Table of Contents
The spread of cloud computing at organizations and its workplaces had brought with it another set of risks often referred to as ‘Shadow IT’. Cloud computing made it easier to provision assets and services by bypassing IT procurement protocols. Employees using cloud services for work or devices, unauthorized apps etc. without the knowledge of the IT department. This enhances productivity but at the cost of data security.
In today’s blog we will learn about a new term ‘Shadow IT’, what causes shadow IT, risks of shadow IT, strategies to manage it and future of shadow IT.
Understanding Shadow IT
The biggest threat to company data is not just from outsiders but from its own employees or insiders. They put data at risk to work faster with shadow IT. Shadow IT is the use of technology components, devices, applications, software and services without following the IT approvals. Most of the shadow IT in today’s world is software, especially SaaS. Sometimes it is also known as unsanctioned SaaS, SaaS sprawl or shadow SaaS. The shadow IT occurs when employees use software without IT knowledge and these can range from personal systems to freemium cloud applications. Shadow IT is generally used when employees are chasing deadlines to complete the tasks such as product releases, new deployments etc.
Real World Examples
Let’s look at some common examples of shadow IT in the real world.
- Marketing Teams Using Unauthorized SaaS Applications: Marketing teams subscribing to new social media analytics platforms without intimating IT to gain real-time insights into competitor workspace.
- Personal Cloud Storage Used by Finance: Finance team might use personal cloud storage services such as Dropbox or Google drive to access their documents remotely unintentionally exposing financial data sensitive in nature.
- Healthcare Professionals and Mobile Applications: Doctors might download unapproved apps on their phones and upload patient information
- Engineering Teams Deploying Unvetted Software: Engineering group might implement a new source code repository or collaboration tool which is not scanned for potential vulnerabilities
- Senior Executives Using Unauthorized AI Tools: Executive turning to AI tools may often bypass security protocols.
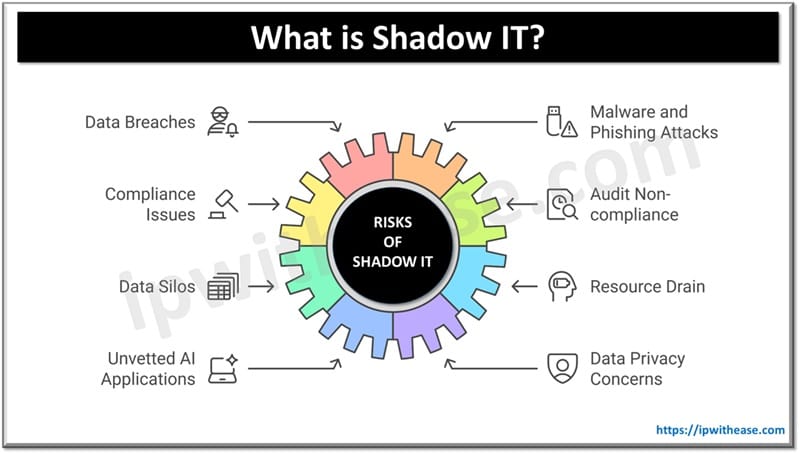
Risks of Shadow IT
- Data breaches – unauthorized tools often not having strong security controls resulting in exposure of sensitive data to cyber-attacks.
- Malware and phishing attacks – Shadow IT solutions might introduce malware in the organization network. Employees downloading unsolicited or unapproved software open the door for phishing attacks or other forms of malicious activities.
- Compliance and regulatory issues – several regulated industries such as finance, healthcare etc. strictly need to abide by regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA etc. Using unauthorized applications or services could lead to non-compliances resulting in penalties and reputation damage.
- Audit non-compliances – unauthorized systems or services lead to giving right records of base inventory, data access and processing activities leading to audit non-compliance.
- Data silos – systems which are installed in unauthorized manner and not integrated with organization’s systems lead to fragmented data storage.
- Resource drain – IT teams are diverted to fix issues raised by use of shadow IT systems.
- Unvetted AI applications – shadow AI tools adopted without proper checks bring with them risks of using algorithms which lack transparency in data processing resulting in biased outcome or unintended exposure.
- Data privacy concerns – storing data at locations not compliant with data residency requirements or data sharing with third parties can be done by shadow AI systems resulting in data privacy concerns
- Contracts and technical debt – often employees signed a contract without approvals for shadow IT services or tools which may contain terms violating the regulatory requirements leading to exceeding budgets and these sunk costs force organizations to continue using sub-standard tools.
- Surprise expenses – as per Gartner survey shadow IT accounts for 30-40% of IT spending in larger enterprises.
How to Manage Shadow IT in Future
It is important to realize first that it is impossible to completely eliminate shadow IT. Tactics to manage shadow IT need to be revised by enhancing the discovery and prioritization capabilities.
- Visibility and monitoring – Out of sight is out of mind so visibility is the key control. Without that insight you will have to bear all risks of shadow IT with no controls. There are many tools available in the market to perform Shadow IT discovery.
- SaaS management platforms help in detection of all SaaS and SaaS AI tools running in the organization. Tools such as Torri can be integrated with existing technology stack and deployed to get holistic SaaS discovery. These tools provide centralized monitoring of application discovery, monitoring usage and managing contracts and expenses.
- Network monitoring tools like SolarWinds, wireshark etc monitor the performance of network traffic and detect anomalies in the network. They ensure that all devices and applications accessing the network behave normally and as expected.
- Asset discovery tools like Lansweeper or Spiceworks identify and catalogue all IT assets physical and virtual , on premises or hardware.
- Mobile device management tools like jamf and Kandji focus on managing smartphones, tablets and laptops. They enforce security policies, deployment of applications, and monitoring compliance for BYOD devices especially.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj