Introduction:
It’s difficult to imagine how the management, storage and organization of data take place on the USB flash, hard drive or portable SD card? Actually it’s in form of only 0’s and 1’s on the physical disk. Such data get its structure and meaning with the help of the file system.
When a disk is referred to as FAT or NTFS, its actual reference is to the file system that the operating system makes use of. In this article, we will list the differences between NTFS and FAT32 file systems that the Windows operating systems make use of.
Related Blog – NTFS File System Guide
This information may help in selecting the appropriate system that best matches with customer IT demands. Microsoft has introduced both these file systems for meeting the requirements of their applications and business.
FAT32 and NTFS: Basic definition:
FAT32 is the extension of FAT (file allocation table) that refers to storage of data in 32 bits chunks. This file system is somewhat older and is not used commonly used these days.
NTFS (New technology file system) has replaced FAT as the major file system used by Windows nowadays. This is a secure file system and also offer support to files and hard drivers of larger size.
It is certainly important to have an idea regarding their abilities before you can make decision between the two. Following comparison will give an idea regarding both of these systems.
NTFS: FEATURES
Brought into usage in 1993, July, for Windows, NTFS is a file system used by the Operating systems of Windows. NTFS is abbreviated for New Technology File System used in Windows. NTFS is a secure option for storing larger files in hard drives.
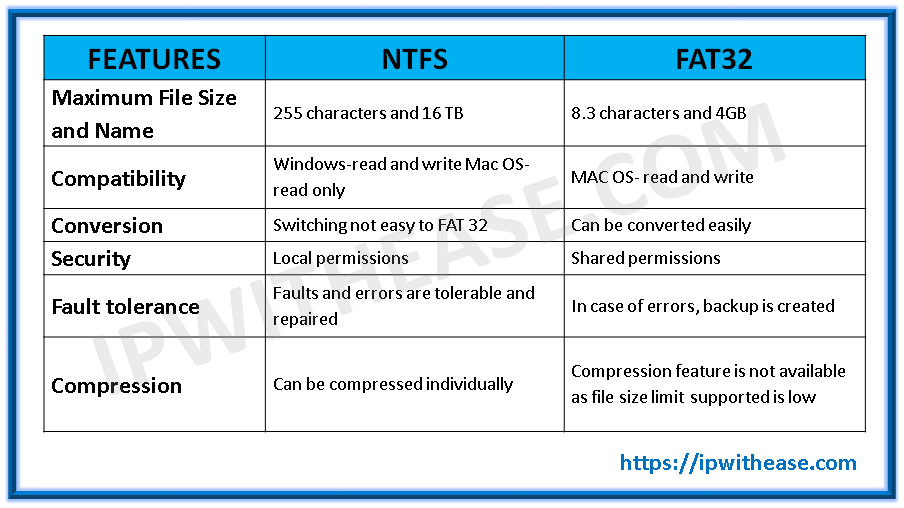
A file size as large as up to 255 characters is supported. Files of up to 16 terabytes can be easily stored.
- Fault tolerance: This file system repairs any data, folders, files by itself in case of any abrupt power cut offs or errors without sending across any message or notification to the user. So, it can tolerate and solve the faults that occur.
- Security: New Technology File System sets up permissions on local folders.
- Compression: The files can be compressed separately, and one at a time, not making the system to lag behind due to divided compression. Also, the NTFS file system is capable enough to handle large file sizes on your hard drives or SD cards, so you don’t have to worry about the storage of your favourite web series or movies.
- Conversion: Switching between the file systems is not easy in case of NTFS file system as it is protected with a sheltered set of codes and protocol. So in that case, to prevent your data from being lost, you need to create a backup of it and reset the drive or storage disk to factory settings.
- Compatibility: Discussing about the compatibility features, NTFS is well-suited and can function in Windows operating systems. This file system can go down well with an operating system as old as Windows XP. Talking about the MAC operating system, it is only allowed to read the drives and not write to it.
- File Size: Thankfully, the NTFS system allows bigger partitions of the files.
FAT32: FEATURES
- Fault tolerance: Two different copies are maintained by FAT32 of file allocation table. In case of any sort of damage, a mechanism of backup is also used by FAT32.
- Security: The security dependence in FAT32 is on the share permissions. This reflects that in Network, they are somewhat better but are vulnerable locally.
- Compression: No feature of file compression is offered by FAT32. It is also not able to handle the files of large size since 4GB is the limit of its file size.
- Conversion: A FAT32 system could be easily converted to NTFS but the reverse is not true since a secure protocol is used by NTFS.
- Compatibility: To the drives of FAT32, MAC OS can perform both the functions of writing and reading.
- Volume size and File size: FAT32 can offer support to maximum file size of 4GB and the maximum volume size that it can support goes around 2TB.
Now that we have high level understanding on features of NTFS and FAT32, below table enumerates there differences and how one is in contrast to other –
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj