks
- Implementation of access control policies
- Optimization of bandwidth by grouping devices having similar bandwidth requirements
- Creation of guest networks
- Can be used in conjunction with QoS policies for network traffic prioritization
- Ease of scalability for networks
Comparison Table: MACVLAN vs VLAN
| Parameter | VLAN (Virtual LAN) | MACVLAN (MAC Virtual LAN) |
| Purpose | Network segmentation at Layer 2 | Assign multiple MAC addresses to a single host interface |
| OSI Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link) | Layer 2 (Data Link) |
| Tagging | Uses 802.1Q VLAN tags in Ethernet frames | No tagging, appears as separate MAC addresses |
| MAC Addresses | Single MAC per physical interface | Multiple MACs per host interface |
| Switch Requirement | Requires VLAN-capable managed switches | Works on any switch (no special config needed) |
| Isolation | Complete L2 isolation between VLANs | Depends on mode (bridge, private, VEPA) |
| IP Subnets | Typically one subnet per VLAN | Can share or use different subnets |
| Communication | VLAN members communicate via L3 routing | macvlan interfaces can communicate directly (depending on mode) |
| Use Cases | – Network segmentation (LANs, security zones) – Traffic isolation | – Container networking (Docker, Kubernetes) – VMs needing direct MAC access |
| Modes | N/A (Standard 802.1Q tagging) | Bridge (interfaces talk to each other) Private (no inter-communication) VEPA (requires external switch support) |
| Implementation | Configured on network switches | Configured on host OS (Linux) |
Download the comparison table: MACVLAN vs VLAN
How they work together in Virtualized Environments
VLANs is an older concept in networking and widely popular. Logical segment creation happens in physical networks using VLANs for efficient traffic management and security. Docker in cloud computing takes this concept to the next level and utilizes VLAN as trunks to carry individual networks on a single link. It is similar to implementing a router on a stick on a host for docker containers.
Each VLAN represents a separate network with a unique IP address. The VLANs are isolated from each other, to provide a secure and organized network environment. Docker achieves this by creating VLAN for each network and forwarding them as link (as trunk) and maintaining separation. MACVLANs support 802.1Q mode. Containers can be connected to the network directly and sub interfaces can be defined thus to allow more control over network segmentation. In 802.1Q mode a link is created as a router on a stick.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj