Table of Contents
Cloud computing has changed the way security has been looked at so far. It was always to be ‘Trust first and verify later’ but this no longer holds true as more and more enterprises are moving their workloads and applications to the cloud. The exposure is beyond imagination as physical boundaries have been diminished and users are spread globally and cloud workloads host critical business data which is the lifeline for enterprises.
In today’s topic we will learn about the zero trust approach towards security, why it is needed, how it works? its advantages and importance for today’s enterprises.
Zero Trust in Cloud
The rapid adoption of cloud computing has changed the way security is being looked at a few years back. The approach was network centric and it was like trust first and verify later so if a user has credentials they are allowed to access any application, site, device they have the privileges. This resulted in high exposure to assets as once a user is a trusted entity in the enterprise network any resources were accessible without any further gate checks.
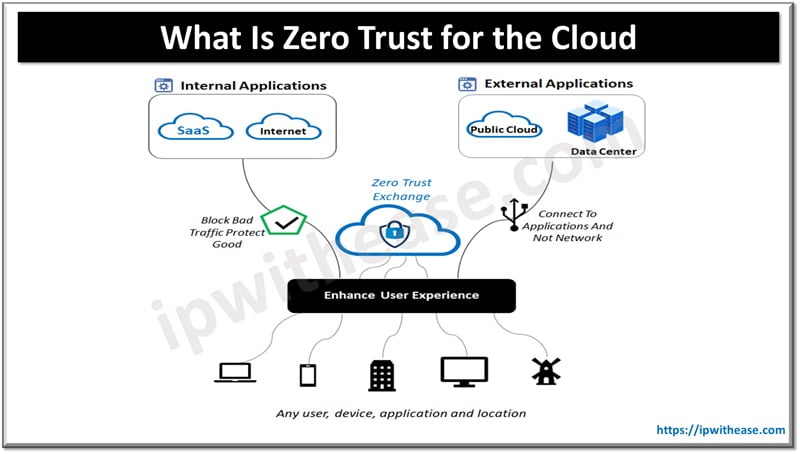
On the other hand, ‘zero trust approach’ means establishing verification at every step as a user coming from an open network. Irrespective of where request originated from or what resources access is requested for, the zero-trust approach means no implicit trust.
Achieving zero trust security relies on a set of principles and practices related to Identity and access management, we will look more in detail on these principles in this article.
Principles of Zero Trust
Let’s look more in detail at zero trust principles.
- Continuous validation and monitoring – the zero-trust approach works on the assumption that attackers can be insiders and not just outsiders so no systems / users should trust implicitly. Zero trust verifies user identity and privileges and system identity and its security. The logins, credentials, timeout of connections are re-verified time and again.
- Least privileges principle – Zero trust security relies on the principle of least privileges hence all accounts should have least privileges minimum enough for users to perform only what access they need and minimize exposure of data and areas of network to users.
- Devices access control – zero trust needs enterprises to have strong control for devices and not just controlling access to them. The systems monitor how many unique systems have access to organization networks, every device needs to be authorized, and do real time threat assessment to ensure devices are not compromised to reduce attack surface.
- Micro-segmentation – security perimeter is segregated into small segments and maintains separate access for different network parts. Access to one zone and another segment need separate authentication.
- Prevention of lateral movement – zero trust models are designed to prevent lateral moment of attackers and architecture of network is segregated in a manner that attacker cannot migrate network microsegments
- Multi-factor authentication – Passwords alone are not enough, at least one more authentication technique is combined to verify user identity such as passwords with OTP, tokens etc. MFA ensures account security in the event passwords are compromised.
Related: ZTNA vs ZTAA
Importance of Zero trust
Zero trust model is a replacement of traditional perimeter centric security approach and ensures security and access decisions are enforced in a dynamic manner based on identity of device, user and its context. A zero-trust framework allows only authenticated and authorized users and devices access to enterprise applications and resources, data hosted on cloud. It protects applications, devices and data from advanced threat vectors. Use of MFA along with passwords provide stronger control. SSO single sign-on feature is often incorporated to enhance user experience and productivity improvements. Solutions focusing on user and device both need authentication and authorization enhances overall security posture in the cloud.
Advantages of Zero trust
- Limiting data exposure from misuse having controls on access / permissions
- Protection from data loss due to use of shadow resources in cloud
- Improves visibility of data movement between network perimeter and cloud services
- Limiting data exposure to remote devices and users
- Data loss prevention due to improper use of cloud services
- Tracking and limiting misconfigured cloud storage objects
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj