Table of Contents
Ransomware can strike any system at any time, locking up your files and demanding payment. The threat is growing, and everyone must stay alert. If you’re unsure how to stay safe, you’re not alone. Many people and companies fall victim due to simple mistakes.
Learning the basics can help you take control. Just follow the steps below to lower your chances of being a victim. Stay informed and take action now to protect your digital space.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software. It locks files or entire systems. Hackers demand a ransom to unlock them. This attack can hit anyone, from a person to a business. It often comes through links or email attachments. Once opened, it spreads fast. Victims lose access to important data. Paying the ransom doesn’t always mean you’ll get your files back.
How Ransomware Spreads
Ransomware can spread in many ways. One common method is phishing emails. These emails trick users into clicking bad links. Other times, hackers use fake software updates. Once clicked, the malware installs quietly. It can also spread through infected websites. Some attacks come through open network ports. Simple mistakes can open the door.
Why Ransomware is Dangerous
This type of attack causes major harm. Files may be lost forever. Businesses may stop running. The damage can cost thousands or more.
Trust is often lost with customers. It can take weeks to recover. Some victims never fully recover. The risk is real and serious.
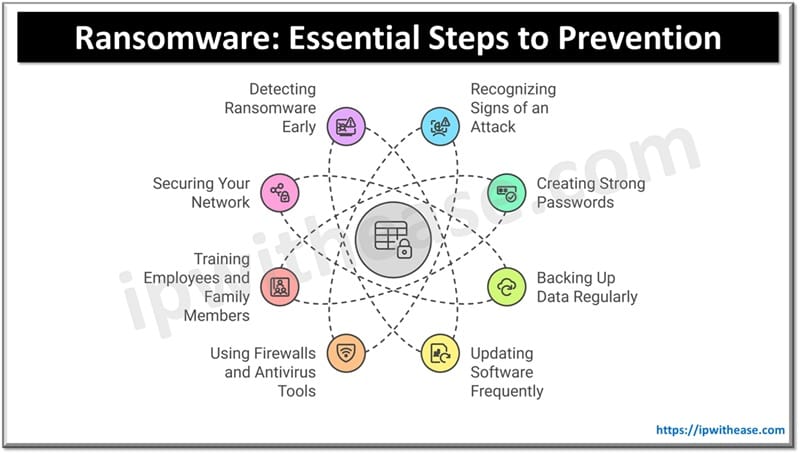
Preventive Measures
Recognizing Signs of an Attack
Early signs are often missed. A slow computer may be one. Files that won’t open are a clue. Strange messages may pop up. Passwords might stop working. Programs may crash often. Unknown software could appear. It’s best to act fast if you notice these.
Creating Strong Passwords
Passwords are a basic defense. Use a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid names or common words. Change them often. Don’t reuse old passwords. Use different passwords for each account. A password manager can help. Keep your passwords private.
Backing Up Data Regularly
Backups are your safety net. If files are locked, you can restore them. Use an external drive or cloud storage. Set a schedule for backups.
Keep backups away from your main system. Test them often to ensure they work. Don’t rely on just one copy. Always keep a recent backup.
Updating Software Frequently
Old software has weak points. Hackers use these to get in. Update your system as soon as updates come out. Enable auto-updates when possible. This includes your apps, not just the system. Don’t delay updates for convenience. Even small updates matter. Stay current to stay safe.
Using Firewalls and Antivirus Tools
These tools add extra protection. Firewalls block harmful traffic. Antivirus tools scan and stop malware. Keep them updated often. Don’t ignore alerts from these tools. Free tools may help, but paid ones offer more. Use both tools together for better safety. Make sure they run daily.
Training Employees and Family Members
Teach others about the risks. Everyone who uses a device should learn. Show them how to spot phishing emails. Teach them not to click unknown links. Explain what ransomware can do. Make safety part of daily habits. Run tests to check what they’ve learned. Learning helps prevent attacks.
Securing Your Network
Your network is a common entry point. Use strong Wi-Fi passwords. Change default settings on routers. Hide your network if you can. Use VPNs for extra safety. Limit who can access your system. Review logs for strange behavior. Keep all network devices updated.
Detecting Ransomware Early
Time is key in stopping ransomware. Use tools that detect early signs. Monitor your system for strange actions. Alert messages should be taken seriously.
Regular scans help find issues. Keep logs to spot trends. Early action reduces damage. Know your system well to see changes.
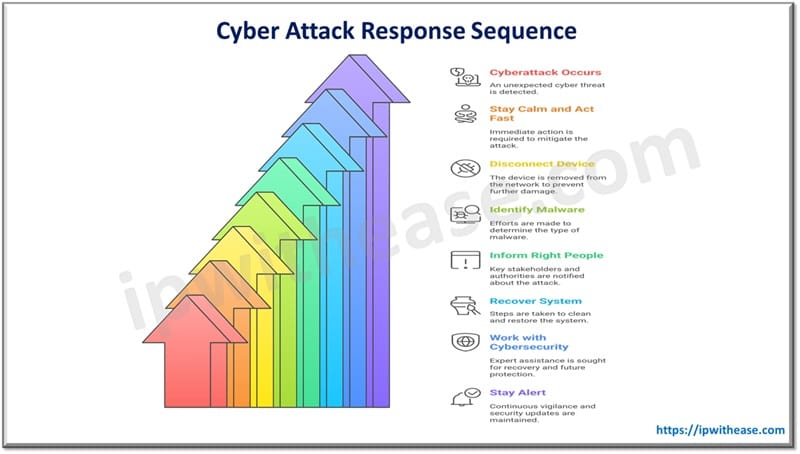
What to Do During an Attack
Stay calm and act fast. Disconnect the device from the network. Don’t turn it off right away. Try to identify the malware. Take a photo of any messages. Call for expert help. Don’t pay the ransom right away. Look at all your options first.
- Informing the Right People: If hit, let others know. Tell your team or family. Report it to local authorities. Some laws require reporting. Help from experts can guide you. Inform anyone whose data may be at risk. It’s part of your duty. Sharing info can stop future attacks.
- Recovering After an Attack: Start with cleaning your system. Remove all traces of the malware. Use backups to restore data. Reset all your passwords. Review how the attack happened. Fix the weak spots. Train others again. Use what you learned to improve your safety plan.
- Avoiding Common Mistakes: Don’t ignore warnings from your device. Avoid downloading unknown files. Never click random links. Don’t use public Wi-Fi without protection. Stop using outdated software. Don’t skip security steps for speed. Avoid using weak passwords. Many attacks happen due to small errors.
- Working With a Cybersecurity Company: Sometimes, you need expert help. A cybersecurity company offers strong protection. They monitor your system for threats. They provide advice and tools. They can help you recover fast. Their experience adds another layer of safety. It’s a smart choice for businesses. Even individuals can benefit from their help.
- Staying Alert at All Times: The threat never really goes away. Stay watchful each day. Review your security often. Talk about safety with others. Don’t trust unknown emails. Keep learning about new threats. Safety is an ongoing job. Stay ready and stay protected.
- Understand Essential Steps to Ransomware Prevention and Response: Ransomware isn’t going away any time soon. But you can lower your risk by taking smart steps. Back up your files, stay updated, and teach others. Simple habits make a big difference.
Don’t wait for an attack to happen. Start protecting yourself now. Small actions today can save big trouble tomorrow. Stay safe and secure every time you go online.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.