Routing management is an important component of networking. Apart from routing packets from source to destination it involves complex management of packets to maintain performance of the network. The protocols which monitor performance of the network and work on detection and removal of redundant links are equally important at layer 2 operations. It tends to solve issues of network performance degradations when systems use shared telecommunication channels on local area networks.
Today we look more in detail about RSTP – Rapid Spanning tree protocol, its features and how it is configured in a network.
What is RSTP-Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol is a fast convergent and advanced version of STP or Spanning Tree protocol. It is used to prevent loops in bridges and broadcast storms in LANs redundant networks. It achieves faster convergence by bypassing the blocking and listening state of STP and permitting only one active path between two devices. Disabled connections are used as backup / redundant paths to support active connection in event of failure. The IEEE standard for Rapid Spanning Tree protocol is 802.1w.
Commonalities between STP and RSTP
- Lowest bridge ID is elected as root bridge in both STP and RSTP connection
- In STP and RSTP BPDUs are forwarded between switches
- Both in STP and RSTP root and designated ports are elected in similar manner
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) are distinguished by their capability to prevent loops in network topologies containing redundant links. While the STP was initially developed to address this issue, it has certain limitations, including a lengthy convergence time and an inability to adapt swiftly to changes in network topology. The RSTP, on the other hand, overcomes these drawbacks and provides a more efficient solution for loop prevention while being responsive to dynamic alterations in the network setup.
RSTP Port Roles
RSTP has four port roles as under:
- Root port is best path port to forward data to bridge.
- Designated port is a non-root port used as forwarded port for each LAN segment.
- Backup port is backup path to segment to which another bridge port connection is established.
- Alternate port is a backup port having less desirable cost of path. They remain in block state.
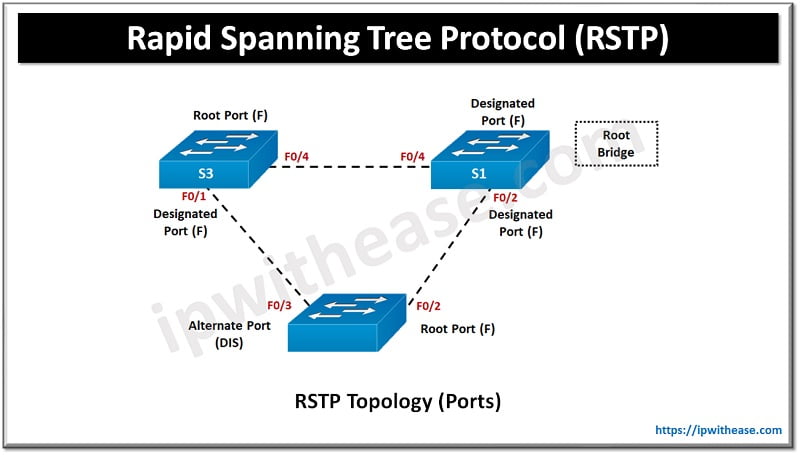
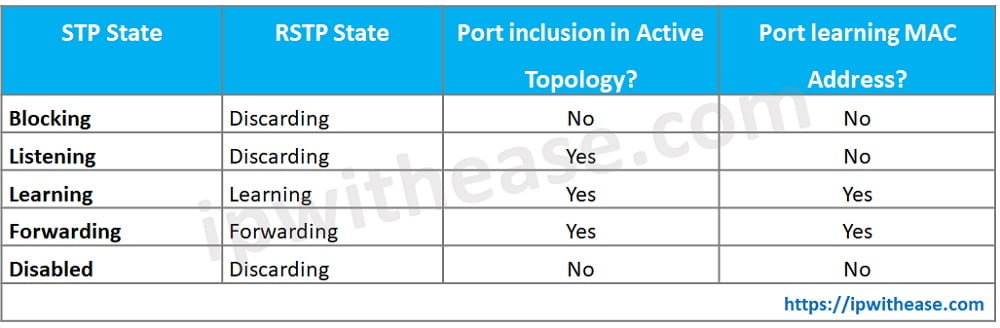
RSTP supports three port states as under:
- Discarding – No data transport happens in this state
- Learning – Ports learn about MAC address but no frames are forwarded
- Forwarding – ports send data and are in full operational state
Features of RSTP
- Network loops prevention
- Prevention of redundancy
- It provides faster convergence
- Backward compatible with STP
- No artificial forward delay timers required
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol: Configuration
Step 1: To configure RSTP – Rapid Spanning Tree protocol it needs to be enabled.
s1# configure terminal
Provide configuration command, one per line, End with CNTL/Z.
s1(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
s1(config)#interface fa0/2
s1(config)#spanning-tree link-type point-to-point
s1(config)#end
s1(config)#clear spanning-tree detected protocols
s1(config)#
To check if switch runs RSTP use below command
S1(config)#show spanning-tree
Step 2: Configure S1 as the ROOT bridge for VLAN1 and 5
s1# configure terminal
Provide configuration command, one per line, End with CNTL/Z.
s1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary
s1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 5 root primary
s1(config)#end
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
s1#
s1(config)#Show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0014.f2d2.4180
Cost 9
Port 216 (Port-channel21)
Hello Time 3 sec Max Age 15 sec Forward Delay 12 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32766 (priority 32765 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 001c.57d8.9000
Hello Time 3 sec Max Age 15 sec Forward Delay 12 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
——————- —- — ——— ——– —————————
Po21 Root FWD 9 128.216 P2p
Po23 Altn BLK 9 128.232 P2p
s1(config)#Show spanning-tree vlan 5
VLAN005
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 24586
Address 0014.f2d2.4180
Cost 9
Port 216 (Port-channel21)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 15 sec Forward Delay 12 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32777 (priority 32767 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 001c.57d8.9000
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 15 sec Forward Delay 12 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
——————- —- — ——— ——– —————————
Po21 Root FWD 9 128.216 P2p
Po23 Altn BLK 9 128.232 P2p
Continue Reading:
Top 50 STP Interview Questions
Types of Virtual Private Network (VPN) & its Protocol
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj