Table of Contents
In this article we will learn about the concept of load sharing and BGP load sharing under different scenarios. Load Sharing works by splitting the traffic and then distributing the load across multiple links. eBGP (Flavour of BGP protocol) is the best answer which uses Load Sharing mechanism for incoming traffic by utilizing AS- Path attribute.
Concept of Load Sharing
Load sharing is the forwarding process of a router to share the traffic if the routing table has multiple paths to a destination. This still bears the possibility of unbalanced forwarding. If unequal paths, the traffic is distributed inversely proportionally to the cost of the routes. Paths with lower costs will carry more traffic and paths with higher costs will carry less traffic.
Load Sharing Using BGP (eBGP)
BGP Load Sharing is a common scenario however it is usually done in two or more links connected to a unique Autonomous System (ISP). If we have two or more ASs, a customized configuration is needed to distribute traffic across AS.
Scenario 1
When Dual-Homed to One Internet Service Provider (ISP) Through a Single Local Router
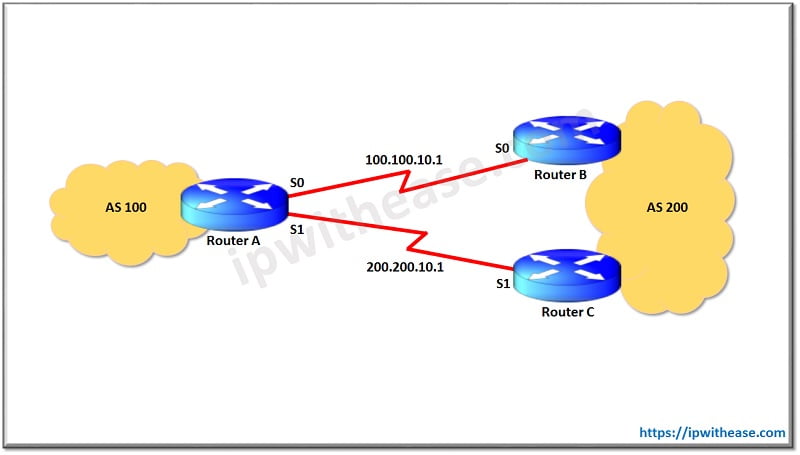
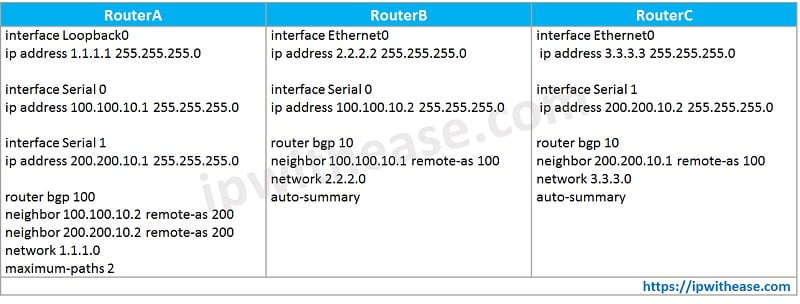
This scenario shows how to achieve load sharing in BGP when multiple links exist between a remote AS and a local AS. These links are terminated on one router at the local AS and on multiple routers at remote AS in a single-homed BGP environment. This sample configuration uses the maximum-paths command. By default, BGP chooses one best path among the possible equal-cost paths that are learned from one AS.
However, you can change the maximum number of parallel equal-cost paths that are allowed. In order to make this change, include the maximum-paths paths command under the BGP protocol configuration. Use a number between 1 and 6 for the paths argument.
Scenario 2
When Multi homed to Two ISPs through a Single Local Router
In this scenario, achieving load balancing using BGP protocol is not an option (for a multi homed environment), so you can only do load sharing. Load balancing is not possible because BGP selects only a single best path to a destination among the BGP routes that are learned from the different ASs. The idea is to set a better attribute value (weight or Local Preference) for the routes that are learned from ISP(A) and a better attribute value for the rest of the routes that are learned from ISP(B).
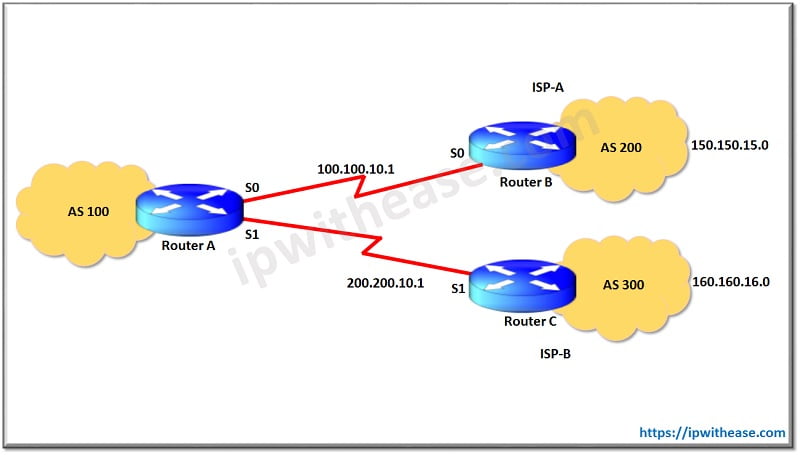
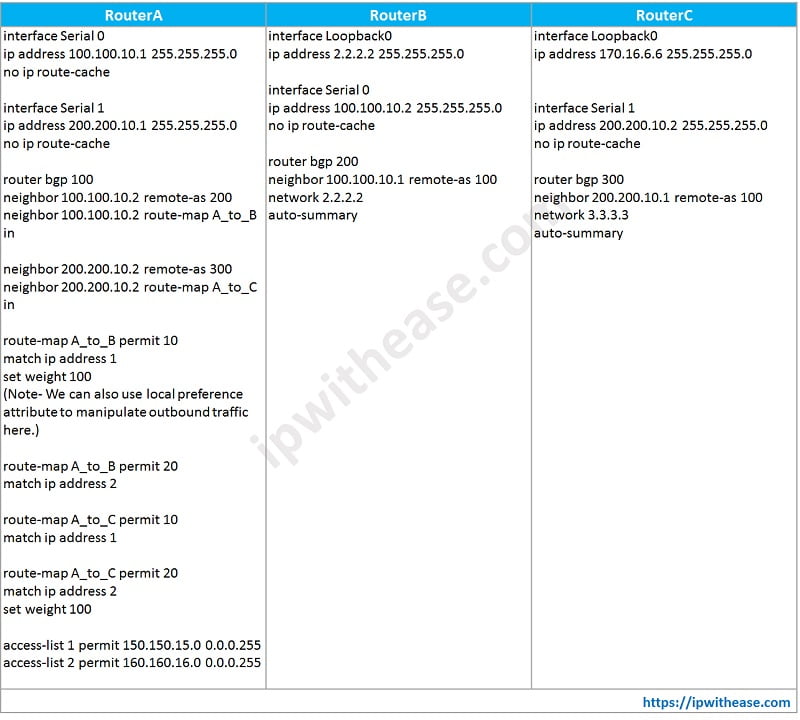
In the above config, weight attribute is used to manipulate outgoing traffic path from Router A towards Router B and Router C. By setting weight 100 in Route Map, Router A to B link becomes preferred path for Network 150.150.15.0/24 and Router A to C Link becomes preferred path for Network 160.160.16.0/24.
Remark – It was assumed that networks 150.150.15.0/24 and 160.160.16.0/24 both are advertised by Router B and C.
Scenario 3
When Multi homed to Two ISPs through Multiple Local Routers
Load balancing is not possible in a multi homed environment with two ISPs. BGP selects only the single best path to a destination among the BGP paths that are learned from different ASs, which makes load balancing impossible. But, load sharing is possible in such multi homed BGP networks. On the basis of predetermined policies (using attribute manipulation), traffic flow is controlled with different BGP attributes.
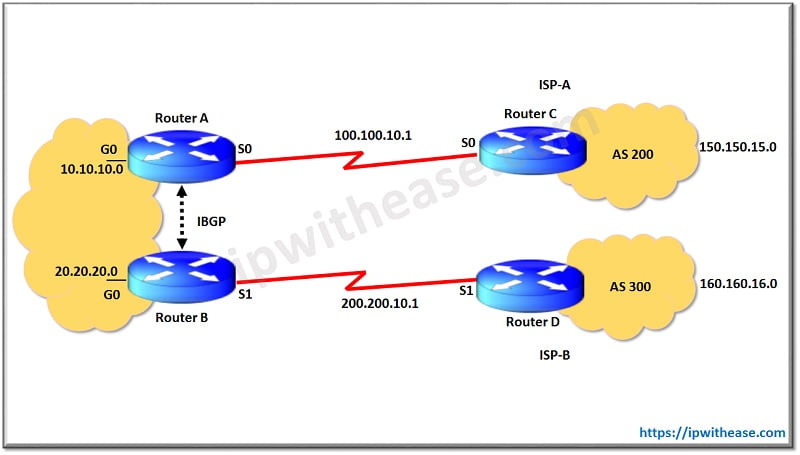

In the above config, local preference attribute is used to manipulate outgoing traffic path from Router A to Router C and Router B to Router D. By setting local preference to 200 via Route Map, Router A to C link becomes preferred path for Network 150.150.15.0/24 and Router B to D Link becomes preferred path for Network 160.160.16.0/24.
Remark – It was assumed that networks 150.150.15.0/24 and 160.160.16.0/24 both are advertised by Router C and D.
Conclusion
Load sharing is distributing the load across multiple links. This is being possible by using attributes of BGP (eBGP) and leveraging NAT-ACL technique.
Continue Reading
BGP Load Sharing for Inbound Traffic
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj