Table of Contents
In this blog we will discuss 3 types of EtherChannel modes, namely PAGP Mode, LACP Modes & On Mode with configuration examples. And we will learn how they differ from each other.
EtherChannel
Etherchannel is a link aggregation technology used primarily on Cisco switches. EtherChannel enables bundling of multiple physical Ethernet links to create one logical Ethernet link which provides high throughout and resilient links. EtherChannel can be provisioned across Cisco Switches and Routers.

Up to 8 active links can be bundled to form EtherChannel for Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet and 10-GigabitEthernet links.
Related – Power over Ethernet (POE) Interview Questions
We can create an EtherChannel on a standalone switch, on a single switch in the stack, or on multiple switches in the stack (known as cross-stack EtherChannel). EtherChannel configuration can be in one of below enlisted 3 modes-
| Etherchannel Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| PAgP | Cisco Proprietary protocol |
| LACP | Open Standard used by most of Vendors |
| ON | Forced to form Etherchannel without using negotiation protocol |
EtherChannel Modes
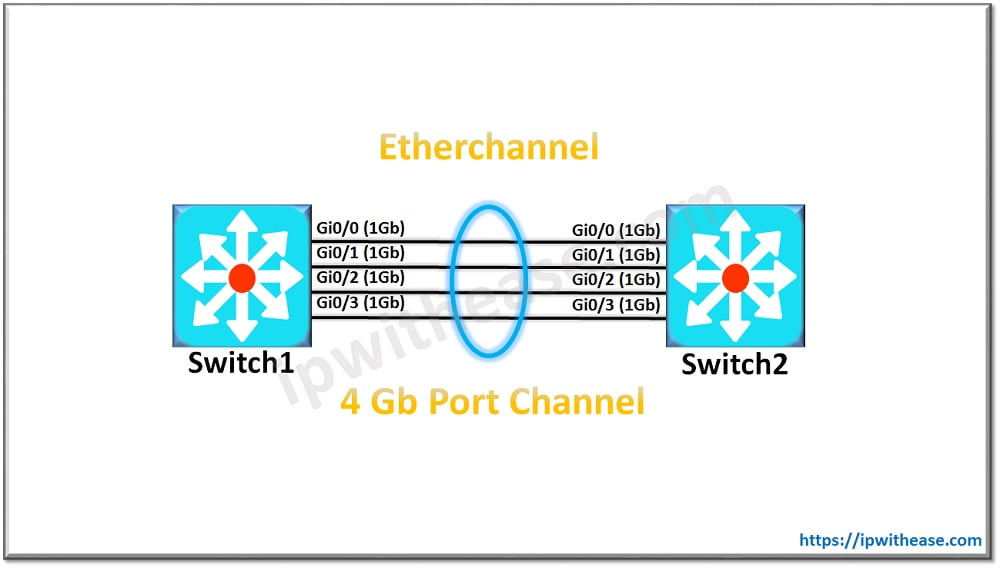
Below diagram will be referred to while forming and configuring EtherChannel in –
- PAgP Mode
- LACP Mode
- ON Mode
PAGP (Port-Aggregation Protocol) Mode
PAgP is Cisco proprietary Etherchannel technology. It uses the multicast address of 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC for communication.
Switch/Router Ports can form an EtherChannel when they are in different PAgP modes as per below criteria –
- A port in the desirable mode can form an EtherChannel with another port that is in the desirable or auto mode.
- A port in the auto mode can form an EtherChannel with another port in the desirable mode.
The port in desirable mode is one which sends requests to the other side to see if it is also using PAgP. The port in auto mode defines using PAgP but does not send requests.
PAgP Mode Negotiation
| PAgP Mode | Desirable | Auto |
|---|---|---|
| Desirable | Yes | Yes |
| Auto | Yes | No |
Example Configuration
EtherChannel Configuration between Switch1 and Switch2 using PAgP is shown below –
Switch1(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Switch1(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunkSwitch2(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode auto
Switch2(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
Note – Switch1 is configured under desirable mode while Switch2 under Auto mode to negotiate and form EtherChannelRelated – PORT Channel vs EtherChannel
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) Mode
LACP is an open standard protocol and published under the 802.3ad specification. It uses the multicast address of 01-80-c2-00-00-02.
Switch/Router Ports can form an EtherChannel when they are in different LACP modes as per the below criteria –
- A port in the active mode can form an EtherChannel with another port that is in the active or passive mode.
- A port in the passive mode cannot form an EtherChannel with another port that is also in the passive mode because neither port starts LACP negotiation.
The port in active mode negotiates with the other side to form Etherchannel while the interface in passive mode indicates using LACP, but responds to requests only and does not send any request.
LACP Modes negotiation
| LACP | Active | Passive |
|---|---|---|
| Active | Yes | Yes |
| Passive | Yes | No |
Example Configuration
EtherChannel Configuration between Switch1 and Switch2 using LACP modes is shown below –
Switch1(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode Active
Switch1(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunkSwitch2(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode Passive
Switch2(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
Note – Switch1 is configured under Active mode while Switch2 under Passive mode to negotiate and form EtherChannelManual “ON” EtherChannel Mode
When using an EtherChannel mode “ON”, EtherChannel will be created only when another interface group is in EtherChannel “on” mode.
One major drawback of using manually configured “On” EtherChannel Mode is that any layer one device like media convertor or modem between 2 Etherchannel devices will not be able to diagnose link failure and keep on sending the traffic while PAgp/LACP configured devices will detect the failure and respond to it.
Related – Difference Between PAGP and LACP
Example Configuration
EtherChannel Configuration between Switch1 and Switch2 using “ON” configuration mode is shown below –
Switch1(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on
Switch1(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunkSwitch2(config)#interface range Gi0/0-3Switch2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on
Switch2(config-if-range)#interface port-channel 1
Switch2(config-if)#switchport mode trunkNote – Both Switch1 and Switch2 are configured under ON mode to forcefully form EtherChannel without negotiation.
Etherchannel Modes Comparison: PAGP Mode vs LACP Mode vs On Mode
| Feature | PAGP Mode | LACP Mode | On Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Port Aggregation Protocol | Link Aggregation Control Protocol | Static Mode |
| Standard | Cisco proprietary | IEEE 802.3ad | None (Static configuration) |
| Compatibility | Cisco devices | Multivendor, IEEE standard | Limited, depends on vendor support |
| Negotiation | Yes | Yes | No |
| Modes | Auto: Passive, waits for PAGP packet Desirable: Active, sends PAGP packet | Active: Sends LACP packets Passive: Waits for LACP packets | On: Forces aggregation without negotiation |
| Load Balancing | Supports | Supports | Supports |
| Fault Tolerance | High | High | Low |
| Configuration Complexity | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Dynamic Link Addition/Removal | Yes | Yes | No |
| Loop Prevention | Yes | Yes | No |
| Multivendor Support | No | Yes | No |
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

Nice 👍