Table of Contents
With increased focus on privacy and regulatory laws have become more stringent the requirements of personal data protection including its retention and erasure has become major concerns for all organizations. While data protection is important, its destruction and erasure is an essential aspect of data security. The GDPR privacy regulation mandates ‘Right to erasure’, the Indian data protection law follows ‘right to erase’ data once its purpose is served.
In today’s topic we will learn about data erasure, why it is important to erase data, compliance and regulation requirements on data erasure.
Understanding Data Erasure
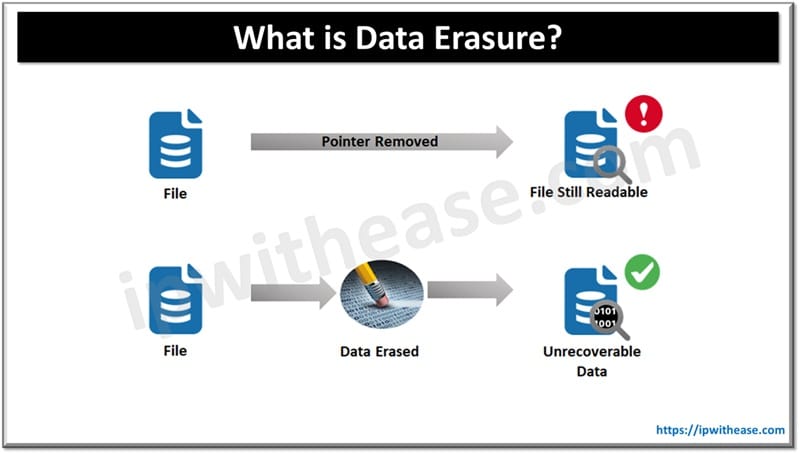
Data Erasure (also known as data wiping/data clearing/ data sanitization/ data destruction) process involves removal of data permanently or its sensitization or data wiping so no traces of it remain available for recovery once the purpose is over for which it was collected or stored. Just like a well-defined data breach response plan is essential, proper data erasure is also crucial. This helps in prevention of undue risk of data leakage and protection of sensitive personal information and data such as trade secrets, patents, formulas, patient history, intellectual property and customer information.
As the volume of data grows continuously it is expected that by year 2025 data has grown up to 175 Zettabytes. Managing such a huge volume of data in itself is a big responsibility. Key data breaches statistics indicate 21% of folders in data repositories are open to all leading to malicious attacks and loss of data.
Typically, when we delete a file or folder having data on the system it never gets permanently deleted and there are tools and utilities available to recover the deleted data for which pointer still exists on the storage medium. The data erasure involves permanent destruction of data from storage media such as hard disks, solid-state devices or any other form of digital media using software or by some other means. This ensures data remains fully unrecoverable via any data recovery techniques however the device remains reusable.
‘Overwriting’ is another word for a data erasure which involves writing data into series of 0s and 1s to make it an undiscoverable or unreadable format. The type of overwriting depends on the nature of the storage device, type of data and security levels required.
The overwriting process uses ‘passes’ and ‘patterns’.
- Passes means the number of times the overwriting process is performed for a storage device. More is the number of passes the changes of data recovery become impossible.
- Patterns means making data recovery challenging using different sequences and patterns during the data overwriting process.
Data Erasure Methods
Here are the main methods of data erasure:
1. Software-Based Data Erasure
This method uses specialized software to overwrite data multiple times, making recovery nearly impossible. Examples include:
- DoD 5220.22-M – A U.S. Department of Defense standard that overwrites data multiple times.
- Gutmann Method – A 35-pass overwrite method for high-security needs.
NIST 800-88 Purge – A standard developed by NIST, using multiple overwrites or cryptographic erasure.
2. Physical Destruction
For highly sensitive data, physical destruction ensures complete data removal. Common methods include:
- Shredding – Cutting hard drives or SSDs into small pieces.
- Degaussing – Using a powerful magnet to disrupt magnetic storage (works for HDDs, not SSDs).
- Drilling/Punching – Physically damaging the platters or chips to make data recovery impossible.
3. Cryptographic Erasure (Crypto Shredding)
- Encrypt the data using a strong encryption algorithm.
- Delete the encryption key, rendering the data unreadable.
- Used commonly in cloud storage and modern SSDs.
4. Secure File Deletion
For deleting specific files securely, tools like Eraser, SDelete, or CCleaner overwrite files multiple times to prevent recovery.
5. TRIM Command for SSDs
- SSDs use TRIM to permanently erase data blocks no longer in use.
- Secure erase tools built into SSD firmware (e.g., manufacturer utilities like Samsung Magician, Crucial Storage Executive) can wipe SSDs securely.
How to choose the Right Method
- Standard data removal: Software-based erasure
- Highly sensitive data: Physical destruction or cryptographic erasure
- SSDs: TRIM & manufacturer’s secure erase utilities
Need for Data Erasure
There are numerous reasons due to which data erasure is required including to maintain data confidentiality, prevention of data leakage, regulatory or compliance demands.
There could be some operational reasons also which calls for data erasure such as managing device storage thresholds, relocation, repurposing, managing costs of storage etc.
But the primary reason for data erasure is protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access and leakage. When the amount of data becomes unmanageable for organizations they prefer to dispose of it.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirement of Data Erasure
Data life cycle management process includes storage of data securely but also it necessitates its disposal properly to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements to minimize unwanted data exposure or loss risk.
Data protection regulations across the world require organizations to ensure privacy and security of personal data collected to deliver business services. The importance of data erasure is a sensitive area especially in the time of cloud computing and AI.
As organizations data is hosted with third party cloud providers it is more concerning that how secure is personal or sensitive data in external entities. Healthcare, financial sectors have mandated guidelines and regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS to handle data erasure requirements.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj