Table of Contents
Introduction to Cloud Supporting Services
Organisations migrating applications and services to cloud are apprehensive about the many things, major ones being that software is moving from in-house physically secured environment to service provider cloud where many other customer services are running in tandem. Nevertheless, sharing more detail will make the cloud technologies known to customers and provide assurance on security and performance experience. Below are the 3 cloud supporting services cloud providers provide to customer:
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)

Difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
These three services (SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS) provide the different ways of usage of cloud for an organization. These models provide an alternative to the traditional on-site self managed IT solutions.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service offers a pay-as-you-go approach for storage, networking, and virtualization.
- Platform-a-a-Service also provides services like hardware and software development tools available via web.
- Software-as-a-Service provides the highest degree of vendor management providing complete software solutions.
Below diagram describes the difference between the three types of services on the basis of the level of vendor management provided by each model.
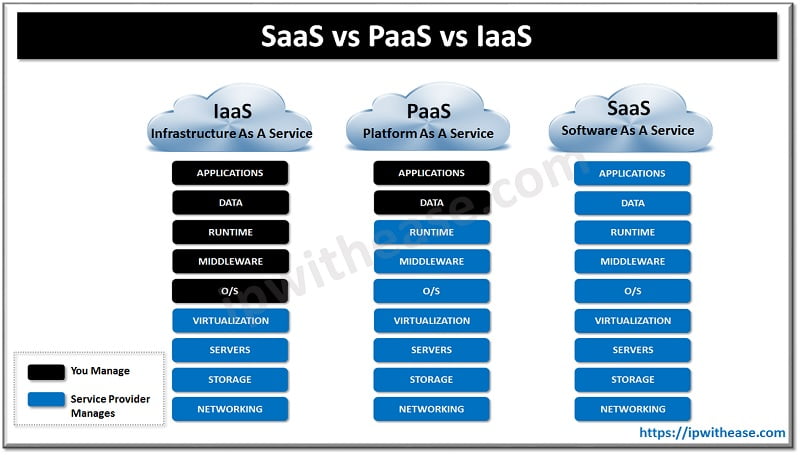
Comparison Table: SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
The Cloud services differ in the following ways –
PARAMETER | SAAS | PAAS | IAAS |
| Full Form | Software As a Service | Platform as a Service | Infrastructure as a Service |
| General Users | Business Users | Developers and Deployers | System managers |
| Services Available | Email , Office automation , CRM , website testing , social media management Virtual desktop | Service and application test , development , integration and deployment | Virtual machines, operating systems, network, storage, backup services. |
| Business Justification | To complete business tasks | Create and deploy service and applications for users | Create platform for service and application test, development. |
| Abstraction | Complete abstraction | Abstraction of underlying hardware, software and application services. | Abstraction of underlying hardware resources |
| Examples | Paypal , Salesforce.com | Azure Service platform, Force.com | Amazon EC2 , GoGrid |
| Control | Highest degree of control and flexibility | Good degree of control and flexibility | Minimal degree of control and flexibility |
| Operational Cost | Minimal | Lower | Highest |
| Portability | No portability | Lower | Best |
| Risk Of Vendor Interlock | Highest | Medium | Lowest |
| Security | Requires transparency in service provider’s security policies to be able to determine the degree of sensitive corporate data. | Additional security is required to make sure rogue applications don’t exploit vulnerabilities in software platform. | Should consider Virtual and physical servers security policy conformity. |
Continue Reading:
Saas vs Paas: What’s the difference?
What is Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj