DHCP Snooping
As we know that DHCP server provides all the basic information to the clients i.e. IP address, subnet mask, Default gateway and DNS server.DHCP snooping is a layer 2 security technology usually used on the access layer switches in layer 2 switched networks.
Related- DHCP Interview Questions
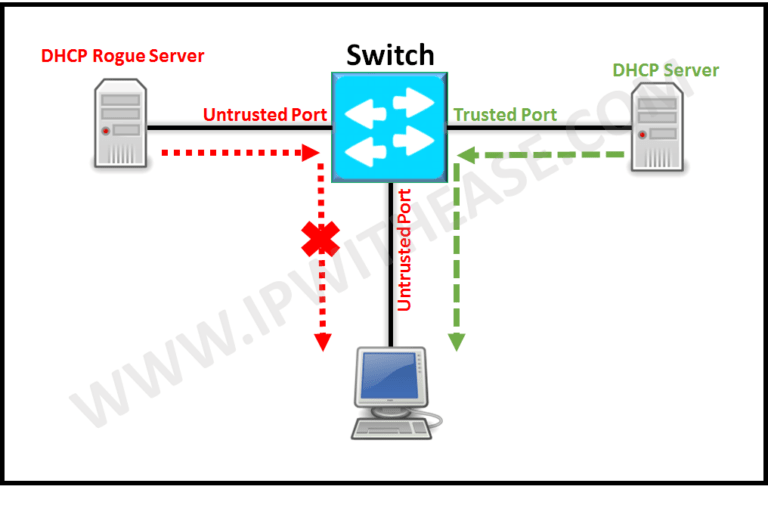
If an attacker connects a rogue DHCP server on a machine in the same subnet as client machine then all packets from client machine can go to the rogue server if the DHCP offer from the rogue server reaches the client before the offer is received from the legitimate DHCP server.
Related- Dora Process in DHCP
To avoid these the switch ports are divided into two categories:
If a DHCP reply comes from an untrusted port it is discarded and a log message is generated.DHCP server messages can flow through switch ports that have a DHCP snooping trusted state. DHCP server messages will be dropped if attempting to flow through a switch port that is not trusted. Related- DHCP vs RARP By default, all the switch ports are in untrusted mode. To enable DHCP snooping: To configure a port in trusted mode: To configure DHCP snooping for a particular VLAN We can also limit DHCP request on a port which by default is unlimited. The show ip dhcp snooping command displays all VLANs (both primary and secondary) that have DHCP snooping enabled. You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj –
DIAGRAM:
CONFIGURATIONS:
VERIFICATION:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR