Table of Contents
OSPF DBD packets or Database Descriptor Packets are used to describe the contents of the link-state database (LSDB). They help routers exchange summaries of their LSDBs to determine what link-state information they have in common and what needs to be requested, thus helping OSPF databases between neighbours.
Introduction to OSPF DBD
IP routing is the most important aspect of networking. There are several types of protocols which support IP routing using distance vector mechanism or link state mechanism. Ultimate goal of IP routing is to find the best shortest path for packet delivery in the network. Link state routing protocols are more commonly and widely used as they support large enterprises, IPv4, IPv6 networks, CIDR and VLSM addressing models. Some routing protocols use transport protocols such as TCP and UDP for data transmission, however protocols such as Open Shortest path first (OSPF) will not carry data using TCP and UDP.
Today we look more in detail about OSPF DBD (database descriptor) packet type, its purpose, working and features.
Download the OSPF DBD Packet Cheatsheet
OSPF Database Descriptor (DBD) Packet: Working & Features
The link state routing protocols required their link state database should remain synchronized across all routers to function properly. The synchronization starts as soon as adjacency is performed between neighbouring routers. The OSPF uses a database descriptor (DBD) packet to achieve this purpose. The database comprises multiple packets. The poll response procedure is used to describe multiple packet usage. The routers are designated as Master and slaves. Database description is sent by slave router after master sends the database description packet.
- OSPF router performs summarization of database descriptor (DBD) packets and LSA set belongs to that database.
- When the neighbour views LSA , having a more recent copy of its own database, it requests a new LSA from the neighbour.
- Routers holding LSA do not send packets immediately after hearing hello and parameter check; instead each router will create and send the database descriptor (DBD) packets which contain each LSA header.
- The header includes information for unique identification of LSA and the revision.
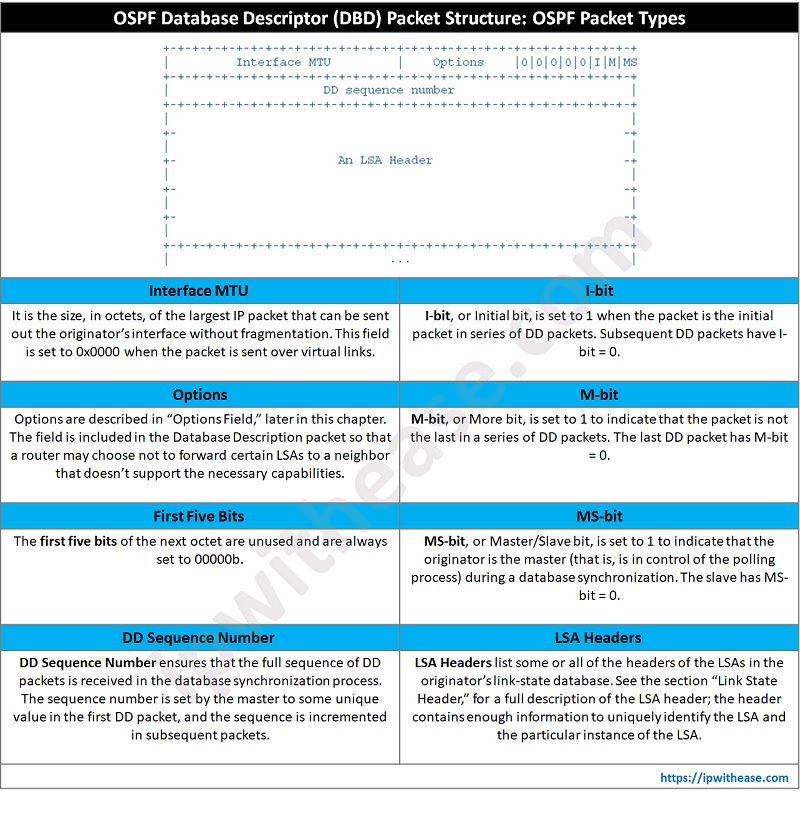
- The DD message will use OSPF defined simple error recovery process. Each DD packet has several LSA headers, with an assigned sequence number.
- The receiver acknowledgement happens for received DD packets by sending DD packets with the same sequence number.
- Sender will use a window size of 1 packet before sending the next DD packet and wait for acknowledgement.
- As the relationship between two routers is formed by neighbours it determines which router will be master and which router will be slave during the exchange of database.
- During DD packet exchange the role of master and slave determine routers responsibilities. The LSA header has a local router database.
- DD sequence number is used to sequentially arrange database descriptor (DBD) packet collection. The sequence number increments by 1 until the overall database description is sent.
- Interface MTU is having MTU value of outgoing interface. For virtual fields this value is set to 0x0000.
Also Refer: OSPF Packet Types: The Ultimate Guide
A Typical OSPF DBD (database descriptor) Packet
A typical OSPF DBD packet looks like as under:
Open Shortest path first
OSPF header
OSPF version : 2
Message type: DB Descr. (2)
Packet length : 72
Source OSPF router : 10.3.3.2 (10.3.3.2)
Area ID: 0.0.0.0 (backbone)
Packet checksum :0x9d6b
Auth type: null
OSPF DBD (database description)
Interface MTU: 1500
Options: 0x52 (O,L,E)
DB description: 0x03 (M,MS)
………….0…. = R: OOBResync bit not set
………….0…. = I: Init bit not set
………….1…. = M: More bit set
………….1…. = MS: Master/Slave bit set
DD sequence : 9755
LSA header
LS age : 972 seconds
Do not age: False
Options: 0x22 (DC,E)
Link-state advertisement type: Router-LSA (1)
Link-state ID : 10.2.2.2
Advertising router: 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
LS sequence number: 0x8000002a
LS checksum: 0xc970
Length: 48
LSA header
LS age : 11 seconds
Do not age: False
Options: 0x22 (DC,E)
Link-state advertisement type: Router-LSA (1)
Link-state ID : 10.2.2.1
Advertising router: 10.2.2.1 (10.2.2.1)
LS sequence number: 0x80000031
LS checksum: 0xc9948
Length: 36
Continue Reading
EIGRP Packet Types: The Complete Guide
OSPF Router Types: Detailed Explanation
Are you preparing for your next interview?
If you want to learn more about OSPF, then check our e-book on OSPF Interview Questions and Answers in easy to understand PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj