Table of Contents
Automate-automate-automate is the buzz word in the digital landscape. Reducing fatigue, rework, efforts, and bringing down operations costs are the biggest challenges for organizations globally. Cost of operations are sky rocketing, cloud computing subscription models where pay as you go model is applicable, still finance and operations need to be on their toes at all times to keep running costs under check.
AI had further fueled the desire to automate as much as possible and reduce workforce and bring down running costs.
In all domains including networks this trend is evident, there are many network automation tools and scripting solutions available in market which help in deployment faster with less human intervention using automation one such popular tool is Ansible.
In this article we will learn more in detail about Ansible network automation tool, understand how it works, its benefits and characteristics.
What is Ansible
Ansible is an open source automation solution written in python language and available on various flavours of Linux such as Redhat, Ubuntu, Debian and also for Mac. It helps in reduction of manual tasks and can be used for several use cases such as network provisioning, configuration management, network management, security tasks, orchestration, continuous delivery and application development.
Features of Ansible
- Free and open source software
- Written in python language and uses YAML
- It is agentless and not require installation on remote devices
- Automate repetitive network tasks
- Management of heterogeneous network devices with separate data model (In playbook) and execution layer (Ansible module)
- Secure communication using SSL / SSH
Architecture of Ansible
Ansible manages the network using client-server architecture. The Ansible control machine manages network devices and from here you run Ansible CI tools. The network devices or clients receive commands from this machine and SSL/SSH is used for communication with network devices for ease of managing dispersed devices across the network. Ansible has several modules to aid in network automation. These are pre-built scripts which can be used to automate network configuration tasks. A wide range of network devices such as switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers is covered by Ansible. Some of the popular modules are:
- ‘ios Config module for Cisco IOS devices. It is used to configure access control lists (ACLs), interfaces and VLANs.
- ‘nxos Config module is for Cisco Nexus devices. It is used to configure access control lists (ACLs), interfaces and VLANs.
- ‘junos Config module is for juniper devices and is used to configure security policies, interfaces, VLANs etc.
Ansible network modules also offer privilege escalation where certain tasks must be done by a privileged user only. The top level parameters of Ansible such as become: true and become_method: enable can have a playbook with escalated privileges for any network platform which supports it. Let’s look at the example here:
ansible_connection: ansible.netcommon.network_cli
ansible_network_os: junos
ansible_become: true
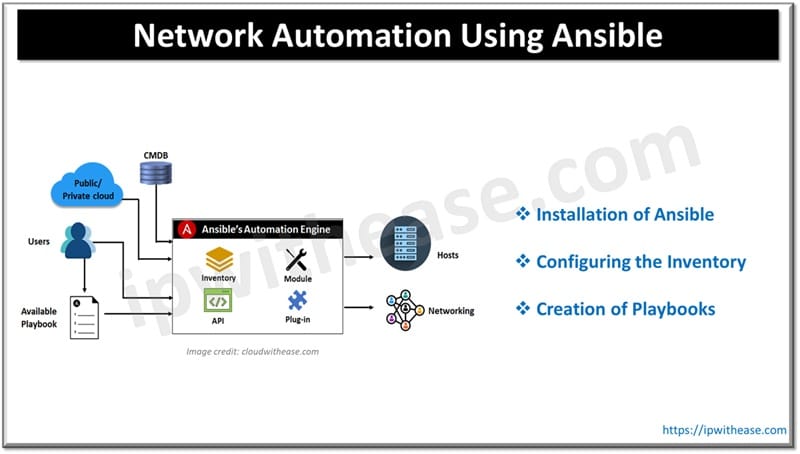
ansible_become_method: enableAnsible architecture comprises inventory, modules, APIs and Plugins. Each of them perform a set of functions as under and are part of Ansible orchestration engine. Apart from these 4 main components Ansible has playbooks, hosts, CMDB, networking and cloud.
The playbook file has code written in YAML which is a human readable format language. It has tasks to be executed by Ansible.
Using Ansible for Network Automation
To start using Ansible for network automation one has to follow below steps:
Installation of Ansible
Ansible is pre-bundled with Operating system and it can also be installed using Yam package or apt-get or using pip basis which operating system you are using
Configuring the Inventory
Inventory is a file also known as ‘hosts’ as it contains information about network devices, IP addresses etc. which needs to be managed.
Creation of Playbooks
Playbook file has code written to in YAML which is a human readable format language. It has tasks to be executed by Ansible. Below is example of Ansible playbook for network automation which configures FastEthernet1/0 interface on network device having IP address 143.168.1.1
- name: Configure Juniper Devices
hosts: Device1
Tasks:
- name: Configure Interface
junos_config:
lines:
- "interface FastEthernet1/0"
- "ip address 143.168.1.1 255.255.255.0" - " delete disable" ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj