Table of Contents
In this blog, we discussed the DORA (Discover Offer Request Acknowledge) process in detail, 4 main steps of DORA process and frequently asked queries related to the topic.
This post is in continuance to the previous post on DHCP fundamentals.
Introduction
Now, we will understand the DORA process in DHCP in detail –
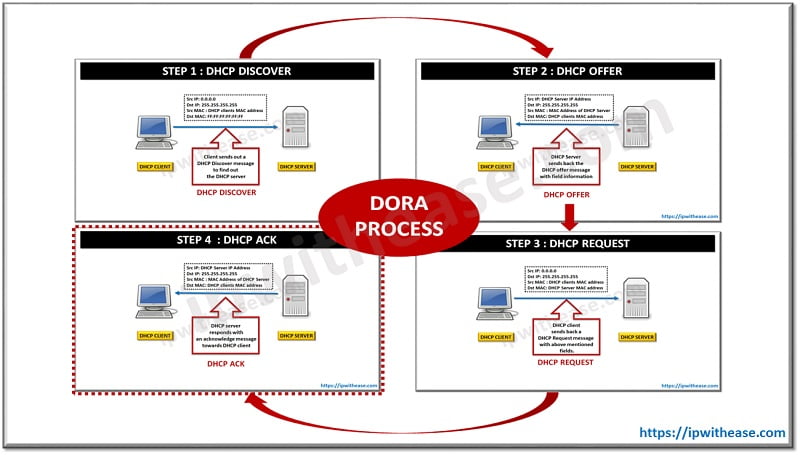
DHCP DORA process stands for the following message flows between the client and the server.
- Discover
- Offer
- Request
- Acknowledge
Below diagram depicts the message flow between the DHCP client and the DHCP Server –
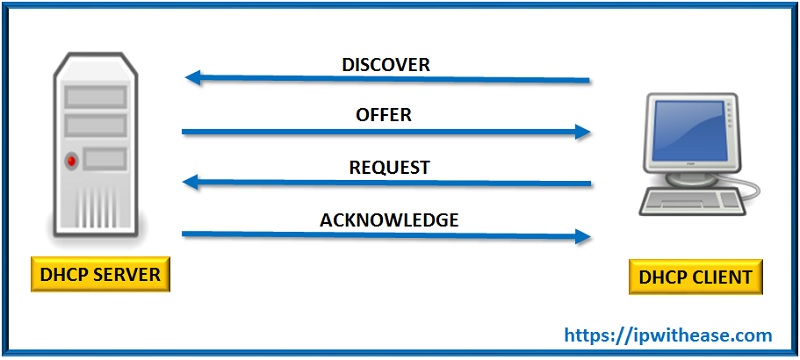
Related- DHCP Snooping
Steps of DORA process in DHCP
Now let’s take a look at what happens when these messages are exchanged between DHCP Client and DHCP Server.
Two key items should be kept in mind which are also important from interview point of view as well.
These are –
- Network layer broadcast and
- Data Link Layer broadcast.
STEP 1: DHCP DISCOVER
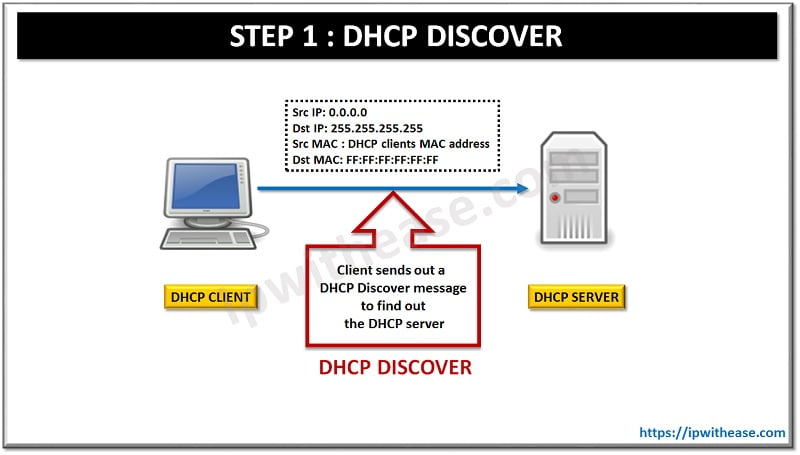
DHCP client sends out a DHCP Discover message to find out the DHCP server. DHCP discover message is a layer 2 broadcast as well as layer 3 broadcast.
Fields in DHCP Discover Message:
Src IP: 0.0.0.0
Dst IP: 255.255.255.255
Src MAC : DHCP clients MAC address
Dst MAC: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF Hence from the above fields it is clear DHCP Discover message is a Network Layer and Data Link Layer Broadcast.
STEP 2: DHCP OFFER
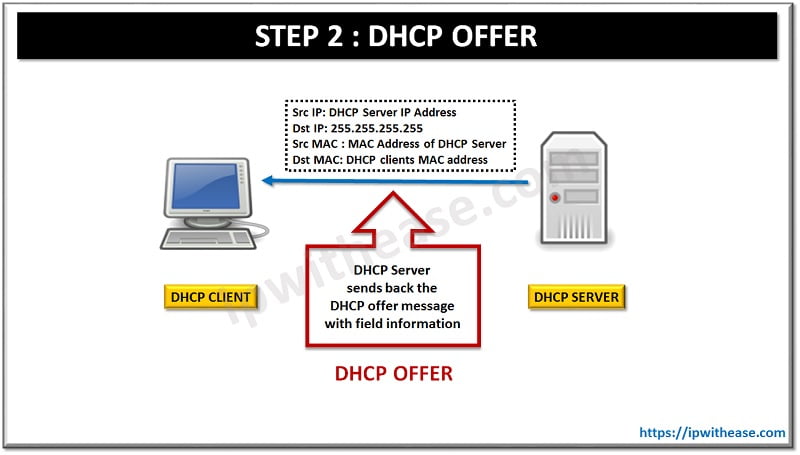
DHCP server receives the DHCP discover a message from the client and sends back the DHCP offer message with field information as below:
Src IP: DHCP Server IP Address
Dst IP: 255.255.255.255 #Still Broadcast as Client still has no IP Address#
Src MAC : MAC Address of DHCP Server
Dst MAC: DHCP clients MAC addressHence from above field it is clear that DHCP offer message is a layer 2 unicast but still as layer 3 broadcast.
STEP 3: DHCP REQUEST
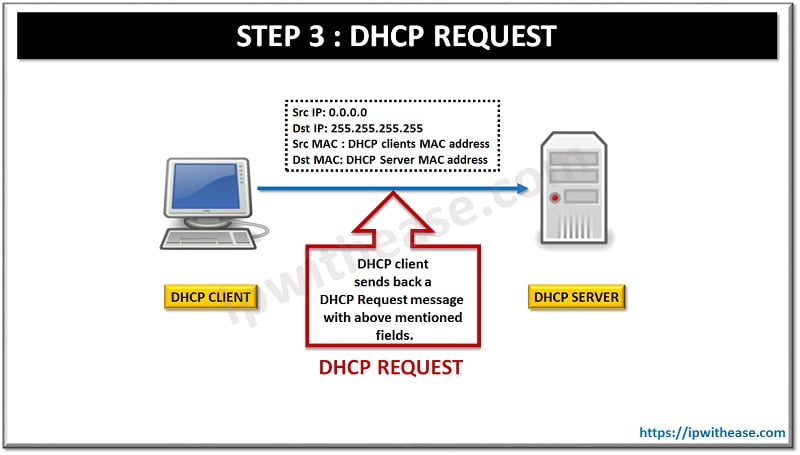
DHCP client receives the DHCP offer from DHCP server and sends back a DHCP Request message with following fields:
Src IP: 0.0.0.0 #As still the IP address hasn’t been assigned to Client#
Dst IP: 255.255.255.255 #Still Broadcast as Client must have received Offer from more than one DHCP server in their domain and the DHCP client accepts the Offer that its receives the earliest and by doing a broadcast it intimates the other DHCP server to release the Offered IP address to their available pool again #
Src MAC : DHCP clients MAC address
Dst MAC: DHCP Server MAC addressAbove fields concludes that DHCP request message is also a layer 2 unicast and a layer 3 broadcast.
STEP 4: DHCP ACK
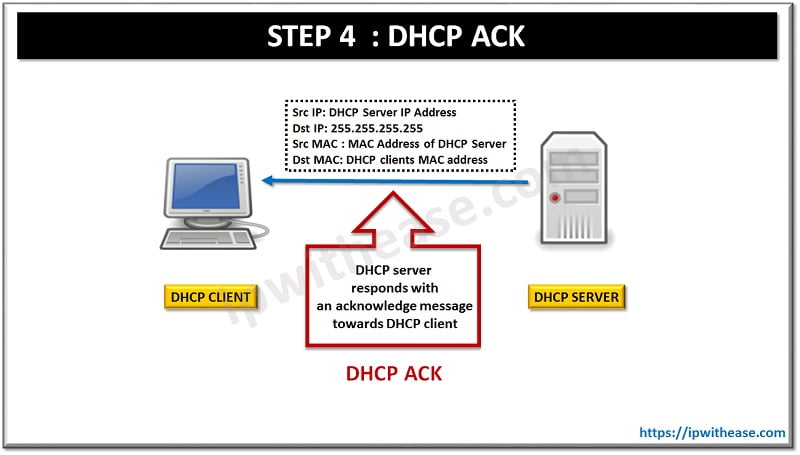
Once the DHCP client sends the request to get the Offered IP address, DHCP server responds with an acknowledge message towards DHCP client with below fields:
Src IP: DHCP Server IP Address
Dst IP: 255.255.255.255
Src MAC : MAC Address of DHCP Server
Dst MAC: DHCP clients MAC addressFrom above fields substantiates that DHCP Acknowledge is a layer 2 unicast but still a layer 3 broadcast.
For more details on the information you must get familiar with the DHCP header fields. Few important fields from DHCP header for our reference are as below –
Ciaddr: Client IP address.Yiaddr ‘your’ (client) IP address: Server’s response to client.
Siaddr Server IP address: Address of sending server or of the next server to use in the next Bootstrap process step.
Giaddr: Relay agent IP address, used in booting via a relay agent.
Chaddr: Client hardware address.Hope you would have understood the DHCP Dora Process. Read our other blogs for more information –
>> What is NIC?
>> Router IOS Firewall vs Network Firewall
>> DHCP vs RARP
FAQs Related to DORA Process
Is DHCP OFFER a Unicast/Multicast?
DHCP OFFER is a layer3 broadcast as the server doesn’t know client’s IP address. It only knows the client’s MAC address.
What is an IP lease in DHCP?
DHCP server allocates a dynamic IP address to the client for a period(lease) known as the IP lease.
What is the default duration of IP lease in DHCP?
The default duration of IP lease is 8 days.
What is DHCP port number?
DHCP uses UDP port number 67 for the DESTIANTION SERVER and UDP port number 68 for the CLIENT.
What do you understand by NACK in DHCP?
DHCP NACK message is sent to the client to tell that the requested IP address can’t be provided by the DHCP server.
Related video for better understanding
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

Please correct the step 3 request message it is wrongly written