Table of Contents
Modern approach to manage computer networking is known as software defined networking (SDN) as it is called. Traditional networks are controlled by hardware components such as routers and switches which are complex, hard to manage, and configure. DNS changed the way networking is managed by separation of control of the network from actual data movement. Control and management of network components is performed using software components using open APIs.
In today’s topic we will learn about SDN controllers, where SDNs are used, what is the architecture of SDN and its key features.
About SDN Controller
Traditional networks devices such as routers and switches make use of distributed control plane. Where each device has its own control plane to control the data plane. In Software defined networking (SDN) a centralized control plane is used. In a centralized control plane – a device (typically runs on a server) and uses protocols to tell other devices where to send packets. SDN controllers direct traffic according to forwarding policies established by network administrators thereby minimizing manual configurations for individual access of network devices. The centralized controller takes control of the control plane (Network hardware) and run as a software component instead.
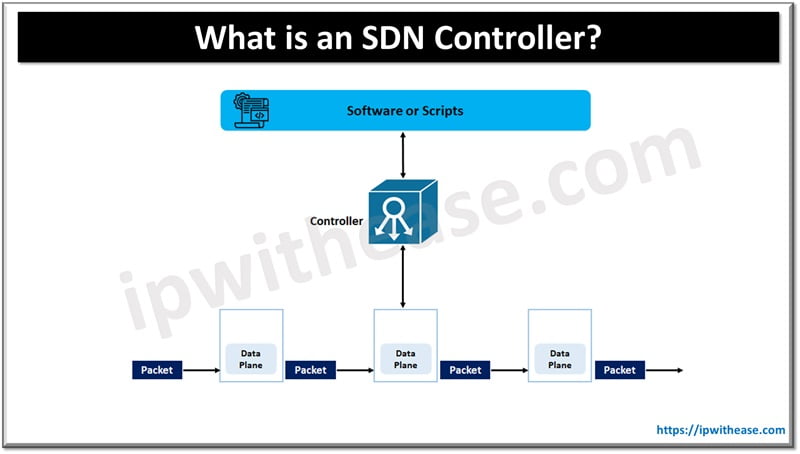
In SDN all network devices connect to controllers so that it can regulate the data plane for all network devices. Interface between controller and networking devices lies south of controller and these interfaces are named as Southbound interfaces.
Network programmer provides all information regarding the network that is required to control the data plane of network devices to the controller. The software and scripts placed above the controller. This placement makes the interface between controller and software in north direction hence it is called Northbound interface. These interfaces enable programmability for networks. Both these South and Northbound interfaces are Application Program Interface (API).
SDNs are used by enterprises for application deployments and let network administrators manage and provision network services quickly and from a single location. The controllers communicate with applications such as load balancers, firewalls etc. using Northbound interfaces. Using the Southbound interface controller talks with individual network devices. This southbound API enables controllers to configure network devices and choose an optional network path for application generated traffic.
Functions of SDN
SDNs provide a variety of functions. Let’s look at them more in detail below.
- Network state management – the management and distribution of network state which may involve a database. The database serves as a repository of information obtained from controlled network components and related software as well as information which is controlled by SDN and its related software such as network state, configuration, learned topology and session information.
- To capture relationships between managed resources, policies and other services from the controller.
- RESTful API interfaces to expose controller services to an application and facilitates controller and application interaction.
- Secured TCP control session between controller and associates agents in networking components
- Standard based protocol to provision application driven network state on networking components
- Device, topology and service delivery mechanism, path computation system for network or resource centric information services
Pros and Cons of SDN
PROS
- Centralized controller which is aware of all available network paths and can direct packets based on requirements of traffic management
- Automatic modification of traffic flows and send notification of congested networks to administrators
- Optimization of resources usage as and SDN controller can optimize packet paths for better network efficiency)
- Can use more than one controller for redundancy (supports up to three controllers) to enable redundancy in the event of connectivity loss or controller failure
CONS
- Require change in entire network architecture if you plan to implement SDN protocol and controller
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.