Google ADs
Table of Contents
Switchport mode access is essential for configuring network devices in environments where end devices (e.g., computers, printers) connect to a switch. These ports are typically placed in “access” mode to carry traffic for a single VLAN. Below are common issues that arise with switchport mode access configurations and how to troubleshoot them.
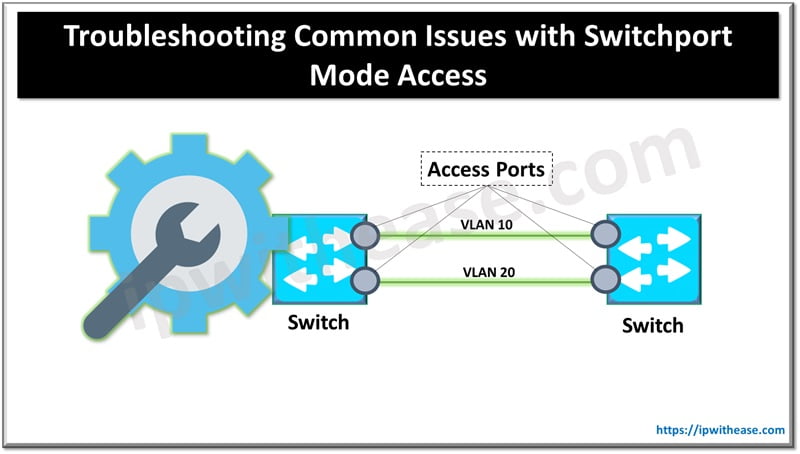
Switchport Mode Access Troubleshoot Issues
1. Mismatched VLANs
- Symptom: Devices connected to the switchport can’t communicate with others on the network.
- Cause: The VLAN assigned to the switchport is incorrect or doesn’t match the VLAN used by the devices it’s trying to communicate with.
- Solution:
- Verify the VLAN ID assigned to the switchport using show running-config interface <interface-id>.
- Ensure the correct VLAN is created and active on the switch using show vlan brief.
- Assign the port to the correct VLAN using switchport access vlan <vlan-id>.
Related: Switchport Access Mode vs Trunk Mode
2. Trunk Mode Misconfiguration
- Symptom: Switchport unexpectedly carrying traffic for multiple VLANs.
- Cause: The switchport might be in trunk mode rather than access mode.
- Solution:
- Check the mode of the switchport with show running-config interface <interface-id>.
- Set the switchport to access mode with switchport mode access to ensure it only carries traffic for a single VLAN.
3. Port Security Issues
- Symptom: The switchport is shutting down or not passing traffic after connecting a device.
- Cause: Port security may be misconfigured, leading to violations that cause the port to go into an error-disabled state.
- Solution:
- Check for port security violations using show port-security interface <interface-id>.
- If a violation has occurred, disable or adjust the port security settings. You can either clear the error by shutting down and bringing up the port (shutdown followed by no shutdown) or modify the security policy.
- Reconfigure port security to allow more MAC addresses if needed using switchport port-security maximum <number>.
4. Access Port Not Assigned to VLAN
- Symptom: Devices connected to the port cannot communicate or ping any other devices.
- Cause: The switchport has not been assigned a VLAN or is assigned to a non-existent VLAN.
- Solution:
- Use show vlan brief to verify if the VLAN exists.
- Assign the port to the correct VLAN using switchport access vlan <vlan-id>.
5. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Issues
- Symptom: Switchport does not forward traffic or is in a “blocking” state.
- Cause: STP may place the port in a blocking or listening state to prevent loops.
- Solution:
- Check STP status with show spanning-tree interface <interface-id>.
- Ensure that there are no network loops causing STP to block the port.
- Use spanning-tree portfast on access ports to bypass the STP listening/learning states, but only if you’re sure there are no loops.
6. Duplex or Speed Mismatch
- Symptom: Poor performance, slow speeds, or erratic connectivity.
- Cause: The speed and duplex settings between the switchport and the connected device are mismatched.
- Solution:
- Check the port settings with show interfaces <interface-id>.
- If the settings are mismatched, manually configure the speed and duplex using speed <10/100/1000> and duplex <full/half> commands, or allow both ends to auto-negotiate.
7. Cabling Issues
- Symptom: Port shows as down or does not pass any traffic.
- Cause: Faulty cables, incorrect pinouts, or loose connections.
- Solution:
- Test with different cables to rule out cable issues.
- Use show interfaces <interface-id> to check the port’s physical status (e.g., “up” or “down”).
- Replace the cable if necessary and ensure proper pinouts if using custom cables.
General Commands for Troubleshooting
- show interface status – To view port status and VLAN assignment.
- show vlan brief – To confirm VLAN membership.
- show running-config interface <interface-id> – To verify switchport configurations.
- show port-security interface <interface-id> – To check for port security violations.
- show spanning-tree – To verify STP status on the interface.
By methodically addressing these common issues, you can quickly restore proper network connectivity on switchports configured in access mode.
Google ADs
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Founder of AAR TECHNOSOLUTIONS, Rashmi is an evangelist for IT and technology. With more than 12 years in the IT ecosystem, she has been supporting multi domain functions across IT & consultancy services, in addition to Technical content making.
You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj