Table of Contents
Introduction to SD-WAN
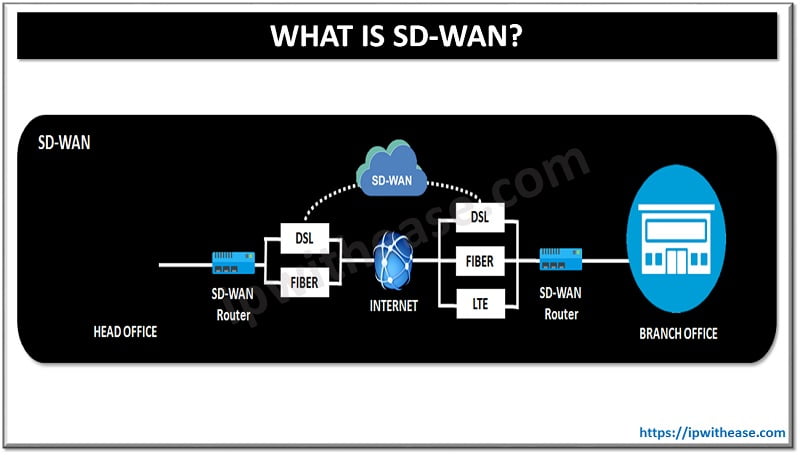
SD-WAN (Abbreviation for Software-Defined Wide Area Network) works by abstracting the software to create a network overlay and disunite network software services from the underlying hardware.SD-WAN has come up as paradigm shift to simplify branch office networking, reduce cost and provide improved application performance with minimal disruption.
Software-Defined WAN has evolved from Software-Defined Networking (SDN), the underlying principle of which is to abstract the network hardware and transport features from the applications that use the network. Traffic is automatically and dynamically forwarded across the most appropriate WAN path based on network attributes (like Jitter, delay, throughput etc.) the security and QoS requirements of the application traffic at hand.
Key Challenges with Traditional Networks
Key Challenges with Traditional Networks are:
- Inefficient Bandwidth control – This becomes a challenge when the Multiple WAN Link circuits need to be evenly split for load balancing the traffic. Even Dynamic Protocols like BGP struggle when equal load needs to be shared over WAN Links or when application behaviour changes frequently (like Bandwidth dynamically changes in the day) .It can be very challenging to effectively split traffic between multiple WAN circuits.
- Lack of application visibility – Obtaining insights into traffic flows, application usage and performance levels often requires expensive solutions with additional management overhead.
- Poor Internet performance – Internet based VPNs may be preferred at locations where MPLS is not cost effective , but it is challenging to deliver a high-performance network using Internet .Technology issues like last-mile quality issues and variable performance on the Internet tend to be show stopper at times.
- High Cost of Infrastructure and bandwidth – MPLS and PTP cost much higher and take bulk of total IT budget cost. The Organizations need to compromise either on low SLA or low Bandwidth when using MPLS links when budgeting for new branch sites.
SD-WAN tends to resolve the above shared issues . For benefits we can reap out from SD-WAN.
Key Attributes of SD-WAN
Key Attributes of SD-WAN are given below:
- Centralised and automated provisioning –SD-WAN platform allows site templates to be defined, automating the process of adding new sites or changes to device configurations of existing sites without manual intervention.
- WAN link aggregation –Leveraging all available capacity of the underlying circuits and awareness of the quality, bandwidth and performance of all circuit help SD-WAN to optimize performance and select the appropriate path at a per-packet level..
- Routing , Security and QoS policies – Includes creating and deploying business, application routing and security policies and pushing them into the respective end devices to foster control of policy and flow.
- Application visibility – SD-WAN can address application issues and provides a rich application-visibility dashboard to show how applications are behaving, but also has the necessary gearshifts to control (prioritise) the applications.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj