Table of Contents
Before understanding SAN vs NAS, let’s discuss the two terms separately.
What is SAN?
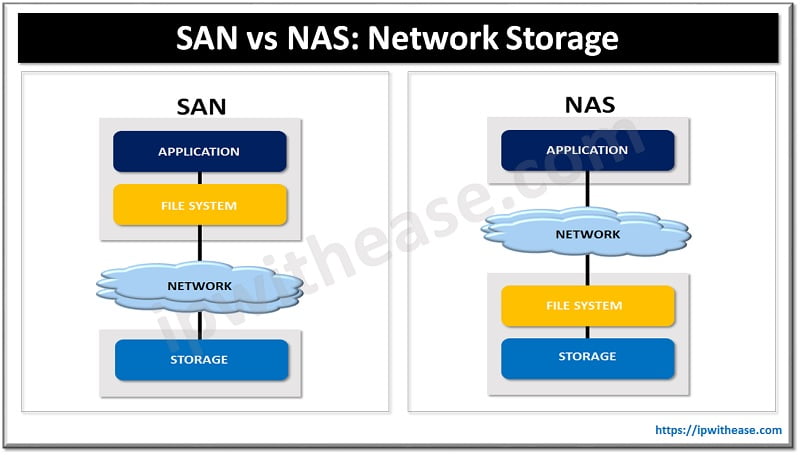
SAN stands for Storage Area Network which is a centrally managed storage pool. With SAN, the storage traffic from the LAN can be separated which leads to an improved and efficient performance. Through SAN, the distribution and management of resources of the organizations is simplified. SAN is a dedicated host of interconnected storage devices and switches. The block level storage can be accessed by this high speed network.
There are two layers present in Storage Area Networks:
- The Storage-Plumbing Layer
- The Software Layer
Storage-Plumbing Layer connects the network nodes and carry out device centered commands.
Software Layer contains the software that carries out the operations of the first layer.
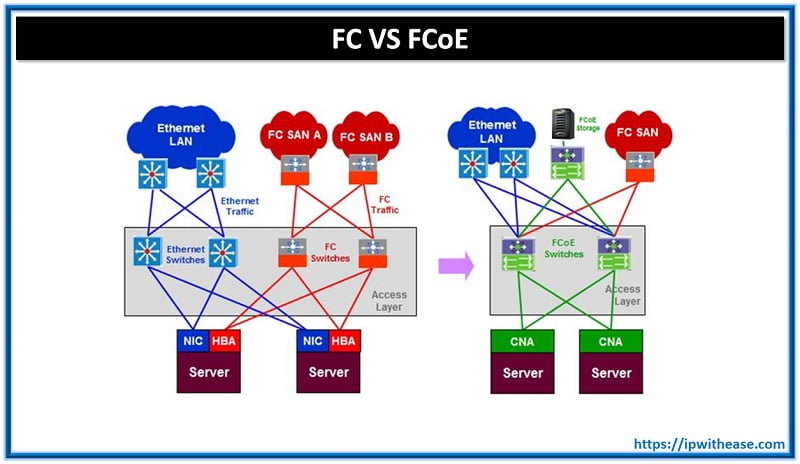
The standard protocol of Storage Area Networks is Fiber Channel, but, Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) can also be preferred. It enables Fiber Channel traffic transportation over the Ethernet.
Laying it out in simple words, Storage Area Network is a connected network of many storage devices which store the data in the form of block level storage. It is complex in terms of maintenance and management and is also an expensive choice for data storage.
Benefits
- The most striking benefit of SAN lies in its high speed access to files, all of which is done over the Ethernet.
- SAN is highly extensive in nature and provides a high quality service.
Limitations
- The major limitation of SAN lies in the cost and management.
- Even though they provide high speed data access, different networks of Ethernet are to be maintained- one for carrying out the Fibre Channel network and the other for handling the requests of metadata files.
What is NAS?
NAS stands for Network Attached Storage which is a computer device connected with a network. NAS provides file storage services over that network. NAS is the most effortless to set up. The standard protocols used by network attached devices are NFS (Network File System), Server Message Block (SMB) protocol or Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol.
The files that are stored in such devices are typically arranged in a logical order or storage containers. The NAS device is a node of the network itself, having its own IP address and is able to strike a communication with other devices on the same network.
Benefits
- Through NAS, as many users can access the data or the files easily. The security control of NAS is also good offering even a non-IT professional to handle the permissions for access.
- It is inexpensive as compared to SAN and also provides remote availability of data for the users.
- It is the right choice for smaller enterprises to go opt for NAS to fulfill their data storage needs.
- If you want your files to be available every time, even so that you can access the files from a remote location, Network attached storage is just the choice for you.
Limitations
- The area where NAS limits itself is in the scalability and performance. After crossing a certain limit of users’ access of files over NAS, it will ask for scaling up of horsepower of the server.
- Another major limitation of NAS lies in the Ethernet. The data over the Ethernet is shared in the form of packets, which simply means that one source or file is divided into a number of packets. If even one reaches late or goes out of sequence, the user won’t be able to access that file until each and every packet is reached and converted back into the sequence.
Comparison Table: SAN vs NAS
Below table summarizes the key points of comparison i.e. SAN vs NAS
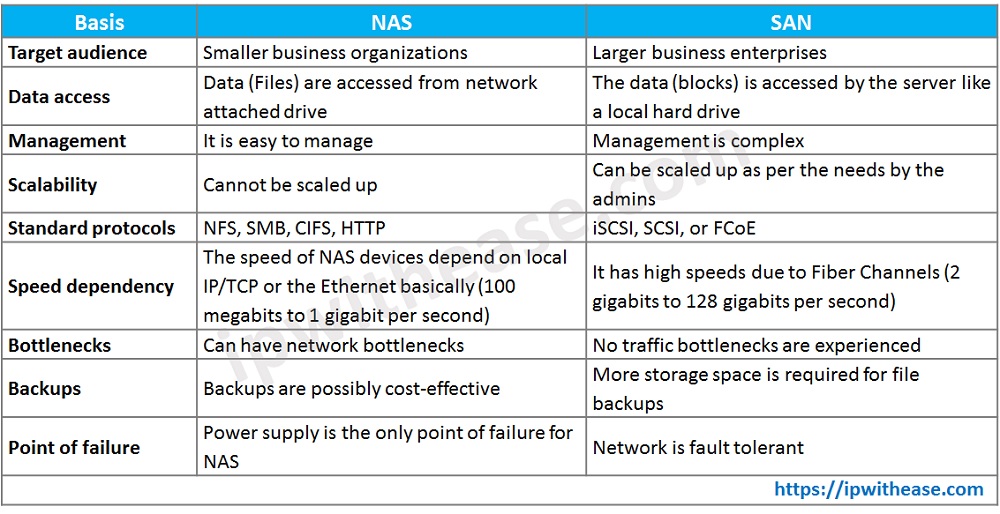
Download the comparison table: SAN vs NAS
Watch Related Video
Continue Reading:
What is object storage and its benefits?
If you want to learn more about SAN, then check our e-book on SAN Interview Questions and Answers in easy to understand PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj