Table of Contents
Whenever the digital world and technology landscape is thought about, then word authentication comes into everyone’s mind. It is the very first basic step towards security as it achieves user identification and identity legitimate entity to grant suitable access to perform job roles and operations in a secure manner. There are several ways and techniques to achieve authentication in the digital world from basic ones such as passwords to complex ones such as FIDO alliance.
In today’s topic we will learn about different types of authentication, their key characteristics, how they work and their usage.
What is Authentication
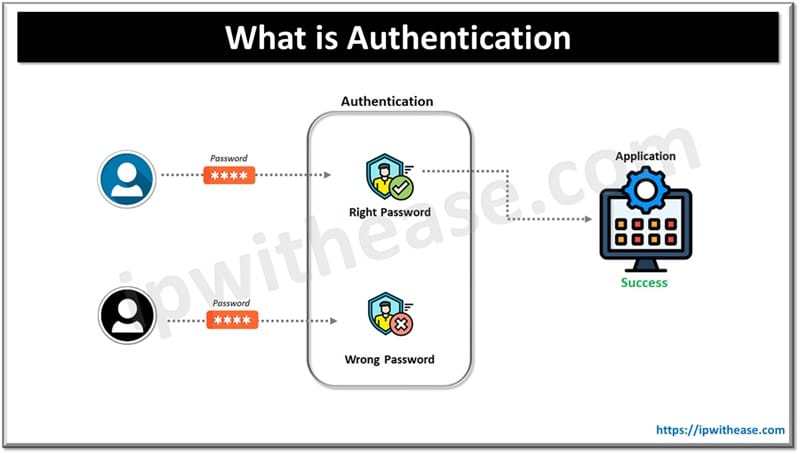
Authentication is a mechanism to identify the identity of a user which requires access to network services, devices and software. Users are authenticated and the access control is enforced via their credentials – Username and password. It enables users to get access to systems and services, and provides support for IP data packet authentication and integrity. The purpose of authentication is to validate and verify the entity of an individual who is trying to access a system, software or service. It is a fundamental security measure and first line of defense.
Related: P2P Authentication – PAP and CHAP Protocols
Various Types of Authentication
Over the years many types of authentication methods have evolved. We will look at some most popular and commonly used forms of authentications and will try to understand how they work.
Password Based
This is the most basic and commonly used authentication technique having a string of alphabets, numbers, special characters of specific length known only to individuals who require access to systems, software and services. Unique user ID and password is assigned here to be used. When a user logs into the system he supplies his user ID and credential password which is compared with the same User ID and password being stored into a database, if it matches the access is granted on the system else access is denied.
Certificate Based
Digital certificates are used to establish the identity of a user, a third party entity. System verifies the certificate and trusts its issuer and becomes a means to give go ahead for secure communication. Certificates are provided by third party organizations or certificate authorities (CA) as they are called such as Verisign, DigiCert etc. X.509 standard format is used to define the public certificates. Certificate authorities (CA) issue digital certificates to declare public key ownership.
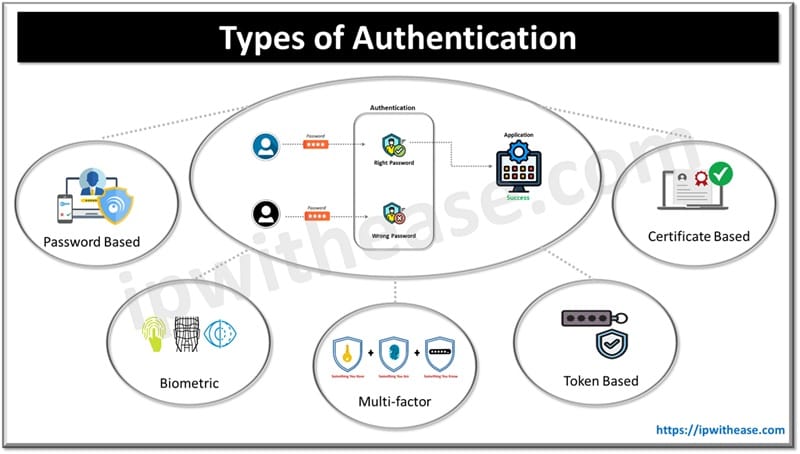
Biometric
This type of authentication is getting popular nowadays. A very common usage of this kind of authentication is unlocking the phone with your fingerprint or face identity. The user’s biometrics such as fingerprint, face, retina, voice etc. are stored in a database. At the time of authentication the user provides a sample of the one with which the system is configured to authenticate. The received biometric is compared with what is stored in the database on the server.
If both match then access is granted. Biometric authentication can be physiological or behavioral types. In physiological techniques face, fingerprint, retina, voice etc. are used as means to authenticate and in behavioral mechanism person behavior is observed to determine he is not impersonating using signatures and keystrokes.
Related: Understanding AAA Authentication
Token Based Authentication
These are one of the alternatives for use of passwords. It is usually done using a small device or an app which generates a random value. This random value is used for authentication. Authentication tokens are pre-programed using a random seed number. This random seed number is unique each time. Authentication tokens are of two types – challenge / response tokens or their combination. The pre-programmed seed is encrypted and stored inside the token. Token server sends random challenges to users in a time based technique. Time is used as a variable input in place of random challenge.
Multi-factor Authentication
In this type of authentication the user passes multiple parameters to gain access to system, software or service. An additional layer of security gets added to basic user ID and password-based authentication. Users need to submit a second factor in the form of unique one-time code received on phone or email. Multi-factor authentications can be of various types such as OTP/TOTP via SMS, via Email, push notification, mobile authenticator and hardware token. MFA techniques can be established based on needs of security.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj