Table of Contents
Large Language Model (LLM) agents represent a revolutionary step forward in the realm of artificial intelligence and natural language processing. These sophisticated AI systems can understand, generate, and manipulate human language with an unprecedented level of accuracy and creativity. As the software development industry evolves, LLM agents are becoming indispensable tools, offering powerful capabilities that extend beyond traditional automation. However, leveraging these advanced models requires careful consideration from decision-makers. This article delves into the critical factors that should guide the integration and use of LLM agents, highlighting unique insights and seldom-discussed aspects that are crucial for informed decision-making.
Understanding LLM Agents
Definition and Basics
Large Language Model (LLM) agents are AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language. These models utilize advanced machine learning techniques, particularly deep learning and neural networks, to process and produce text that can mimic human communication. They can perform a variety of tasks, from answering questions and translating languages to summarizing content and generating creative writing.
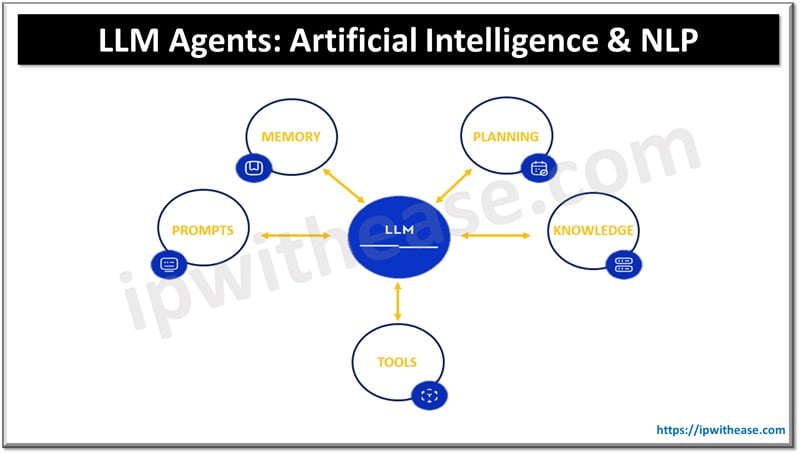
Evolution of LLM Technology
The journey of LLM technology began with basic natural language processing (NLP) systems that could perform simple text manipulations. Over the years, advancements in computational power and algorithmic innovation have led to the development of more sophisticated models like GPT-3 and beyond. These models are characterized by their large-scale architectures and extensive training datasets, enabling them to understand context, nuances, and even the subtleties of human emotions and intentions.
Strategic Benefits of LLM Agents
Enhanced Productivity
One of the primary advantages of deploying LLM agents is the significant boost in productivity they offer. By automating routine and complex tasks, LLM agents free up valuable time for software development teams, allowing them to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their projects. For instance, these agents can handle customer support queries, generate code snippets, and even provide detailed technical documentation.
Cost Efficiency
LLM agents can also lead to substantial cost savings. The automation of repetitive tasks reduces the need for extensive human labor, thereby cutting down on operational expenses. Additionally, the scalability of LLM agents means that businesses can handle larger workloads without proportional increases in staffing costs.
Driving Innovation
The innovative potential of LLM agents cannot be overstated. They enable the development of new business models and applications that were previously unimaginable. For example, LLM agents can facilitate the creation of personalized user experiences, dynamic content generation, and real-time language translation services, pushing the boundaries of what technology can achieve.
Key Considerations for Implementation
Data Security and Privacy
When implementing LLM agents, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. These models require access to large datasets, which often contain sensitive information. Decision-makers must establish robust security protocols to protect data from breaches and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating LLM agents with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging. It is crucial to ensure that these agents are compatible with current systems and can seamlessly interact with other software applications. This often requires thorough planning and the involvement of experienced IT professionals to avoid disruptions.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability is another critical consideration. Businesses need to ensure that their LLM deployments can grow with their needs. This involves choosing flexible models that can adapt to increasing data volumes and evolving business requirements without compromising performance.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Mitigating Bias
One of the ethical challenges associated with LLM agents is the potential for bias. These models learn from vast datasets that may contain biased information, leading to skewed outputs. Implementing strategies to identify and mitigate bias is essential to ensure fair and unbiased results.
Ensuring Transparency
Transparency in how LLM agents make decisions is crucial for building trust with stakeholders. Decision-makers should prioritize clear documentation and communication about the workings of these models, including how they process data and generate outputs.
Navigating Legal Frameworks
The legal landscape surrounding LLM agents is complex and continually evolving. Decision-makers must stay informed about relevant regulations and ensure their use of LLM agents complies with legal standards. This includes considerations around data ownership, intellectual property, and the ethical use of AI.
Best Practices for Leveraging LLM Agents
Choosing the Right Model
Selecting the appropriate LLM agent for a specific business need is critical. Decision-makers should consider factors such as model accuracy, training data relevance, and the specific functionalities required. Comparing different models and conducting thorough evaluations can help in making an informed choice.
Training and Fine-Tuning
Training and fine-tuning LLM agents to meet specific business requirements is essential. This involves providing the models with relevant datasets and continuously updating them to improve their performance. Fine-tuning ensures that the agents can handle the unique challenges and nuances of different business environments.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Ongoing monitoring and maintenance are vital to ensure the long-term effectiveness of LLM agents. Regularly updating the models, addressing any performance issues, and ensuring they remain aligned with business objectives are crucial steps in maintaining their utility.
| Consideration | Description |
| Data Security | Protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance |
| System Integration | Ensuring compatibility with existing IT infrastructure |
| Scalability | Choosing models that can grow with business needs |
| Bias Mitigation | Implementing strategies to ensure fair and unbiased results |
| Transparency | Maintaining clear communication about model operations |
Conclusion
Leveraging Large Language Model agents offers transformative potential for businesses in the software development industry. By considering factors such as data security, system integration, scalability, and ethical implications, decision-makers can harness the full benefits of these advanced AI systems. Implementing best practices for choosing, training, and maintaining LLM agents will ensure they deliver maximum value and drive innovation within organizations. As the technology continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to successfully integrating LLM agents into business strategies.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.



